VITA
RENEWABLE ENERGY DICTIONARY
DICCIONARIO DE ENERGIA RENOVABLE
DICTIONNAIRE DE L'ENERGIE RENOUVELABLE
This
publication was made possible, in part,
through the generous support of
the United States Agency
for International Development
and the United Nations Education,
Scientific and Cultural Organization
VITA
1600
Wilson Boulevard, Suite 500
Arlington, Virgnia 22209 USA
Tel:
703/276-1800 * Fax:
703/243-1865
Internet: pr-info@vita.org
Copyright [C] 1982 Volunteers in Technical Assistance
All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be
reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means,
electronic or mechanical, including photocopy, recording,
or any information storage and retrieval system without
the written permission of the publisher.
Manufactured in the United States of America.
Designed by Margaret Crouch.
Published by
VITA
1600
Wilson Boulevard, Suite 500
Arlington, Virgnia 22209 USA
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Library of Congress Cataloging in Publication Data
Renewable energy dictionary
Bibliography: p. 479
1.
Renewable energy sources--Dictionaries.
2.
Power
(Mechanics)--Dictionaries.
I. Volunteers in Technical
Assistance.
TJ163.16.R48
1982 333.79
82-50309
ISBN 0-86619-161-5
PREFACE
Soon after
beginning a major program in
renewable energy in 1979, VITA (Volunters
in Technical Assistance) found that many of
the technical terms commonly used in renewable
energy literature were not understood
by many of the laypeople for whom the information
was meant. VITA also
realized
that it was no easy task to find definitions
for many of these terms.
There were
specialized glossaries for the various areas
of renewable energy, but there was no
one source devoted to defining renewable
energy terminology.
The Renewable Energy
Dictionary is designed to meet this need.
This encyclopedic
dictionary is comprised
of up-to-date and authoritative definitions
of terms used in renewable energy.
Definitions
are presented in the clearest and
most concise language possible without detracting
from their technical accuracy.
They are thoroughly cross-referenced for
ease of use.
The terms that were
selected for this
dictionary are primarily those not commonly
defined in their renewable energy context
in conventional dictionaries.
Some of the
terms are now considered to be archaic.
Mostly related to wind energy, they are included
because of their usefulness in developing
an overall understanding of the
field.
VITA's 22 years in
international development
and technology transfer have brought a
sensitivity to the need in developing countries
for technical materials in languages
other than English.
This dictionary is
translated into French and Spanish in an
effort to help meet this need.
In addition to
1,000 entries in each language,
many with illustrations, the dictionary
includes comprehensive conversion
tables and a bibliography.
Our research
indicates that this is the
only published reference work of its kind
available. We feel
it is a significant resource
for those working with renewable energy
technologies and concepts.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
No work of this
scope and magnitude could
be completed without the assistance and
contributions of many individuals.
Along
with Dr. William Sorsby, our primary contributor,
we wish to acknowledge the invaluable
contributions made by VITA Volunteers
who gave their time freely to make this
book a reality. Our
deepest thanks go out
to: Dr. Sam Baldwin,
Thomas J. Beckman,
Richard A. Boettcher, Jean-Claude Bruffaerts,
Jerome E. Dobroski, George S. Erskine,
H. Speer Ezzard, Hal Finkelstein,
Dr. Peter B. Hammond, Robert W. Hawthorn,
James L. Hogan, and Dr. Norbert J. Kreidl.
We also wish to
thank the following members
of VITA's technical staff for their
reviews, contributions, and constant support:
John M. Downey, Alan Wyatt, Dr. Gary
L. Garriott, Stephen H. Hirsch, Fred Hopman,
William R. Breslin, Dr. William A .
Gross, Richard J. Fera, O. Christopher
Ahrens, Balla Sidibe, and Hector Reyes, and
research assistant Vandana Malhotra.
Special thanks go
to artist Christopher
P. Schmidt for the excellent illustrations.
Finally, we
acknowledge the editorial and
production contributions of Kristine
Stroad Ament, Julie Badger, Margararet
Crouch, Bonnie Duley, Gregory James, and
David Jarmul, who put the whole thing
together.
TRANSLATIONS
This dictionary was
translated into
French and Spanish by Berlitz International
Translation Service.
<Select this link for French>
<Select this link for Spanish>
ENGLISH
INGLES
ANGLAIS
HOW
TO USE THIS DICTIONARY
This dictionary is thoroughly cross-referenced for ease of
use and to provide for the most thorough understanding of
each term.
The terms are
organized alphabetically in each language.
Each term is printed in bold type and capital letters.
The
term is followed by a parenthetical classification
reference.
Some terms have more than one reference, which helps
to clarify the ways in which they can be used.
These references
are defined at the beginning of each language section.
Some words within
the definition are also in capital
letters. These are
words that are defined elsewhere in the
dictionary.
Subsequent use of these words within the same
definition is in lower case letters.
At the end of each
definition are translations of the
term itself into French and Spanish.
The preferred usage
is listed first, with secondary or less common usages
following.
The preferred term is the one that appears in the
other language section.
For example:
Defined
Term
References
elsewhere
ABSORPTANCE (sol)
(meas). The ratio between the SOLAR
RADIATION absorbed
by a surface and the total amount of
solar radiation
that strikes it.
F - absorptance;
coefficient d'absorption
S - coeficiente
de absorcion
Spanish
French (preferred
term first)
Second reference
This is a
measurement (meas) term used in the field of
solar (sol) energy.
The term "Solar Radiation" is defined
in the "S" section of the dictionary.
The primary translation
of this term into French is "absorptance," though
in
some French documents, the term "coefficient
d'absorption"
may be found. The
translation of this term into Spanish is
"coeficiente de absorcion."
DEFINITION OF ABBREVIATIONS
agri Relating to
agriculture.
alc Alcohol
production or alcohol fuels.
ani Relating to
animal power.
arc Archaic.
Terms that are outdated but are still
useful.
auto Relating to
internal combustion engines or
automobiles.
bio Relating to
the field of biological science or a
biological
substance.
biocon Relating to
bioconversion. Includes methane and
woodfuel.
chem Relating to
the field of chemical science or a
chemical
substance.
constr Relating to
construction methods, materials, and
structures.
elec Relating to
the production and use of electricity.
fos Relating to
fossil fuels.
gen General
terms, which may apply to various areas of
energy,
particularly renewable energy technologies.
geo Geothermal
power concepts and applications.
heat Relating to
heating or the use of heat for space
heating and
to produce other forms of energy.
hydr Relating to
water and the application of water
power.
Also closed hydraulic systems, which may
use fluids
other than water.
impl
Implement. Tools, utensils, or
devices that work
in conjunction with other equipment.
meas Measuring
instruments, scales, or types of
measurement.
ocean Methods or
devices for extracting energy from the
ocean.
prod Relating to
producer gas.
refrig Relating to
refrigerants or methods of
refrigeration.
sol Relating to
the field of solar energy.
wind Relating to
wind power or other aspects of air
movement.
A
ABSORBENT (refrig).
The less VOLATILE of the two working
FLUIDS used in an
absorption cooling device.
F - absorbant
S - absorbente
ABSORBENT OIL (refrig).
A type of oil used in an absorption
cooling device.
F - huile
absorbante
S - aceite
absorbente
ABSORBER PLATE (sol).
A dark surface that absorbs SOLAR
RADIATION and
converts it into heat; a component of a
FLAT-PLATE SOLAR
COLLECTOR.
F - plaque
d'absorption
S - placa de
absorcion
ABSORPTANCE (sol) (meas).
The ratio between the SOLAR
RADIATION absorbed
by a surface and the total amount of
solar radiation
that strikes it.
F - taux
d'absorptivite
S - coeficiente
de absorcion
ABSORPTION AIR CONDITIONER (sol).
An air conditioner
designed to use a
SOLAR HEATED liquid. Such a system
provides space
cooling through use of ABSORBER PLATES,
VOLATILE FLUIDS,
HEAT EXCHANGERS, and CONDENSERS.
F - climatiseur a
absorption
S - aire
acondicionado por absorcion
ABSORPTION REFRIGERATION (refrig).
A cooling system that
uses heated liquid
to activate the chilling process.
F - refrigeration
par absorption
S - refrigeracion
por absorcion
AC (elec).
Abbreviation for ALTERNATING CURRENT.
F - CA
S - C.A.
ACCELERATOR (impl).
A mechanism that controls the speed of
a vehicle or other
device.
F - accelerateur
S - acelerador
ACCUMULATION (gen) (elec).
The action of collecting or
gathering.
In electricity, the charging of a BATTERY or
the storage of
electric POWER.
F - accumulation
S - acumulacion
ACCUMULATOR (gen). A
CELL, SOLAR POND, THERMAL MASS, or
other device to
store ENERGY.
F - accumulateur
S - acumulador
AC-DC
AC-DC (elec).
Pertaining to a device that will operate on
either ALTERNATING
CURRENT or DIRECT CURRENT.
F - CA-CC
S - CA-CC
ACETATE (chem) (sol).
A compound composed of the SALTS of
ACETIC ACID or the
acetylation products of acetic acid,
such as CELLULOSE
acetate. Certain acetates can be used
as GLAZING on SOLAR
COLLECTORS.
F - acetate
S - acetato
ACETIC ACID (chem).
An important raw material in the
chemical
industry. It is a by-product of the
DESTRUCTIVE
DISTILLATION of
wood. It can also be obtained by
oxidizing
ALCOHOL.
The chemical make-up of acetic acid is
[CH.sub.3]COOH.
F - acide
acetique
S - acido acetico
ACID (bio) (biocon).
A compound that dissociates or separates
in a water solution
to provide hydrogen ions. Acid
forms a SALT when
mixed with ALKALI, and is important in
ANAEROBIC DIGESTION
and FERMENTATION.
F - acide
S - acido
ACID DIGESTION (biocon).
The "first phase" of BIOGAS production,
in which complex
molecules are broken down into
smaller ones.
F - digestion
acide
S - digestion de
acido
ACID HYDROLYSIS (chem) (alc).
A chemical process that uses
ACID to convert
STARCH to sugar. This is the
"first
phase" in
ETHANOL production.
F - hydrolysation
acide
S - hidrolisis de
acido
ACROMETER (gen) (meas).
An instrument used to measure the
density of gases.
F - acrometre
S - acrometro
ACTINOMETER (sol) (meas).
An instrument used to measure
DIRECT RADIATION
from the sun.
F - actinometre
S - actinometro
ACTIVE DRIED YEAST (alc).
YEAST that has been dried, but
in which the yeast
cells still can be activated.
F - levure seche
active
S - levadura
activa secada
ACTIVE SOLAR HEATING (sol).
Warming an interior space with
heat collected
mechanically through SOLAR COLLECTORS.
The collection and
distribution of this warm air requires
additional external
ENERGY to operate pumps,
motors, valves,
etc.
F - chauffage
solaire actif
S - calefaccion
solar activa
AIR BRAKES
ADAPTED SEED (biocon).
INOCULUM used during the START-UP
of a BIOGAS
DIGESTER that has been obtained from another
digester with
similar FEEDSTOCK composition and operating
under similar
conditions.
F - germe adapte
S - semilla
adaptada
ADOBE (constr) (sol).
Sun-dried brick of clay and straw.
Also the clay and
soil used for making such bricks.
Adobe is high in
THERMAL MASS and is useful in low-cost
building
construction.
F - adobe
S - adobe
ADSORPTION (chem).
The process through which carbonaceous
materials are able
to compress and hold on their surfaces
large quantities of
gas. Also, the physical adhesion
of molecules to the
surfaces of solids without
causing a chemical
reaction.
F - adsorption
S - adsorcion
AEOLIAN (wind).
(See: EOLIAN)
F - eolien, -
ienne
S - eolico
AEROBIC (bio).
Pertaining to micro-organisms that require
FREE OXYGEN to
live.
F - aerobie
S - aerobio
AEROBIC BACTERIA (bio) (biocon).
BACTERIA living on FREE
OXYGEN that is
derived from the air. Aerobic bacteria
break down ORGANIC
MATTER during COMPOSTING.
F - bacteries
aerobies
S - bacteria
aerobia
AEROBIC DECOMPOSITION (biocon).
(See: AEROBIC BACTERIA)
F - decomposition
aerobie
S -
descomposicion aerobia
AFFORESTATION (gen).
Forest crops established by purposeful
planting on land
previously not used for tree crops.
F - boisement
S - conversion en
bosque
AFTERBURNER (gen).
An air pollution abatement device that
removes undesirable
organic gases through incineration.
F -
postcombustion
S - quemador
auxiliar
AIR BRAKES (wind) (arc).
Longitudinal SHUTTERS that are
sometimes
incorporated in PATENT SAILS to reduce the
speed of SAIL
rotation in strong winds.
F - freins
d'ailes
S - frenos de
aire
AIR DIFFUSER
AIR DIFFUSER (gen).
A device that delivers air into a room
to mix with the
room air.
F - diffuseur
d'air
S - difusor de
aire
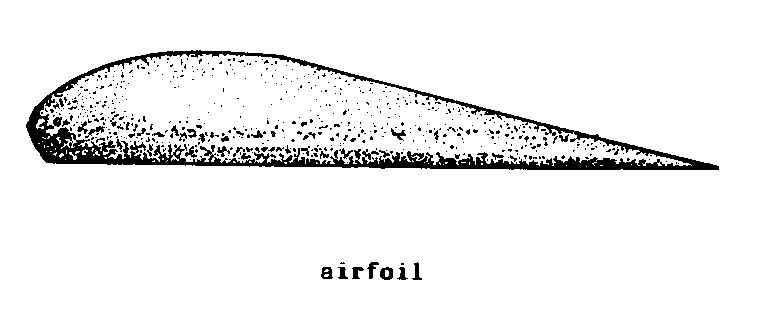
AIRFOIL (wind). A
curved surface designed to create aerodynamic
LIFT forces when
air flows around it.
F - voilure
d'aile
S - plano
aerodinamico
<FIGURE>
10p06.gif (207x600)
AIR-GAS RATIO (chem).
The ratio of the air volume to the
gas volume.
It can be adjusted to change the character
of combustion.
F - rapport
air-gaz
S - relacion de
aire-gas
AIR HEATING SYSTEM (sol).
A SOLAR HEATING system, which
heats air in a
SOLAR COLLECTOR and uses the heated air
as the
HEAT-TRANSFER MEDIUM to the rest of the system.
F - chauffage
d'air, systeme de
S - sistema de
calefaccion del aire
AIR-TYPE COLLECTOR (sol).
A SOLAR COLLECTOR designed to
use air as its
HEAT-TRANSFER MEDIUM.
F - capteur a air
S - colector
solar tipo aire
AIR VELOCITY (wind).
(See: WIND VELOCITY)
F - vitesse
d'ecoulement de l'air
S - velocidad del
aire
ALBEDO (sol) (meas).
The ratio of the amount of light
reflected by a
surface to the light falling onto it.
F - albedo
S - albedo
ALCOHOL (chem). A
class of compounds composed of carbon,
hydrogen, and
oxygen, which occurs widely in nature and
is used in
solvents, antifreezes, chemical manufacture,
and as a fuel.
Alcohol commonly is obtained by
FERMENTATION.
(See also:
BUTYL ALCOHOL, ETHYL ALCOHOL, and
METHYL ALCOHOL)
F - alcool
S - alcohol
ALKALINE BATTERY
ALCOHOL CONDENSER (alc).
(See: CONDENSER)
F - condenseur
d'alcool
S - condensador
de alcohol
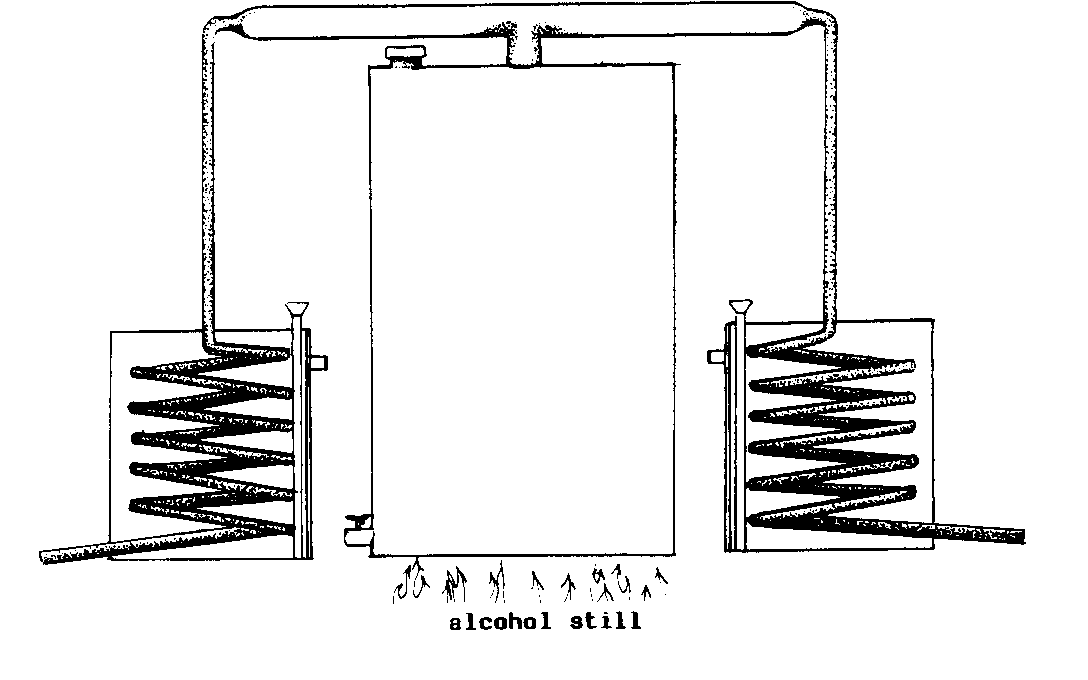
ALCOHOL STILL (alc).
(See: STILL)
F - alambic de
distillation
S - alambique de
alcohol
<FIGURE>
10p07.gif (486x486)
ALCOHOL VAPOR (alc).
ALCOHOL in its gaseous state.
F - vapeur
d'alcool
S - vapor de
alcohol
ALGAE (bio) (biocon) (gen).
Fresh and saltwater aquatic
plants, usually
microscopic in size, but including seaweed.
They are valuable
in waste treatment, as a protein
source for humans,
as animal feed, and as a FEEDSTOCK
for BIOGAS
DIGESTERS.
F - algues
S - algas
ALKALI (chem) (biocon).
Any of various BASES, which neutralize
ACIDS to form
SALTS. Bases are important in
maintaining the
chemical balance in a BIOGAS DIGESTER.
F - alcali
S - alcali
ALKALINE BATTERY (elec).
A BATTERY that uses sodium or
potassium hydroxide
as an electrolyte, and nickel-oxide
flakes and powdered
iron or nickel-cadmium for its
active plates.
F - accumulateur
alcalin
S - pila alcalina
ALKANE
ALKANE (chem). A
general name for hydrocarbons of the
METHANE series.
F - paraffine
S - alcano
ALTERNATING CURRENT (elec).
An electric current that periodically
reverses its
direction. Generally abbreviated
as ac.
F - courant
alternatif
S - courriente
continua
ALTERNATIVE COMBUSTION ENGINES (auto).
Alternatives to the
spark ignition and
the diesel combustion engines. Among
the more developed
designs are the GAS TURBINE and STIRLING
ENGINES.
F - substituts
aux moteurs a combustion
S - motores de
combustion alterna
ALTERNATIVE ENERGY SOURCES (gen).
Sources of ENERGY
different from
those generally employed by a user. The
term usually refers
to RENEWABLE ENERGY sources such as
SOLAR ENERGY, WIND
ENERGY, GEOTHERMAL POWER, HYDROPOWER,
etc.
The use of alternative energy sources is
attractive
because of the [1]
high price and limited availability
of petroleum-based
fuels; [2] the pollution that is
associated with the
burning of FOSSIL FUELS; and [3] the
expense and dangers
of nuclear power.
F - sources
d'energie de substitution
S - fuentes
alternas de energia
ALTERNATOR (elec). A
GENERATOR that changes mechanical
ENERGY into
electrical energy (ALTERNATING CURRENT) by
the rotation of its
ROTOR. Alternators are used in motor
vehicles to
recharge and minimize the drain on the
BATTERY.
They are also commonly adapted to be driven
by
WINDMILLS or by
STEAM TURBINES and WATER TURBINES.
F - alternateur
S - alternador
ALUMINIZED MYLAR (constr) (sol).
A very strong, thin sheet
of plastic material
coated with aluminum. Used as a
reflective surface
for SOLAR COOKERS.
F - Mylar
aluminise
S - Milar
aluminizado
AMBIENT (gen).
Referring to undisturbed environmental
surroundings,
particularly to air and temperature.
F - ambiant
S - ambiente
ANAEROBES (bio).
(See: ANAEROBIC BACTERIA)
F - anaerobies
S - anaerobes
ANAEROBIC (bio).
Pertaining to micro-organisms that can
live in an airless
environment.
F - anaerobie
S - anaerobio
ANCHOR
ANAEROBIC BACTERIA (bio) (biocon).
BACTERIA, known as
ANAEROBES, that can
live in an airless environment by
obtaining oxygen
through the DECOMPOSITION of compounds.
F - bacteries
anaerobies
S - bacteria
anaerobia
ANAEROBIC DIGESTER (biocon).
(See: BIOGAS DIGESTER)
F - digesteur
anaerobie
S - digestor
anaerobio
ANAEROBIC DIGESTION (bio) (biocon).
The DECOMPOSITION of
ORGANIC MATTER by
ANAEROBIC BACTERIA. This process
involves
ACID-forming BACTERIA and METHANE-forming
bacteria.
F - digestion
anaerobie
S - digestion
anaerobia
ANAEROBIC FERMENTATION (bio) (biocon).
(See:
ANAEROBIC
DIGESTION)
F - fermentation
anaerobie
S - fermentacion anaerobia
ANAEROBIC ORGANISMS (bio) (biocon).
(See:
ANAEROBIC
BACTERIA)
F - organismes
anaerobies
S - organismos
anaerobios
ANCHOR (wind) (impl).
A rod or stake driven into the
ground, to which
GUY WIRES for a WINDMILL TOWER are
attached.
F - ancrage
S - ancla
<FIGURE>
10p09.gif (317x317)

ANDIRON
ANDIRON (impl).
Raised metal bars placed on a fireplace
hearth to support
firewood for burning. Andirons allow
air to pass under
the burning wood for more EFFICIENT
combustion.
F - chenets
S - morillo
ANEMOMETER (wind) (meas).
An instrument for measuring WIND
SPEED.
F - anenometre
S - anemometro
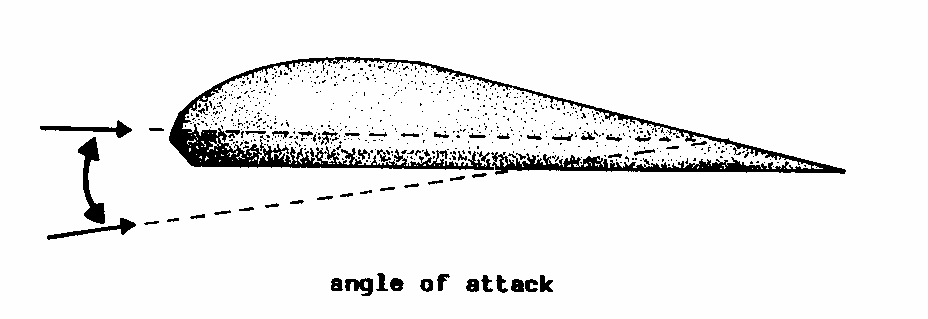
ANGLE OF ATTACK (wind).
The angle between the CHORD of an
AIRFOIL and the
wind. It is considered in WINDMILL
ROTOR
design.
F - angle
d'attaque
S - angulo de
ataque
<FIGURE>
10p10.gif (150x437)
ANGLE OF INCIDENCE (sol).
(See: INCIDENT ANGLE)
F - angle
incident
S - angulo de
incidencia
ANGLE OF REFLECTION (sol).
(See: INCIDENT ANGLE)
F - angle de reflexion
S - angulo de
reflexion
ANHYDROUS (alc) (biocon).
Free from moisture. The term
applies to oxides,
SALTS, and other substances that do
not contain water.
F - anhydre
S - anhidro
ANHYDROUS ALCOHOL (alc).
ALCOHOL that is almost completely
free from
water. Alcohol must be ANHYDROUS to be
mixed
with gasoline to
form GASAHOL. Alcohol and water cannot
be separated beyond
199.99 PROOF. At that CONCENTRATION,
they form an
AZEOTROPE and vaporize at the same
temperature.
F - alcool
anhydre
S - alcohol
etilico anhidro
ANIMAL-DRAWN (ani).
(See: ANIMAL-POWERED)
F - animal de
trait
S - traccion
animal
ASH BOX
ANIMAL-POWERED (ani).
Driven or impelled by animals.
F - traction
animale
S - impulsado por
animales
ANIMAL WASTE CONVERSION (biocon).
The process of directly
burning or
obtaining ENERGY PRODUCTS from animal wastes.
F - conversion
des dechets animaux
S - conversion de
los desechos animales
ANNUAL LOAD FRACTION (sol) (meas).
That portion of annual
heating that is
supplied to a building by SOLAR ENERGY.
F - part de la
charge annuelle
S - fraccion de
la carga anual
ANNULAR SAIL (wind) (arc).
A ring-like SAIL with radial
SHUTTERS.
F - aile
annulaire
S - aspa circular
ANTICLOCK SAIL (wind) (arc).
A SAIL ROTOR that runs
counterclockwise
when observed from the front of the
WINDMILL.
F - aile a
rotation positive
S - aspa
sinistrorsa
AQUATIC BIOMASS (biocon).
BIOMASS grown in fresh or saltwater,
including ALGAE,
seaweed, etc.
F - biomasse
aquatique
S - biomasa
acuatica
AQUEDUCT (hydr). A
CHANNEL or trough built to convey water
For irrigation, to
operate a HYDROPOWER plant, or for
household use.
The water in aqueducts generally flows by
means of gravity,
although pumps may also be used.
F - aqueduc
S - acueducto
AQUIFER (hydr). Any
geological formation containing water,
especially one that
supplies the water for wells,
springs, etc.
F - aquifere
S - acuifera
ARTICULATED WINDMILL (wind) (arc).
A WINDMILL constructed
to provide maximum
EFFICIENCY in winds of various speeds
and from different
directions.
F - eolienne
articulee
S - molino de
viento articulado
ASH BOX (heat). A
removable box below the GRATE in a WOOD
STOVE or a PRODUCER
GAS GENERATOR that collects ash
residue from
combustion.
F - cendrier
S - caja de
cenizas
ASYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR
ASYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR (elec) (wind).
An electrical GENERATOR
that produces
ALTERNATING CURRENT, matching an
existing POWER
source so the two sources can be combined
to power one
LOAD. These generators are often used
with
WINDMILLS to
provide power to buildings that already
receive power from
an electric utility.
F - generateur
asynchrone
S - generador
asincronico
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE (gen).
The pressure exerted by the
Earth's atmosphere
at any given point, generally measured
on a scale based on
the pressure of air at sea
level.
F - pression
atmospherique
S - presion
atmosferica
ATRIUM (sol). An
unroofed, partially roofed, or fully
roofed courtyard or
room in a dwelling, which allows
sunlight to reach
adjoining rooms. It is often used for
PASSIVE SOLAR
HEATING.
F - atrium
S - atrio
ATTENUATION (alc).
The fall in SPECIFIC GRAVITY of the
WORT during
FERMENTATION. This is caused by the
weakening
of BACTERIA or
FUNGI in a CULTURE.
F - attenuation
S - atenuacion
AUGER (impl) (alc).
A rotating, screw-type device that
moves material
through a tube. In ALCOHOL production,
it
is used to transfer
grains from storage to the grinding
site, and from the
grinding site to the COOKER.
F - vrille
d'alimentation
S - barrena
AUTOMATIC DAMPER (impl).
A device that automatically maintains
the FLOW of hot or
cold air into a room.
F - registre
automatique
S - regulador de
tiro automatico
AUTOMATIC TRACKING (sol).
The use of a device that allows
SOLAR COLLECTORS to
"track" or follow the sun during the
day without manual
adjustment.
F - poursuite
automatique
S - aparato de
seguimiento automatico
AUXILIARY GENERATOR (gen) (elec).
A small, engine-driven
GENERATOR that
supplements a RENEWABLE ENERGY POWER
source.
F - generateur
auxiliaire
S - generador
auxiliar
AVAILABLE ENERGY (gen) (meas).
That part of the total
ENERGY produced by
a system that can be applied usefully.
EFFICIENCY is a
measure oF available energy.
F - energie
disponible
S - energia
disponible
AZEOTROPE
AVERAGE WIND SPEED (wind) (meas).
The most common WIND
VELOCITY over a
specified period of time.
F - vitesse
moyenne du vent
S - velocidad
promedio del viento
AXIS (gen). An
imaginary line passing through the center
of a body, about
which the body rotates. (Plural:
axes)
F - axe de
rotation
S - axis
AXLE (gen). A
supporting member that carries a wheel.
It
either rotates with
the wheel to transmit mechanical
POWER, or allows
the wheel to rotate freely on it.
F - essieu
S - eje
AZEOTROPE (chem) (alc).
The chemical term for two liquids
that, at a certain
CONCENTRATION, boil at the same
temperature.
For example, ETHANOL and water cannot be
separated further
than 199.9 PROOF because at this concentration
they form an
azeotrope and vaporize together.
F - azeotrope
S - azeotrope
B
BABO'S LAW (biocon).
A law stating that the VAPOR PRESSURE
of a liquid is
lowered when a non-VOLATILE substance is
dissolved in
it. The pressure is lowered by an
amount
proportional to the
CONCENTRATION of the solution.
F - loi de von
Babo
S - ley de Babo
BACKPUFFING (gen).
The emission of smoke through cooking
holes or other
openings in a wood-burning or CHARCOAL
stove.
It occurs when poor DRAFT in the CHIMNEY
causes
air to pass back
down into the stove.
F - retour de
fumee
S -
contracorriente de humo
BACK STAYS (wind) (arc).
Support bars across the back of
the SAILS of a
WINDMILL.
F - galhaubans
S - soporte
posterior
BACK WATERING (hydr).
The braking effect caused by the
immersion in water
of the lowest BLADES of an OVERSHOT
WATER WHEEL.
F - frein
d'immersion
S - remanso
BACTERIA (bio). Any
of numerous single-celled micro-organisms
occurring in a wide
variety of forms, existing
either as
free-living organisms or as parasites, having
a wide range of
biochemical properties. Bacteria are
necessary for DIGESTION
and FERMENTATION. (Singular:
bacterium)
F - bacteries
S - bacteria
BACTERIAL DECOMPOSITION (biocon).
The chemical breakdown
of ORGANIC MATTER
by micro-organisms.
F - decomposition
bacterienne
S -
descomposicion bacteriana
BAFFLE (gen). A
metal plate or other artificial obstruction
used to check or
deflect the FLOW of FLUIDS.
F - deflecteur
S - desviador
BAGASSE (biocon).
The fibrous residue remaining after the
extraction of the
juice from sugar cane. It may be used
as a fuel.
F - bagasse
S - bagazo
BANCO (biocon).
(See: LORENA STOVE)
F - banco
S - banco
BASES
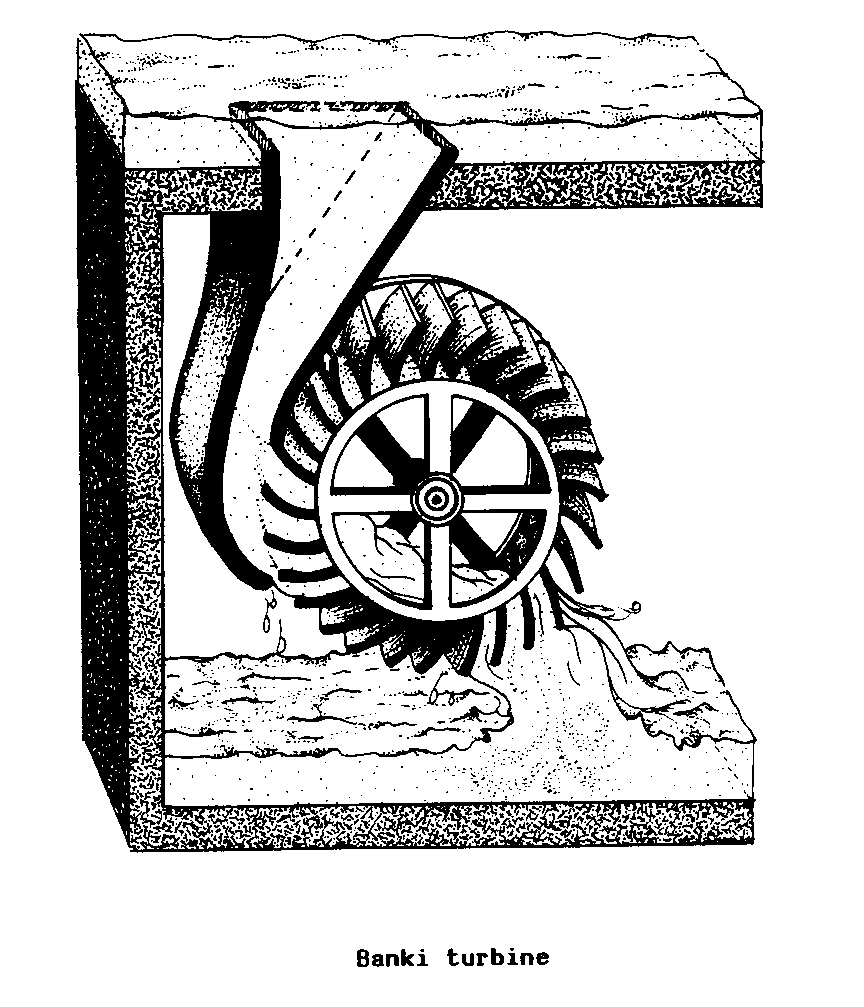
BANKI TURBINE (hydr).
A WATER TURBINE with curved BLADES,
GUIDE VANES, and a
hallow interior. Water passing
through it propels
the RUNNER both on entering and leaving.
This turbine
operates well under a wide HEAD range
and FLOW rates.
F - turbine de
Banki
S - turbina de
Banki
<FIGURE>
10p15.gif (486x486)
BAROMETER (meas). A
device used to measure ATMOSPHERIC
PRESSURE.
F - barometre
S - barometro
BASES (alc) (chem).
Compounds that dissociate in water
solution to form
HYDROXYL ions. Bases react with ACIDS
to form SALTS, and
can be used to maintain the proper pH
(POTENTIAL HYDROGEN) balance in an ALCOHOL
STILL.
F - bases
S - bases
BATCH DIGESTION
BATCH DIGESTION (biocon).
A process of BIOGAS production
in which the
material to be digested is loaded into the
DIGESTER at the
start of the process. A SEED may also
be
added at this
time. The digester is then sealed and
the
contents left to
FERMENT. At completion, the digested
SLUDGE is removed
and the tank reloaded. Daily gas
production
varies during the
process. It is slow at the
start, increases,
and finally declines toward the end of
the DIGESTION
cycle.
F - digestion a
charge initiale
S - digestion por
tandas
BATCH DISTILLATION (alc).
A batch DISTILLATION process
of ALCOHOL
production in which the material to be distilled
is loaded into a
STILL at the start of the process.
The entire volume
is heated and left to distill.
At completion, the
distilled MASH is removed and the
still
reloaded. Daily alcohol production
varies during
the process.
It is slow at the start, increases, and
finally declines
toward the end of the distillation
cycle.
F - distillation
a charge initiale
S - destilacion
intermitente
BATCH FEED (gen). A
DIGESTER or STILL in which ORGANIC
MATTER is loaded,
allowed to generate gas or FERMENT,
and then
removed. The digester or still then is
cleaned
and prepared for a
fresh load of BIOMASS.
F - alimentation
initiale unique
S - alimentacion
por tandas
BATCH-LOADING DIGESTER (biocon).
(See: BATCH FEED)
F - digesteur a
chargement unique
S - digestor de
carga intermitente
BATCH PROCESSING (biocon).
(See: BATCH FEED)
F - traitement de
charges uniques
S - elaboracion
por tandas
BATTERY (elec). A
group of two or more CELLS or ACCUMULATORS
electrically
connected in series or parallel.
Batteries are used
to store electrical ENERGY.
F - batterie
S - bateria
BATTERY CUT-OUT (wind) (impl).
An automatic switch that
disconnects a
BATTERY during its charge if the voltage
of the wind charger
falls below or rises above that of
the battery, within
certain limits. A battery cut-out is
a battery
protection device.
F - coupe-circuit
de batterie
S - interruptor
de bateria
BEARING (gen). A
machine part that supports and guides a
shaft, pivot, or
wheel that slides, rotates, or oscillates
in or on it.
F - palier
S - cojinete
<FIGURE>
10p17.gif (256x256)
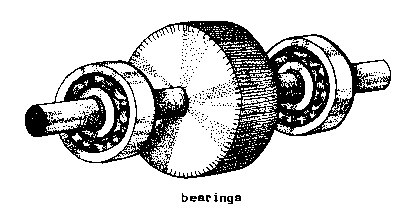
BERM
BEARING ANGLE (sol).
(See: SOLAR AZIMUTH)
F - azimut
S - marcacion
BEAUFORT SCALE (meas) (wind).
A scale of WIND VELOCITIES
ranging from 0 to
12 as follows:
WIND VELOCITY
Code Number
(mph)
Description
0
less than 1
calm
1
1-3
light air
2
4-7
light breeze
3
8-12
gentle breeze
4
13-18
moderate breeze
5
19-24
fresh breeze
6
25-31
strong breeze
7
32-38
moderate gale; near gale
8
39-46
gale
9
47-54
strong gale
10
55-63
whole gale (or storm)
11
64-74
violent storm
12
over 74
hurricane
F - Beaufort,
echelle de
S - escala de
Beaufort
BEER COLUMN (alc).
(See: STRIPPING COLUMN)
F - colonne a
biere
S - columna de
cerveza
BERM (constr). A
manmade mound or small hill of earth
built up against a
house to stop the INFILTRATION of hot
or cold air.
F - banquette
S - monticulo
BEVEL GEAR
BEVEL GEAR (gen).
One of a pair of gears used to connect
two shafts whose
AXES intersect.
F - engrenage conique
S - engranaje
biselado
BICYCLE ADAPTER (gen) (impl).
A device that can be
attached to a
bicycle to supply POWER to pump water,
generate
electricity, etc.
F - adaptateur de
bicyclette
S - adaptador de
bicicleta
BICYCLE GENERATOR (elec).
A small GENERATOR that produces
DIRECT CURRENT (dc)
electricity through PEDAL POWER.
F - generateur a
pedalier
S - generador
accionado por bicicleta
BIOCONVERSION (chem) (gen).
The conversion of ORGANIC
WASTE into ENERGY
PRODUCTS through the action of micro-organisms.
Chemically, this is
the reduction of complex
organic compounds
into simpler, more stable forms.
F - bioconversion
S - bioconversion
BIOGAS (biocon). The
gaseous mixture produced during
ANAEROBIC DIGESTION,
composed chiefly of METHANE and
carbon dioxide.
F - bio-gaz
S - biogas
BIOGAS DIGESTER (biocon).
An airtight vessel in which
ANAEROBIC DIGESTION
takes place and from which METHANE
may be drawn off.
F - digesteur de
bio-gaz
S - digestor de
biogas
<FIGURE>
10p18.gif (540x540)
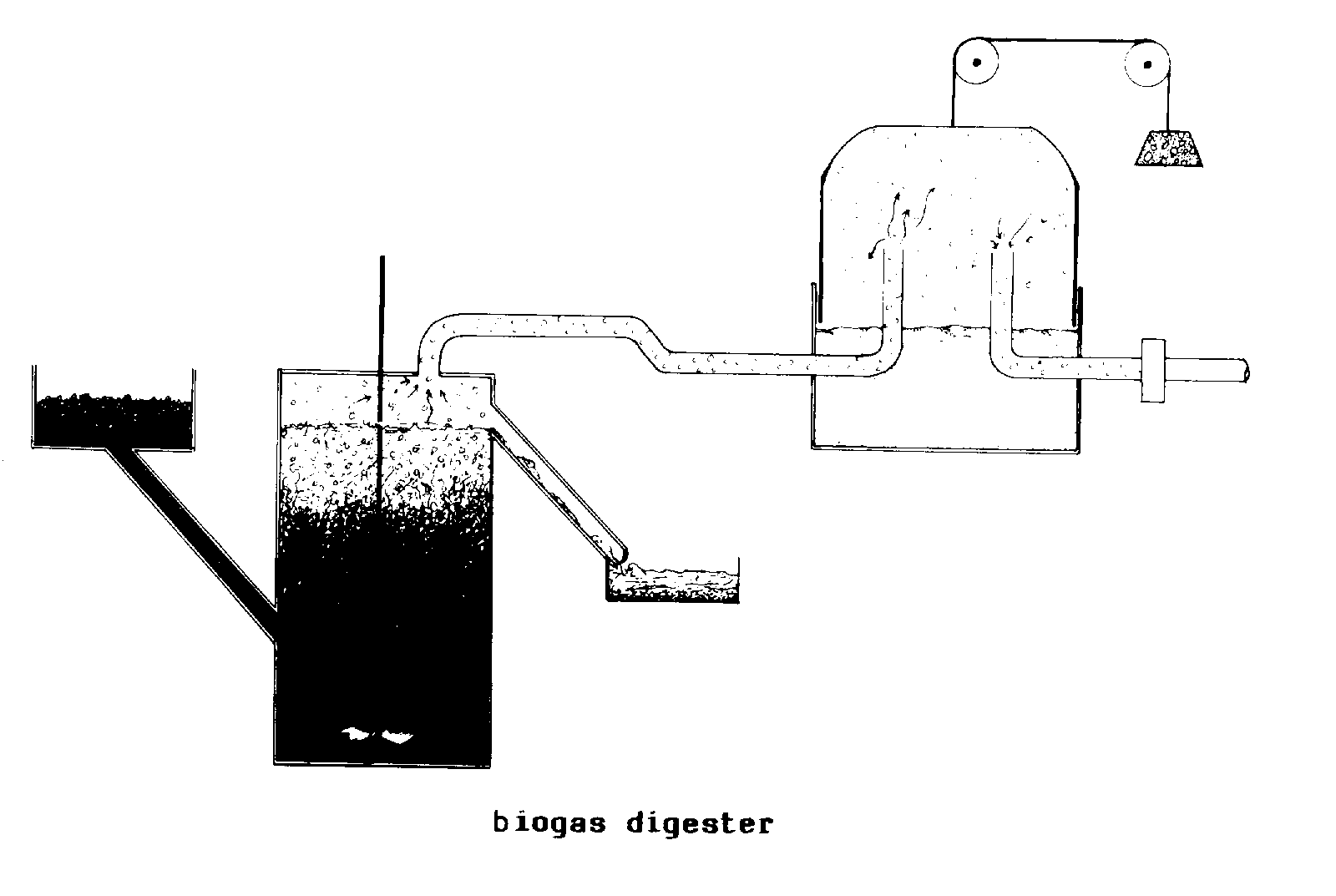
BITUMEN
BIOGAS GENERATOR (biocon).
(See: BIOGAS DIGESTER)
F - generateur de
bio-gaz
S - generador de
biogas
BIOGAS PLANT (biocon).
(See: BIOGAS DIGESTER)
F - reacteur de
bio-gaz
S - planta de
biogas
BIOLOGICAL ENERGY CONVERSION (biocon).
The use of BIOMASS
to convert one form
of ENERGY into another.
F - conversion
biologique de l'energie
S - conversion
biologica de energia
BIOMASS (bio). Plants
and plant materials, trees, crop
residues, wood and
bark residues, and animal manures.
Any ORGANIC MATTER
that can be used in BIOCONVERSION
processes.
F - biomasse
S - biomasa
BIOMASS ENERGY (biocon).
The ENERGY that is released from
BIOMASS when it is
eaten, burned, or otherwise used as
or converted into
fuel.
F - energie de la
biomasse
S - energia de
biomasa
BIOMASS FEEDSTOCK (biocon).
The ORGANIC MATTER used to
produce ENERGY
PRODUCTS through BIOCONVERSION.
F - biomasse
d'alimentation
S - alimento seco
de la biomasa
BIOMASS FUELS (biocon).
Fuels, such as METHANE, produced
from BIOMASS.
F - combustibles
de la biomasse
S - combustibles
de biomasa
BIOMASS YIELD (biocon) (meas).
The amount of BIOMASS that
can be produced in
a given areA. It usually is expressed
in weight units per
area measurement per unit of time.
F - production de
biomasse
S - produccion de
biomasa
BIOMONITORING (biocon (meas).
A pollution-control method
in which living
organisms are used to test the EFFLUENT
from a DIGESTER to
determine whether it is safe to
discharge the
effluent into a body of water. It may
also
be used to test the
quality of waters downstream from a
digester discharge
point.
F - controle
biologique
S - biocontrol
BITUMEN (fos). Any
naturally-occurring hydrocarbon, especially
solid hydrocarbons
such as asphalt, wax, pitch,
and Gilsonite.
F - bitume
S - bitumen
BLACKBODY
BLACKBODY (sol). A
surface that completely absorbs all
SOLAR RADIATION
that strikes it.
F - corps noir
S - cuerpo negro
BLADE (hydr) (impl) (wind).
[1] The curved surface of
certain types of
WATER TURBINES (i.e., CROSS-FLOW
TURBINES).
Water striking the blades causes the turbine
to rotate.
Some turbines, such as the PELTON WHEEL,
have
cups instead of
blades. [2] A single, extended surface
of a WINDMILL
ROTOR.
F - [1] aube; [2]
pale
S - [1] paleta;
[2] aspa
BLADE ANGLE [1] (wind).
The angle of a CHORD of a WINDMILL
BLADE with the
ROTOR plane of rotation. [2]
(hydr). The
INCIDENT ANGLE of a
TURBINE BLADE.
F - [1] angle de
pale; [2] angle d'aube
S - [1] angulo
del aspa; [2] angulo de la paleta
BORE HOLE (gen). A
deep, vertical hole in the earth.
Usually
used to describe a
well.
F - trou de
sondage
S - pozo de
sondeo
BRACE SOLAR STEAM COOKER (sol).
(See: INSULATED STEAM
COOKER)
F - rechaud a
vapeur solaire Brace
S - portahornillo
de vapor solar Brace
<FIGURE>
10p20.gif (540x540)
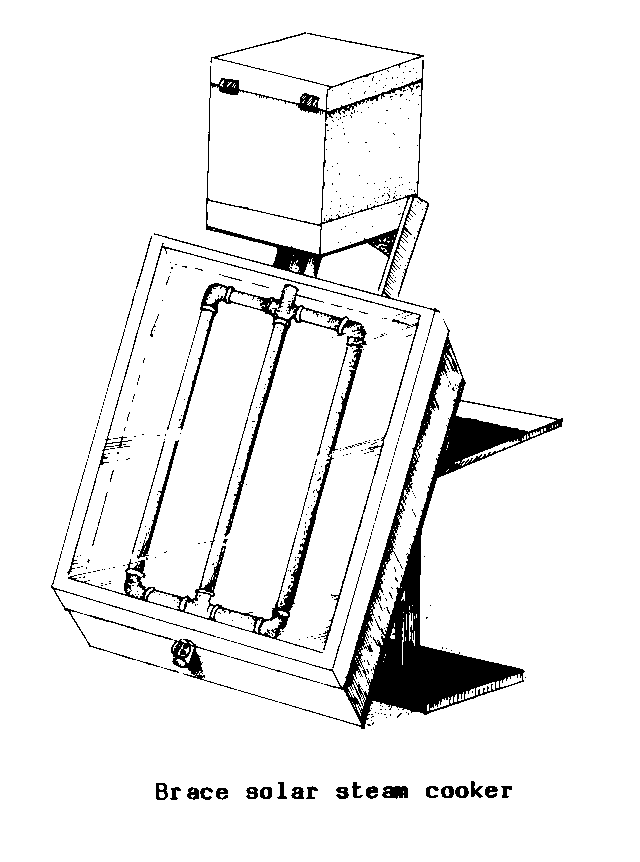
BREAST
WHEEL
BRAKE (gen). A
device used to slow or stop motion, especially
by contact
friction.
F - frein
S - freno
BRAZING (gen). A
process by which two pieces of metal are
joined using a
nonferrous alloy with a lower melting
point than either
of the two metals being joined.
F - brasage
S - soldadura con
laton
BREAST BEAM (wind) (arc).
The main lateral beam below the
WIND SHAFT.
F - poutrelle
maitresse
S - viga de
costado
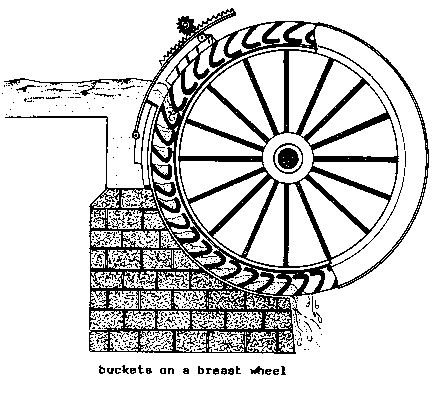
BREAST WHEEL (hydr).
A sophisticated type of WATER WHEEL
into which water
enters below the top of the wheel and
is kept in the
BUCKETS until being discharged at or near
the lowest point on
the wheel. Breast wheels generally
operate best with
HEADS amounting to less than the
diameter of the
wheel. High breast wheels (where the
water enters above
the center shaft) can approach 65
percent ENERGY
CONVERSION EFFICIENCY. (Syn:
breast-shot
wheel)
F - roue de
poitrine
S - rueda de
costado
<FIGURE>
10p21.gif (486x486)
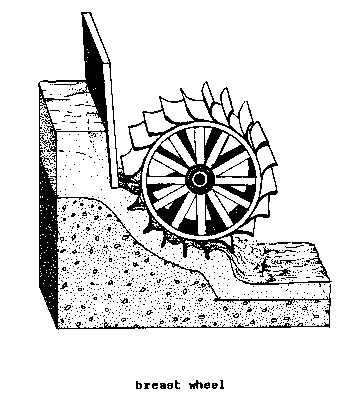
BREEZE
BREEZE (wind). In
general, any light to moderate wind.
(See also:
BEAUFORT SCALE)
F - brise
S - brisa
BREWER'S DRIED GRAIN (alc).
(See: DISTILLER'S GRAIN).
F - grains secs
de brasserie
S - grano seco de
destilacion
BREWING MASH (alc).
Crushed or ground FEEDSTOCK mixed with
warm water in
preparation for FERMENTATION during the
production of
ETHANOL.
F - mout de
brassage
S - mosto
BRINE (refrig). A
heavy SALT solution used in REFRIGERATION.
F - saumure
S - salmuera
BRIQUETTE (fos). A
type of fuel that has been finely
ground and
compressed in pressure molds. It is
usually
made from low-grade
coal, coke, CHARCOAL, or BIOMASS,
and is mixed with a
binder such as STARCH, tar, cement,
pitch, or asphalt.
F - briquette
S - briqueta
BRITISH THERMAL UNIT (heat) (meas).
The amount of heat
required to raise
the temperature of one pound of water
one degree
FAHRENHEIT under stated conditions of temperature
and pressure.
It is a standard unit for measuring
quantity of HEAT
ENERGY. Generally abbreviated as BTU.
F - British
thermal unit
S - unidad
termica britanica
BUBBLE CAP (alc). A
perforated cap on the plates of a
DISTILLATION
COLUMN, used to ensure that the vapor and
condensed liquid
mix thoroughly.
F - cloche de
barbotage
S - casquete de
burbujeo
BUBBLE CHAMBER (biocon).
A safety device attached to a
BIOGAS DIGESTER to
ensure that the gas is free of air,
since an air and
gas mixture would be explosive. The gas
is
"bubbled" through a container of water before being
used or
stored. If LIMEWATER is used instead of
water,
the bubble chamber
can also be used to SCRUB the gas. In
addition, the
bubble chamber serves as a SPARK ARRESTER.
F - chambre a
bulles
S - camara de
burbujas
BUCKET (hydr).
Cup-shaped containers or BLADES attached to
a WATER WHEEL.
F - auget
S - cangilon
BUTYL ALCOHOL
<FIGURE>
10p23.gif (486x486)
BUCKET ANGLE (hydr).
The INCIDENT ANGLE of BUCKETS on a
WATER WHEEL.
F - angle d'auget
S - angulo de los
cangilones
BUCKET CHAIN (hydr).
A chain loop with BUCKETS attached to
it at regular
intervals. The chain runs over sprocket
wheels.
As each bucket passes by a water source,
water
fills the bucket,
providing POWER and propelling the
chain further
along.
F - noria a
godets
S - transportador
de cangilones
BUFFER CAPACITY (biocon) (chem).
The capacity of a solution
to resist pH
(POTENTIAL HYDROGEN) changes when
small amounts of
ACID or ALKALI are added. In the case
of DIGESTED SLUDGE,
the ammonium and bicarbonate ions
are mainly
responsible for buffering.
F - pouvoir
tampon
S - capacidad
amortiguadora
BUTANOL (alc).
(See: BUTYL ALCOHOL).
F - butanol
S - butanol
BUTYL ALCOHOL (alc) (chem).
An ALCOHOL obtained by the
FERMENTATION of
sugar or cornstarch. The chemical
equivalent
of butyl alcohol is
[C.sub.4][H.sub.9]OH. (Syn:
butanol)
F - alcool
butylique
S - alcohol
butilico
C
C (meas).
Abbreviation for CELSIUS.
F - C
S - C
CALCIUM HYDROXIDE (biocon) (chem).
A solution that is
often used in
BUBBLE CHAMBERS to SCRUB BIOGAS. It is
commonly known as
LIMEWATER.
F - hydrate de
calcium
S - hidroxido de
calcio
CALORIE (gen). The
amount of heat required to raise the
temperature of one
gram of water one degree CELSIUS at
ATMOSPHERIC
PRESSURE.
F - calorie [1]
S - caloria
CAM (gen). An
eccentric projection on a revolving shaft,
shaped to produce
variable or reciprocating motion in
another contacted
or engaged part.
F - came
S - leva
CANAL (gen) (hydr).
An artificial watercourse uniting
rivers, lakes, or
seas for purposes of inland navigation,
irrigation, or
conveyance of water to a HYDROPOWER
device.
F - canal
S - canal
CANISTER (wind) (arc).
A piece of metal placed at the
outer end of a
ROTOR SPAR to hold the SAIL in place.
F - douille
S - chapa de
fijacion
CAP (wind) (arc).
The revolving top of a TOWER MILL or
SMOCK MILL.
F - calotte
S - cumbrera
CAPACITY FACTOR (elec) (meas).
The total KILOWATT HOURS
of ENERGY consumed
divided by the total KILOWATTS
produced by an
electricity-generating plant. Generally
calculated on an
annual basis.
F - facteur de
capacite
S - factor de
capacidad
CAPACITY OF THE WIND (wind) (meas).
The total amount of
dirt and dust
particles of a given kind that can be
sustained per unit
volume of air by a wind of a given
velocity.
F - capacite du
vent
S - capacidad del
viento
CELLULASE
CARBOHYDRATE (alc) (chem).
Sugars, STARCHES, CELLULOSE,
and other similar
compounds containing carbon, hydrogen,
and oxygen
only. Carbohydrates are excellent
FEEDSTOCK
for an ALCOHOL
STILL.
F
-
hydrates de carbone
S
-
carbohidrato
CARBON-TO-NITROGEN RATIO (biocon).
The proportion of carbon
to nitrogen in the
material being placed in a BIOGAS
DIGESTER.
This ratio is important for maintaining
biogas
production.
25:1 is the optimal C/N ratio.
Nitrogen
Carbon-Nitrogen
Material Content
Ratio
Cow dung
1.7%
25 to 1
Poultry
manure 6.3%
No carbon
Grass
4.0%
12 to 1
Sheep
manure 3.75%
No carbon
Urine
15-18%
8 to 1
Wheat straw
0.3%
128 to 1
Potato
tops 1.5%
25 to 1
Tomato
3.3%
128 to 1
F
-
rapport carbone-azote
S
-
proporcion de carbon a nitrogeno
CARBURETOR (auto). A
device for mixing and controlling the
amount of air and
fuel supplied to a gasoline engine.
F
-
carburateur
S
-
carburador
CASING (sol). The
framework housing the components of a
FLAT-PLATE
COLLECTOR. It is generally made of
metal and
lined with material
for THERMAL insulation. Inlet and
outlet openings are
provided.
F
-
enveloppe
S
-
envoltura
CATCHMENT APRON (hydr).
A projecting slope on the downstream
side of a SLUICE or
dam, which is provided to
withstand the force
of falling water.
F
-
pente de captage
S
-
plataforma colectora
CELL (elec). A
device that generates electricity, traditionally
consisting of two
plates or conducting surfaces
placed in an
electrolytic FLUID.
F
-
element
S
-
celula
CELLULASE (bio) (alc).
Any of several ENZYMES found in
FUNGI, BACTERIA,
and lower animals that cause CELLULOSE
to break down in
water. These enzymes are needed for
ALCOHOL
DISTILLATION.
F
-
cellulase
S
-
celulase
CELLULOSE
CELLULOSE (chem) (alc).
The main POLYSACCHARIDE in living
plants.
Cellulose forms the skeletal structure of
plant
cell walls and can
be HYDROLYZED to form GLUCOSE.
F
-
cellulose
S
-
celulosa
CELLULOSIC BIOMASS (biocon).
BIOMASS that contains vegetable
matter.
F
-
biomasse cellulosique
S
-
biomasa celulosica
CELSIUS (meas). The
international temperature scale in
which water freezes
at 0 [degrees] and boils at 100 [degrees].
To convert
from degrees Celsius to degrees FAHRENHEIT,
multiply the
temperature in
degrees Celsius by 9/5 (or 1.8) and add
32.
To convert from degrees Fahrenheit to
degrees
Celsius, subtract
32 from the Fahrenheit temperature
and then multiply
by 5/9. Abbreviated as C.
(Syn:
centigrade)
F
-
Celsius
S
-
Celsio
CENTIGRADE (meas).
(See: CELSIUS).
F
-
centigrade
S
-
centigrado
CENTRIFUGAL FORCE (gen).
The inertial force repelling a
body away from the
center of the curvature of a curved
path along which it
is moving, or away from the AXIS
around which it
rotates. The opposite of CENTRIPETAL
FORCE.
F
-
force centrifuge
S
-
centrifuga, fuerza
CENTRIPETAL FORCE (gen).
A force attracting a body toward
the center of the
curvature of a curved path along which
it is moving, or
toward the AXIS around which it
rotates.
The apposite of CENTRIFUGAL FORCE.
F
-
force centripete
S
-
centripeta , fuerza
CHALK ADOBE (constr).
A method of making ADOBE bricks in
which chalk is
added to the clay, straw, and water.
Chalk
adobe is useful as a THERMAL MASS.
F
-
adobe a la chaux
S
-
mezcla de adobe y creta
CHANNEL (hydr). The
bed of a stream or waterway. (See
also:
CANAL)
F
- chenal
[1]
S
-
cauce
CHARCOAL (fos) (gen).
A dark-colored or black porous form
of CARBON made from
vegetable or animal substances.
Charcoal commonly
is made by charring wood in a KILN or
RETORT from which
air is partially excluded. It is used
for FUEL, and in
various mechanical, artistic, and
chemical
processes. By using DISTILLATION and
retorts to
produce charcoal,
several valuable products can be collected
that would
otherwise be lost, including COMBUSTIBLE
GASES, CREOSOTE
OIL, METHANOL, soluble tar, and
combustible pitch.
F
-
charbon de bois
S
-
carbon
CHIMNEY CAP
CHARCOAL GAS (prod).
(See: PRODUCER GAS)
F
-
gaz de charbon de bois
S
-
gas de carbon
CHIMNEY (constr). A
vertical passage or FLUE through
which smoke and
gases escape from a stove or fireplace.
F
-
cheminee
S
-
chimenea
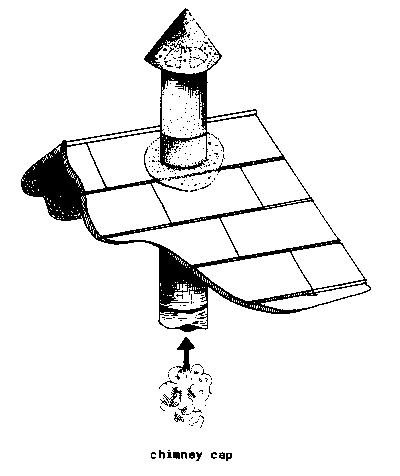
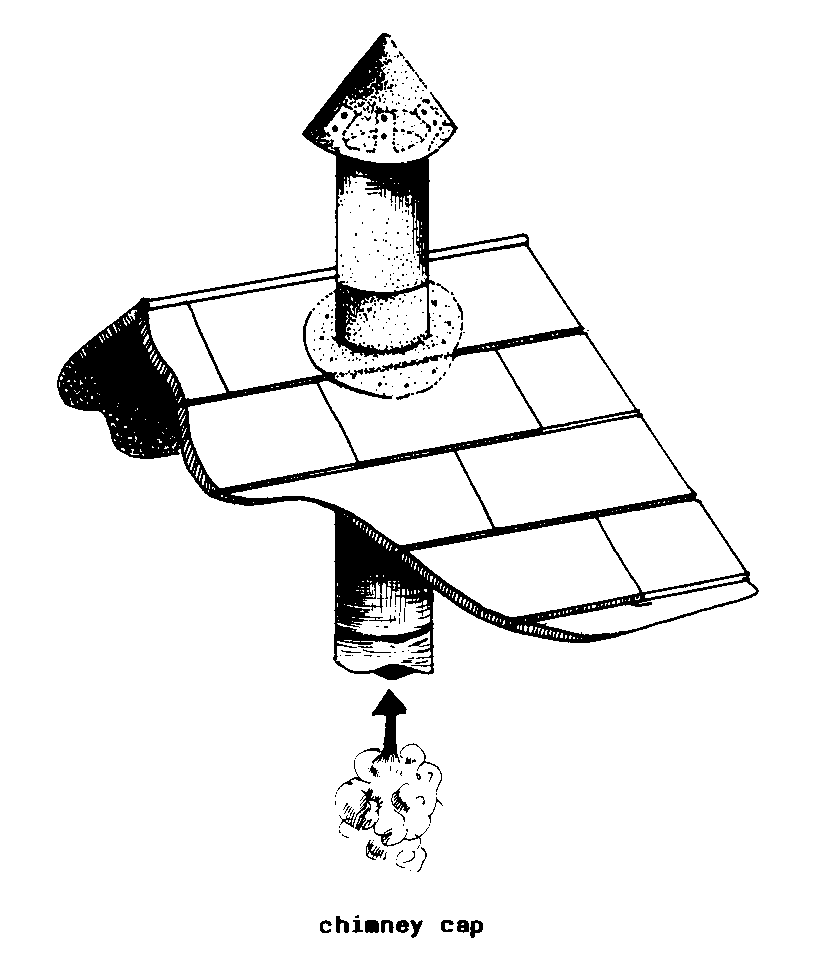
CHIMNEY CAP (constr).
A cone, usually made of sheet metal,
placed pointed end
up slightly above the top of a CHIMNEY.
It prevents rain
and debris from falling into the
chimney.
F
-
mitre
S
-
sombrerete de chimenea
<FIGURE>
10p27.gif (486x486)
CHINESE-TYPE DIGESTER
CHINESE-TYPE DIGESTER (biocon).
A BIOGAS DIGESTER that is
primarily designed
to produce fertilizer. Usually a
FIXED-DOME
DIGESTER.
F
-
digesteur type chinois
S
-
digestor de tipo chino
<FIGURE>
10p28.gif (486x486)
CHORD (wind). The
distance from the LEADING EDGE to the
TRAILING EDGE of an
AIRFOIL. The term refers to WINDMILL
BLADE design.
F
- profondeur de l'aile
S
-
profundidad del aspa
CHULA (biocon). A
small, wood-burning stove, usually made
of mud, clay,
brick, or metal. The term is widely
used
in South Asia.
F
-
chula
S
-
chula
CIRCULAR FOCUSING COLLECTOR (sol).
(See: COMPOUND PARABOLIC
COLLECTOR)
F
-
capteur circulaire a concentration
S
-
colector circular de enfoque
CISTERN (hydr). An
artificial reservoir or watertight tank
for storing water
or other liquids.
F
-
citerne
S
-
cisterna
CLAMPS (wind) (arc).
Wooden splints bolted to the sides of
the STOCKS, locking
the SAIL assembly in the POLL END.
F
-
eclisses
S
-
prensas
COLLECTOR
CLEARNESS INDEX (sol) (meas).
A SOLAR ENERGY concept
introduced to
express the ratio of a particular hour,
day, or month's
SOLAR RADIATION on a horizontal surface
to the
EXTRATERRESTRIAL SOLAR RADIATION on that same
surface for the
same period of time. It is useful in
calculating DIFFUSE
RADIATION and RADIATION falling on a
tilted surface.
F
-
indice de clarte
S
-
indice de claridad
CLERESTORY (sol). A
vertical window that is placed high in
a wall near the
eaves for light, HEAT GAIN, and ventilation.
F
-
lanterneau
S
-
claraboya
CLOSED-LOOP SYSTEM (sol).
A SOLAR HEATING system in which
distilled water,
antifreeze, and/or corrosion inhibitors
are circulated
through the COLLECTORS and storage tanks
in a closed
loop. Heat picked up from the collectors
by
the circulating
FLUIDS is transferred to the water in
the storage tanks
through the closed loop or other HEAT
EXCHANGERS.
F
-
circuit ferme, systeme de
S
-
sistema de ciclo cerrado
C/N (biocon).
(See: CARBON TO NITROGEN RATIO)
F
-
C/N
S
-
C/N
COAL GASIFICATION (prod).
The combustion of coal to form a
gas suitable for
use as a fuel. This is usually done in
a PRODUCER GAS
GENERATOR.
F
-
gazeification du charbon
S
-
gasificacion del carbon
COB ADOBE (constr).
A type of ADOBE in which corn cobs are
added to clay,
water, and straw. Adobe bricks are
reinforced
by this addition of
cobs during the brick-making
process.
Cob adobe is a useful THERMAL MASS.
F
-
adobe a la rafle de mais
S
-
mezcla de paja, arcilla, agua y mazorcas
COLLECTION (sol).
The act of trapping SOLAR RADIATION.
F
-
captation
S
-
captacion
COLLECTOR (sol). A
device to trap SOLAR RADIATION and convert
it into usable
heat. The term collector frequently
refers to an
insulated frame containing a panel made
from an ABSORBER
PLATE and GLAZING. More broadly, a
well-designed
building with windows facing the equator
may also be
considered a collector, as can other solar
devices that capture
SOLAR RADIATION in the form of
heat.
F
-
capteur
S
-
colector
COLLECTOR EFFICIENCY
COLLECTOR EFFICIENCY (sol) (meas).
The ratio of SOLAR
ENERGY absorbed by
a COLLECTOR to the RADIANT ENERGY
falling on the
collector.
F
-
rendement d'un collecteur
S
-
eficiencia del colector
COLLECTOR/HEAT-EXCHANGER CORRECTION FACTOR (sol) (meas).
An index that
indicates how much useful SOLAR ENERGY is
lost during the
exchange of heat from the COLLECTOR to
the storage tank in
LIQUID-BASED SOLAR HEATING SYSTEMS.
F
-
coefficient de correction capteur-echangeur de
chaleur
S
-
factor de correccion del colector/termopermutador
COLLECTOR-HEAT REMOVAL EFFICIENCY FACTOR (sol) (meas).
The
ratio of actual
useful HEAT GAIN of a FLAT-PLATE SOLAR
COLLECTOR to the
heat gain if the entire COLLECTOR PLATE
were at the same
temperature as the inlet FLUID.
F
-
coefficient de rendement capteur-echangeur
de
chaleur
S
-
factor de eficiencia del colector-termoextractor
COLLECTOR PLATE (sol).
A metal sheet in a SOLAR COLLECTOR
whose primary
function is to absorb as much as possible
of the SOLAR
RADIATION reaching it through the GLAZING,
while losing as
little heat as possible as it transfers
the retained heat
to the HEAT TRANSFER MEDIUM.
F
-
plaque collectrice
S
-
placa colectora
COLLECTOR TILT ANGLE (sol) (meas).
The angle between the
plane of the
horizon and the surface of a SOLAR COLLECTOR,
generally used to
maximize the COLLECTION of SOLAR
RADIATION.
F
-
inclinaison d'un capteur
S
-
angulo de inclinacion del colector
COMBUSTIBLE GAS (biocon) (prod).
Gas that will burn. This
includes BIOGAS,
PRODUCER GAS, and other VOLATILE
FLUIDS.
F
-
gaz combustible
S
-
gas combustible
COMBUSTION CHAMBER (heat).
The place in a stove where fuel
is burned.
F
-
chambre de combustion
S
-
camara de combustion
COMBUSTION ZONE (prod).
The section in a PRODUCER GAS
GENERATOR in which
the FEEDSTOCK is burned.
F
-
zone de combustion
S
-
zona de combustion
COMMON SAIL (wind) (arc).
A WINDMILL SAIL that is covered
with a canvas
cloth.
F
-
aile de moulin
S
-
aspa comun
CONING
COMPOSTED SLUDGE (biocon).
SLUDGE that has been rendered
relatively
PATHOGEN-free through COMPOSTING. It
generally
can be used safely
as fertilizer.
F
-
boues compostees
S
-
composte de lodos cloacales
COMPOSTING (biocon).
AEROBIC DECOMPOSITION of ORGANIC
MATTER.
The resulting material is used as a
fertilizer.
F
-
compostage
S
-
composte
COMPOUND PARABOLIC COLLECTOR (sol).
A type of SOLAR COLLECTOR
using parabolic
REFLECTORS.
F
-
capteur parabolique compose
S
-
colector parabolico compuesto
CONCENTRATING COLLECTOR (sol).
A SOLAR COLLECTOR that uses
REFLECTORS to
concentrate DIRECT RADIATION from the sun
onto a narrow
ABSORBER PLATE to produce intense heat.
F
-
capteur a concentration [1]
S
-
colector concentrador
CONCENTRATING PHOTOVOLTAIC ARRAY (sol).
A series of lenses
or mirrors used to
concentrate SOLAR RADIATION onto
PHOTOVOLTAIC CELLS,
which convert the sunlight into
electricity.
The concentrated sunlight increases the
output of each
cell, thus reducing the total number of
cells required to
produce a given amount of electricity.
(See also:
PHOTOVOLTAIC ARRAY)
F
-
groupe photovoltaique de concentration
S
-
conjunto concentrador fotovoltaico
CONCENTRATING THERMAL COLLECTOR (sol).
(See:
CONCENTRATING
COLLECTOR)
F
-
capteur thermique a concentration
S
-
colector termico concentrador
CONCENTRATION (gen).
The amount of a substance contained
in a FLUID per unit
volume.
F
-
concentration
S
-
concentracion
CONDENSER (gen) (impl).
A device used to change a vapor
into a liquid.
This can be done either by exposing to
air a tube that
contains vapor, or by passing the tube
through a WATER
JACKET.
F
-
condenseur
S
- condensador
CONDUCTION (heat).
Heat transfer from direct contact
between a hot body
and a cold body.
F
-
conduction
S
-
conduccion
CONING (wind). The
practice of tilting up the WIND SHAFT
of a WIND MACHINE
at a small angle.
F
- fuseler
S
-
movimiento de la pala
CONTINUOUS DIGESTION
CONTINUOUS DIGESTION (biocon).
The continuous feeding of
BIOMASS into a
BIOGAS DIGESTER, with the removal of an
equivalent volume
of EFFLUENT. The process is usually
started with the
addition of a SEED. It may take several
DETENTION TIMES
before the process becomes steady. For
many purposes, this
is a more EFFICIENT and convenient
process than BATCH
DIGESTION. Processes involving daily
addition and
removal are more properly described as
semi-continuous.
F
-
digestion en continu
S
-
digestion continua
CONTINUOUS FLOW DIGESTER (biocon).
A DIGESTER into which
BIOMASS may be
loaded and gas and EFFLUENT recovered
without
discontinuing digestion.
F
-
digesteur a flux continu
S
-
digestor de circulacion continua
CONTINUOUS PROCESSING (biocon).
(See: CONTINUOUS
DIGESTION)
F
-
traitement en continu
S
-
proceso continuo
CONTINUOUS STILL (alc).
An ALCOHOL STILL into which MASH
may be loaded and
ALCOHOL recovered without discontinuing
alcohol production.
F
-
alambic a distillation continue
S
-
alambique continuo
CONTROLLED BURNING ATMOSPHERE (fos).
An atmosphere in
which oil or
natural gas is burned with just enough oxygen
to prevent all the
carbon from being consumed. The
recovered carbon
may be used as a fuel.
F
-
atmosphere a combustion controlee
S
-
atmosfera de combustion controlada
CONVECTION (heat).
The transfer of heat between one location
or surface and
another by the motion of a heat-carrying
FLUID.
Also, the transfer of heat within a
fluid by movements
within the fluid.
F
-
convection
S
-
conveccion
CONVECTION AIR COOLER (refrig).
A non-electric cooler that
depends on the
natural circulation of air.
F
-
refroidisseur par convection d'air
S
-
enfriador de aire por conveccion
CONVERSION PROCESS (gen).
A process through which ENERGY
is converted from
one form to another, such as RADIANT
ENERGY into heat or
electric energy.
F
-
conversion
S
-
proceso de conversion
COOKER (alc). A
heated tank with an AGITATOR that heats
the MASH as part of
the ALCOHOL production process.
F
-
chaudiere de cuisson
S
-
caldera de coccion
CROSS-FLOW TURBINE
COOKING (alc). A
heating and stirring process that breaks
down STARCH
granules, thus making the starch available
for the
liquefaction and SACCHARIFICATION steps of the
ALCOHOL
manufacturing process.
F
-
cuisson
S
-
coccion
COOK STOVE (biocon).
An apparatus in which fuel is burned
to produce heat for
cooking.
F
-
cuisiniere
S
-
estufa
CO-PRODUCT (alc).
Substances resulting from the production
of ETHANOL by FERMENTATION.
F
-
coproduit
S
-
coproducto
CORRUGATED METAL SOLAR COLLECTOR (sol).
A type of SOLAR
COLLECTOR that uses
a corrugated metal as its ABSORBER
PLATE.
The metal is usually painted with FLAT BLACK
PAINT.
F
-
capteur solaire en tole ondulee
S
-
colector solar de metal corrugado
COVER (sol).
(See: GLAZING)
F
-
revetement
S
-
revestimiento
COVER PLATE (sol).
The transparent material placed over a
COLLECTOR-ABSORBER
PLATE so that heat loss to the atmosphere
is reduced and a
greater fraction of the SOLAR
RADIATION is
collected as useable heat.
F
-
plaque de couverture
S
-
placa revestidora
CREOSOTE OIL (gen).
A by-product from CHARCOAL production
by
DISTILLATION. It may be used as a preservative
to
protect wood from
termites, moisture, etc.
F
-
huile de creosote
S
-
aceite de creosota
CRETAN SAIL WINDMILL (wind).
(See: CRETAN WINDMILL)
F
-
moulin a ailes cretois
S
-
molino de viento con aspas cretanas
<FIGURE>
10p34.gif (540x353)
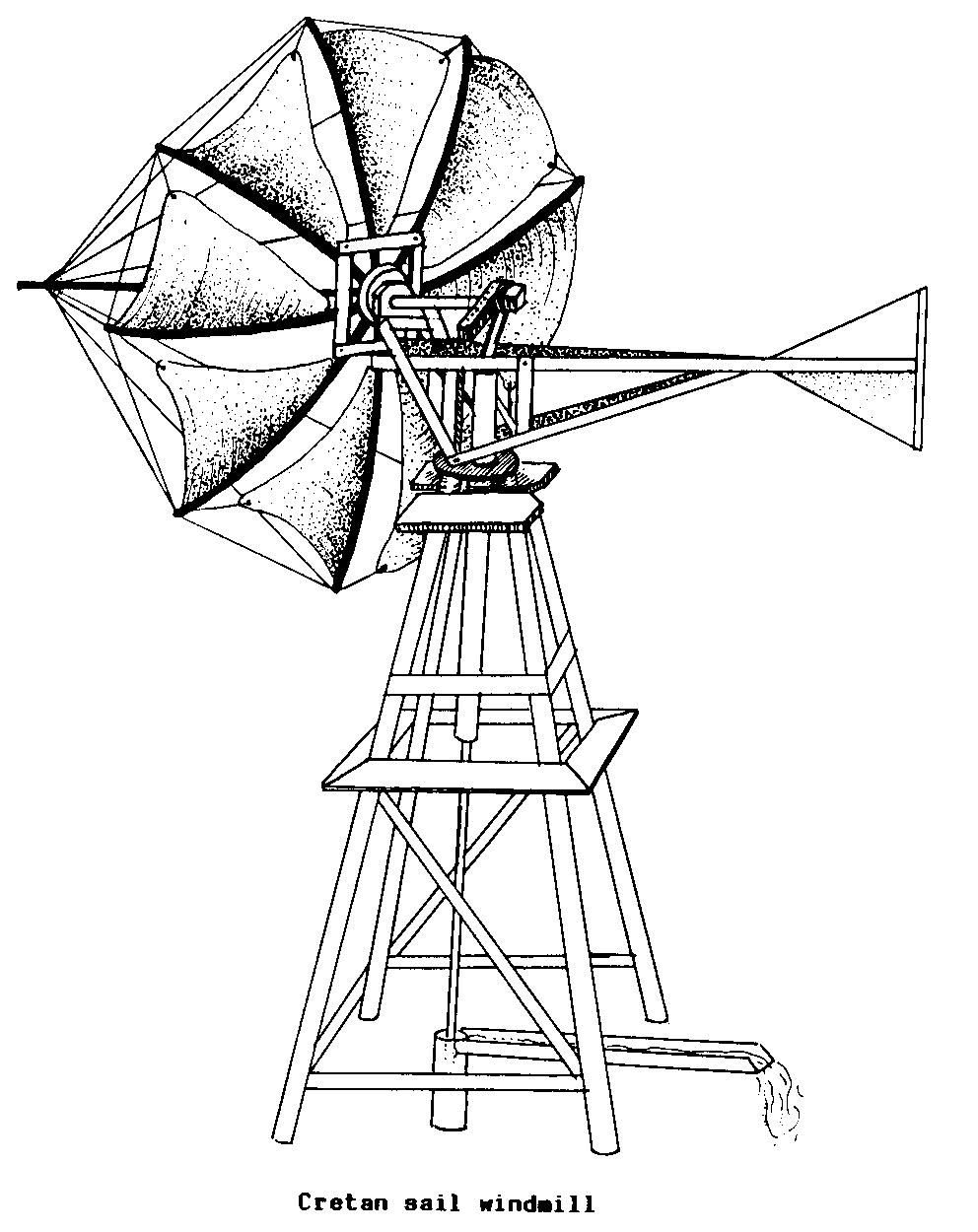
CRETAN WINDMILL (wind).
A type of HORIZONTAL AXIS SAIL
ROTOR WINDMILL
generally having four fixed, triangular
SAILS.
Cretan windmills are used primarily for
low-lift
water pumping.
F
-
moulin a vent cretois
S
-
molino de viento cretano
CROSS (wind) (arc).
A cruciform iron support for the sail
assembly, used as
an alternative to the POLL END.
F
-
croix
S
-
aspa de hierro
CROSS-FLOW TURBINE (hydr).
(See: BANKI TURBINE)
F
-
turbine a ecoulement radial
S
- turbina con rodete de tambor
CROSSWIND
CROSSWIND (wind).
Winds blowing crosswise to the direction
of the wind stream.
F
-
vent de travers
S
-
viento de costado
CULTURE (bio). A
preparation containing micro-organisms
that are growing on
a medium.
F
-
bouillon de culture
S
-
cultivo
CUP ANEMOMETER
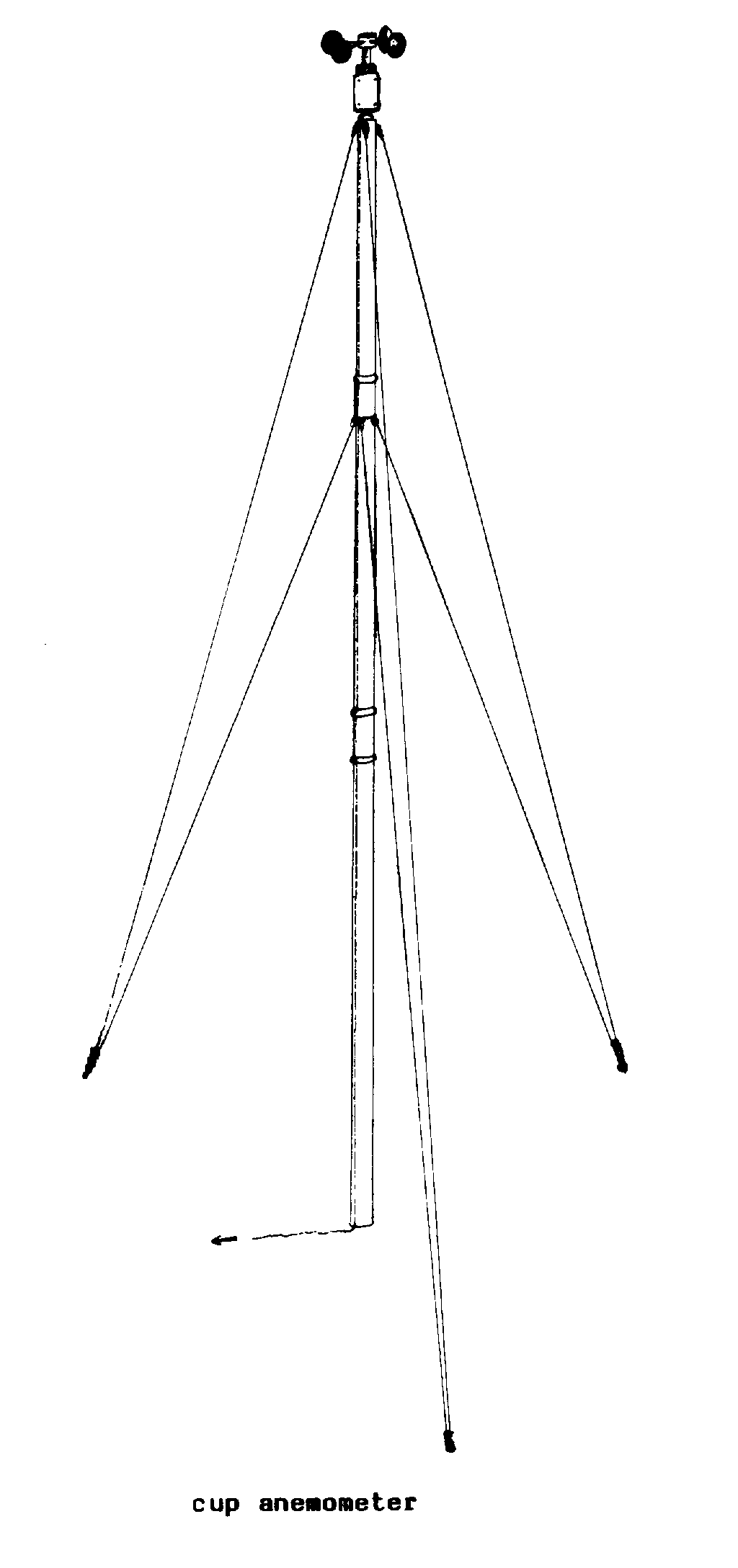
CUP ANEMOMETER (wind) (meas).
An ANEMOMETER with three or
four cups that
rotate with the wind to measure wind
speed.
F
- anemometre a coquilles
S
-
anemometro de tazas
<FIGURE>
10p35.gif (486x486)
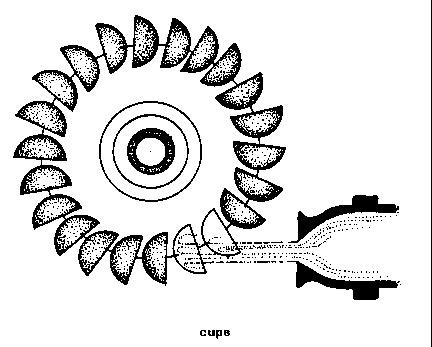
CUPS
CUPS (hydr). Bowl
shaped BLADES found on PELTON WHEELS and
other types of
IMPULSE TURBINES.
F
-
godets
S
-
tazas
<FIGURE>
10p36.gif (486x486)
CURB (wind) (arc).
In SMOCK MILLS and TOWER MILLS, the
circular timber rim
or wall plate supporting the revolving
cap.
F
-
chemin de glissement
S
-
apoyo circular
CURRENT (elec). The
FLOW of electrons through a conductor.
F
-
courant
S
-
corriente
CUT-IN SPEED (wind).
The WIND VELOCITY at which a WIND
MACHINE is
activated.
F
-
vitesse d'enclenchement
S
-
velocidad de accionamiento
CUT-OUT SPEED (wind).
The WIND VELOCITY at which a WIND
MACHINE turns out
of the wind. (See also:
BATTERY
CUT-OUT)
F
-
vitesse de disjonction
S
-
velocidad de interrupcion
CYLINDER (hydr). In
hydraulic systems, a short, hollow
metal tube
containing a piston, piston rod, and end
seals, and fitted
with a system to allow the entrance
and exit of FLUIDS.
F
-
cylindre
S
-
cilindro
D
DAM (hydr). A
structure that detains the FLOW of water in
an open CHANNEL or
watercourse. POWER dams raise the
level of streams or
rivers to create or concentrate HEAD
for power purposes.
F - barrage
S - represa
<FIGURE>
10p37.gif (486x486)

DAMPER (heat). A
movable plate or other device for regulating
the air-FLOW and
burning rate in a stove. It is
often located
either inside the stove or in the FLUE
pipe.
F - registre
S - regulador de
tiro
<FIGURE>
10p38.gif (486x486)

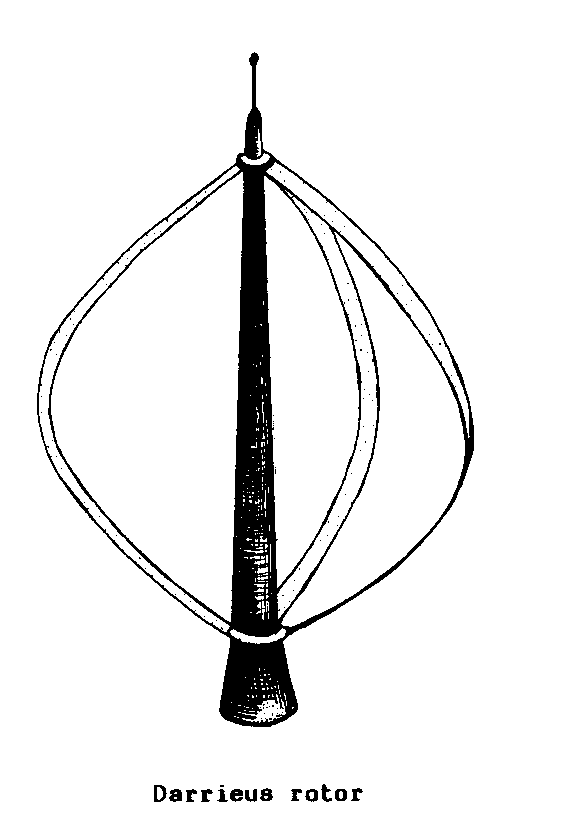
DARRIEUS ROTOR WINDMILL (wind).
A VERTICAL AXIS WIND
MACHINE that has
long, thin, loop-shaped BLADES connected
at the top and
bottom of the WIND SHAFT.
F - eolienne a
rotor de Darrieus
S - molino de viento
de rotor Darrieus
<FIGURE>
10p39.gif (393x393)
DC (elec).
Abbreviation for DIRECT CURRENT.
F - CC
S - C.C.
DDG (alc).
Abbreviation for DISTILLER'S DRIED GRAINS.
(See:
DISTILLER'S GRAINS)
F - GSB
S - G.S.D.
DEADMAN
DDGS (alc).
Abbreviation for DISTILLER'S DRIED GRAINS and
SOLUBLES.
(See:
DISTILLER's GRAIN)
F - G.S.B.S.
S - G.S.D.S.
DEAD AIR SPACE (constr) (sol).
An empty area within the
walls of a building
in which the air remains motionless
and acts as
insulation. Dead air space may be
included
in a SOLAR
COLLECTOR between the ABSORBER PLATE and the
GLAZING, between
glazings, and in the CASING.
F - espace d'air
inerte
S - espacio de
aire no renovado
DEAD CURB (wind) (arc).
A ledge supporting the CAP of a
WINDMILL without
the interposition of WHEELS or ROLLERS.
F - chemin
dormant
S - reborde
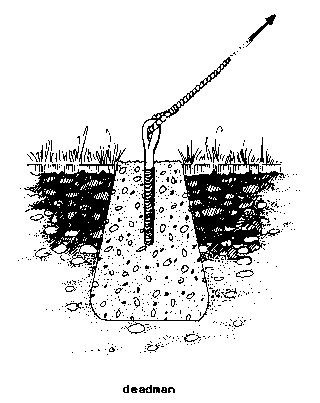
DEADMAN (wind). A
log or a mass of concrete or steel
buried in the
ground, to which GUY WIRES for supporting
towers and poles
are attached.
F - point fixe
d'ammarage
S - macizo de
anclaje
<FIGURE>
10p40.gif (393x393)
DECOMPOSITION
DECOMPOSITION (bio) (chem).
Decay of ORGANIC MATTER due to
the action of
BACTERIA. Also the separation of a
substance
into its component
parts by chemical action.
F - decomposition
S -
descomposicion
DEEP CYCLE BATTERY (elec) (wind).
A BATTERY that can be
fully charged and
discharged without shortening its
life.
They are often used with WIND GENERATORS.
F -
batterie a cycle profond
S -
bateria de gran ciclo
DEGREE DAY COOLING (gen) (meas).
A measurement used to
evaluate the summer
cooling requirements of a given
location.
Each degree that the daily temperature is
above 75 [degrees]
F (24 [degrees] C), one cooling degree day is counted.
F - degre-jour de
refroidissement
S - enfriamiento
de grado-dia
DEGREE DAY HEATING (gen) (meas).
A measurement used to
determine the
winter heating requirements of a given
location.
Each degree that the daily temperature is
below 65 [degrees]
F (19 [degrees] C) is a heating degree day.
F - degre-jour de
chauffage
S - calefaccion
de grado-dia
DIGESTED SLURRY
DEHYDRATION (gen).
The removal of moisture from a
substance.
F -
deshydratation
S -
deshidratacion
DENATURE (alc). The
process of adding a substance, often
METHANOL, to
ETHANOL to make it unfit for human
consumption.
F - denaturer
S -
desnaturalizar
DEPHLEGMATOR (alc).
(See: ALCOHOL STILL)
F - deflegmateur
S - desflegmador
DESIGN HEAT LOAD (heat) (meas).
The total heat loss from a
building during the
most severe winter conditions the
building is likely
to experience.
F - charge
thermique nominale
S - carga de
calefaccion prevista
DESSICANT (gen). A
substance with an affinity for water,
used for drying
purposes.
F - dessiccatif
S - desecante
DESTRUCTIVE DISTILLATION (alc) (gen).
The heating, DECOMPOSITION,
and subsequent
DISTILLATION of FLUIDS from
ORGANIC MATTER
(e.g., METHANOL production from wood).
F - distillation
destructive
S - destilacion
destructora
DETENTION TIME (biocon) (meas).
The amount of time that
incoming material
is retained in a BIOGAS DIGESTER.
F - temps de
retention
S - periodo de
detencion
DIFFUSED RADIATION (sol).
Indirect, scattered sunlight,
which casts no
shadow. It is the opposite of DIRECT
RADIATION.
F - rayonnement
diffus
S - radiacion
difusa
DIFFUSION (chem).
The process by which a substance of a
greater
CONCENTRATION mixes with a substance of a lesser
concentration to
produce a uniform mixture.
F - diffusion
S - difusion
DIGESTED SLUDGE (biocon).
The residue remaining after
DIGESTION.
Digested sludge contains some UNDIGESTED
SOLIDS and
stabilized ORGANIC MATTER.
F - boues
digerees
S - sedimento
digerido
DIGESTED SLURRY (biocon).
(See: DIGESTED SLUDGE)
F - boue digeree
S - fango
digerido
DIGESTER
DIGESTER (biocon).
The tank in which ANAEROBIC DIGESTION
takes place.
F - digesteur
S - digestor
DIGESTER TANK (bio).
The reservoir area in a BIOGAS DIGESTER
in which DIGESTION
of ORGANIC MATTER takes
place.
It usually has some gas holding capacity,
and
provides For the
collection and removal of SCUM and
SLUDGE.
F - reservoir
digesteur
S - tanque
digestor
DIGESTION (biocon).
The process by which ORGANIC MATTER is
decomposed by the
action of ANAEROBIC BACTERIA, producing
METHANE and
high-grade fertilizer.
F - digestion
S - digestion
DILUTION RATE (biocon) (meas).
The frequency with which
water is added to a
BIOGAS DIGESTER.
F - taux de
dilution
S - tasa de
dilucion
DIRECT CONVERSION (sol).
The transformation of sunlight to
electricity without
an intervening thermodynamic cycle.
F - conversion
directe
S - conversion
directa
DIRECT CURRENT (elec).
A continuous, one-directional FLOW
of electricity,
such as that from a BATTERY. Commonly
abbreviated as dc.
F - courant
continu
S - corriente
continua
DIRECT GAIN SYSTEM (sol).
(See: DIRECT SOLAR GAIN)
F - gain direct,
systeme de
S - sistema de
ganancia directa
DIRECT METHODS OF SOLAR HEATING (sol).
SOLAR HEATING techniques
in which SOLAR
RADIATION enters a building
through windows and
SKYLIGHTS and is trapped inside to
warm a room.
F - chauffage
solaire direct
S - metodos
directos de calefaccion solar
DIRECT RADIATION (sol).
Sunlight that has traveled a
straight path from
the sun. It is the opposite of
DIFFUSED RADIATION.
F - rayonnement
direct
S - radiacion
directa
DIRECT SOLAR ENERGY (sol).
ENERGY acquired From conversion
of DIRECT
RADIATION.
F - energie
solaire directe
S - energia solar
directa
DOUBLE-GLAZING
DIRECT SOLAR GAIN (sol).
A PASSIVE SOLAR HEATING system in
which SOLAR
RADIATION passes through and warms a room in
a dwelling before
being stored in THERMAL MASS for
longterm heating.
F - apport solaire
direct
S - ganancia
solar directa
DISCHARGE PIPE (hydr) (biocon).
[1] The pipe through which
water exits from a
WATER TURBINE. [2] The outlet for
EFFLUENT from a
BIOGAS DIGESTER.
F - [1] tube de
decharge; [2] tuyau d'evacuation
S - tubo de descarga
DISTILLATE (alc).
The portion of a liquid that is removed
from a solid or
semisolid as a vapor and CONDENSED
during the
DISTILLATION process. ETHANOL is a
distillate
of FERMENTED
MASH. (See also:
SOLAR DISTILLATE)
F - distillat
S - destilado
DISTILLATION (alc).
An evaporation and recondensation
process by which
liquids are separated into various
fractions according
to their boiling points. ETHANOL is
separated by
distillation from MASH and water.
F - distillation
S - destilacion
DISTILLATION COLUMN (alc).
(See: STILL COLUMN)
F - colonne de
distillation
S - columna de
destilacion
DISTILLER'S DRIED GRAIN (DDG) (alc).
(See:
DISTILLER'S
GRAIN)
F - grains secs
de brasserie (GSB)
S - grano seco de destilacion (GSD)
DISTILLER'S GRAIN (alc).
A by-product of ETHANOL production.
Once ethanol has
been driven from the MASH in an
ALCOHOL STILL, the
remaining solids are known as distiller's
grain.
When dried, these grains can be used as
high protein animal
feed. The dried distiller's grain
commonly is
abbreviated as DDG. (Syn:
BREWER'S DRIED
GRAIN)
F - grains de
distillerie
S - grano de
destilacion
DISTILLER'S MASH (alc).
(See: SPENT MASH)
F -
mout de distillateur
S -
mezcla de destilacion
DOUBLE CHAMBER (biocon).
A type of BIOGAS DIGESTER in
which the GASHOLDER
is separate from the DIGESTER TANK.
F -
chambre double
S -
camara doble
DOUBLE-GLAZING (sol).
[1] A cover for a SOLAR COLLECTOR
that is made from
two layers of GLAZING materials. [2]
Double-glass
windows designed to serve as insulation for
buildings.
F - [1] vitre
double; [2] double vitrage
S - vidriado
doble
DOUBLE-SHUTTERED
DOUBLE-SHUTTERED (wind) (arc).
PATENT SAILS or SPRING
SAILS fitted with
SHUTTERS on both sides of the WHIP.
F - double
volets, a
S - doble postigo
DOWNCOMER (alc) (impl).
A component of an ALCOHOL STILL.
When water is
separated from ALCOHOL during DISTILLATION,
the water falls
toward the bottom of the STILL
COLUMN through a
pipe called a downcomer.
F - deversoir
S - tubo de
descenso
DOWNDRAFT (gen) (prod).
[1] A type of PRODUCER GAS GENERATOR
in which air and
gas FLOWS from the top of the COMBUSTION
ZONE down through
to the bottom. [2] KILNS or
other types of
ovens and stoves in which CONVECTION or
combustion air
flows down through the device.
F - [1] tirage en
bas; [2] tirage inverse
S - corriente
descendiente
DOWNWIND (wind). On
the side opposite the WIND DIRECTION.
F - sous le vent
S - con el viento
<FIGURE>
10p44.gif (393x393)
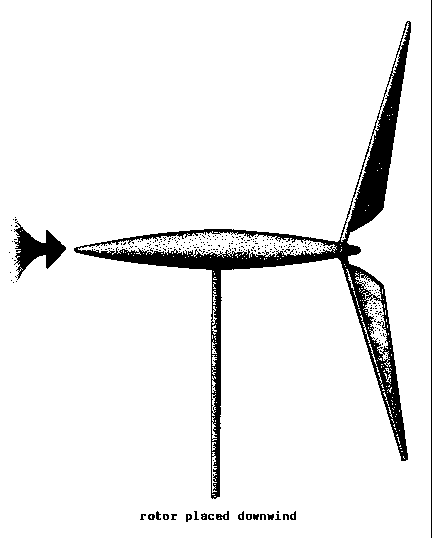
DRYING BED
DRAFT (heat). The
FLOW of air through a KILN, stove, oven,
fireplace, PRODUCER
GAS GENERATOR, etc. Draft affects
both temperature
and rate of combustion.
F - tirage
S - tiro de aire
DRAG (wind). An
aerodynamic force that retards the motion
of lift-type ROTOR
blades, or that causes BLADE motion
in DRAG-TYPE WIND
MACHINES.
F - trainee
S - resistencia
aerodinamica
DRAG-TYPE SYSTEM (wind).
WIND MACHINES that are actuated
by aerodynamic DRAG
in a WIND STREAM (e.g., SAVONIUS
ROTOR).
F - type a
trainee, systeme du
S - sistema del
tipo de arrastre
DRAG-TYPE WIND MACHINE (wind).
A WIND MACHINE that rotates
by being pushed by
the wind instead of by being driven
by LIFT
forces. This is generally a slow-moving
device.
F - eolienne a
trainee
S - aerogenerador
del tipo de arrastre
DRAIN DOWN SOLAR COLLECTOR (sol).
A SOLAR COLLECTOR that
will automatically
drain itself to protect against
freezing.
F - capteur
solaire a evacuation automatique
S - colector
solar con drenaje
DRY BIOMASS (gen).
Moisture-free BIOMASS. It is
valuable
because it can be
conveniently stored for long periods
of time.
(See also:
DRY ORGANIC WASTE)
F - biomasse
seche
S - biomasa seca
DRY-BULB TEMPERATURE (meas).
The temperature of air as
indicated by a
standard thermometer, as contrasted with
WET-BULB
TEMPERATURE that depends on atmospheric humidity.
This measure of
AMBIENT temperature is used in
designing PASSIVE
SOLAR HEATING and SOLAR COOLING
systems.
F - temperature
au thermometre sec
S - temperatura
de bola seca
DRY DIGESTION (biocon).
DIGESTION in which more than 10
percent of the
SLURRY is solid material.
F - digestion
seche
S - digestion
seca
DRYING BED (biocon).
An area prepared for drying EFFLUENT
after it hs been
removed from a METHANE DIGESTER. Dried
effluent can be
used as fertilizer or as animal feed.
F - lit de
sechage
S - lecho secador
DRY ORGANIC WASTE
DRY ORGANIC WASTE (gen).
ORGANIC WASTE that is free from
moisture.
This type of waste can be stored for long
periods before
being used as a fuel or fertilizer.
(See
also:
DRY BIOMASS)
F - dechets
organiques secs
S - desperdicios
organicos secos
DRY SLURRY (biocon).
SLURRY that is more than 10 percent
solid material.
F - boue seche
S - fango seco
DRY STEAM (geo). An
ENERGY source obtained when hot water
boils in an
underground reservoir. As the steam
rises,
some of it
condenses on surrounding rack. The
uncondensed
steam that reaches
the surface is called dry
steam, and may be
tapped and used in STEAM TURBINES.
F - vapeur seche
S - vapor seco
DUAL-FUEL ENGINE (auto) (gen).
A gasoline or diesel
engine equipped to
operate on an alternative fuel,
either alternately
or in combination (e.g., gasoline-BIOGAS,
diesel-biogas,
gasoline-WOOD GAS, diesel-wood
gas).
F - moteur
polycarburant
S - motor a doble
combustible
DYNAPOD
DUNG (bio).
Manure, usually without urine.
Dried dung can
be burned directly
as a fuel or used as a fertilizer.
F - fumier
S - estiercol
DUNG GAS (biocon).
(See: BIOGAS)
F - gaz de fumier
S - gas de
estiercol
DYNAMO (elec). A
device for converting mechanical ENERGY
into electrical
energy by electromagnetic induction.
Dynamos are often
adapted to be driven by WINDMILLS.
(See also:
ALTERNATOR)
F - dynamo
S - dinamo
DYNAPOD (gen) (impl).
A pedal-operated POWER source.
It is
used to drive a
variety of machines and devices.
F - dynapod
S - dynapod
<FIGURE>
10p46.gif (540x540)
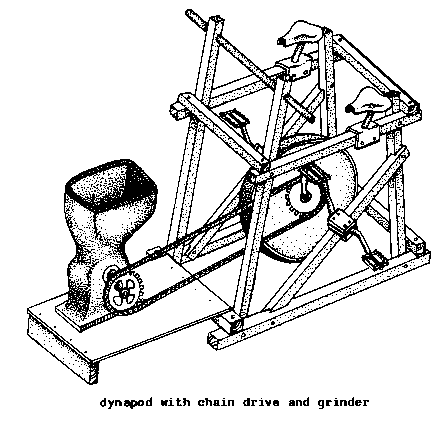
E
EARTH KILN (heat). A
relatively inefficient KILN made by
mounding earth over
the materials to be burned. Used in
traditional
CHARCOAL production.
F - meule a
charbon de bois
S - horno de
tierra
<FIGURE>
10p48a.gif (486x486)
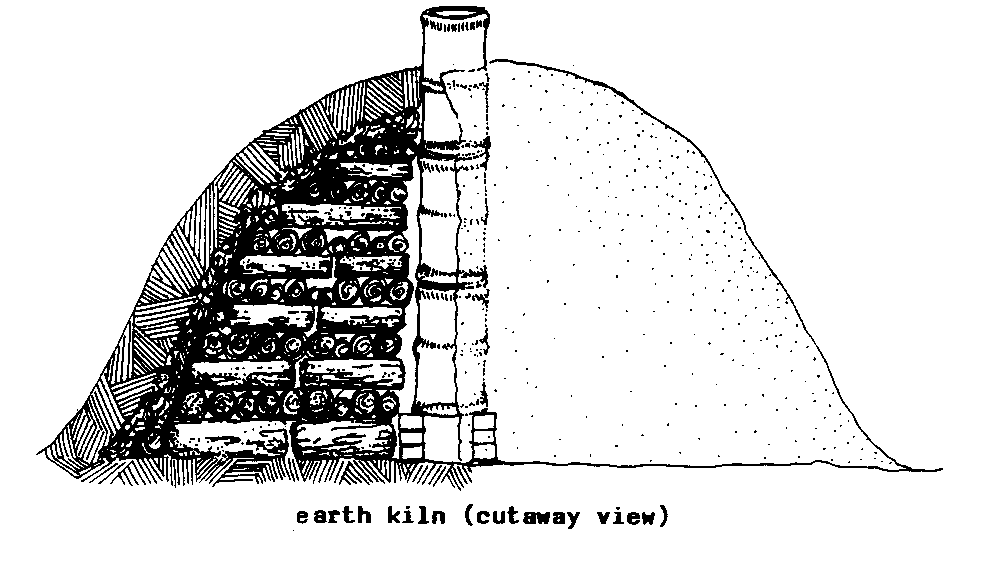
ECCENTRIC WHEEL (gen).
A wheel in which the axle is not at
the center point,
but slightly off-center.
F - roue
excentrique
S - rueda
excentrica
<FIGURE>
10p48b.gif (317x317)
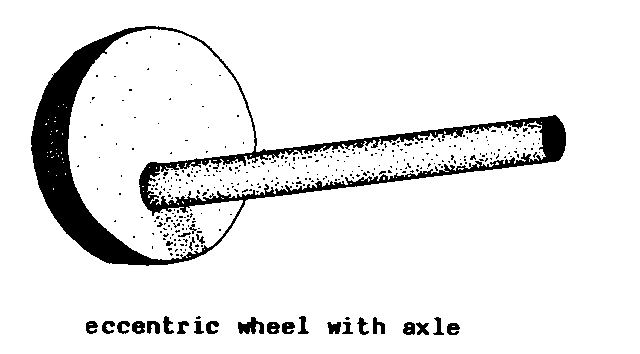
ECONOMIZER (heat). A
HEAT EXCHANGER that recovers heat
from FLUE gases and
uses it to heat feedwater or combustion
air.
F - economiseur
S - economizador
ENERGY CONSUMPTION
EFFECTIVENESS (heat) (meas).
The ratio of actual heat
transfer in a HEAT
EXCHANGER to the maximum possible
heat transfer.
F - efficacite
S - eficacia
EFFICIENCY (gen).
The ratio of the ENERGY output to the
energy input.
Efficiency is usually expressed as a
percentage.
F - rendement
S - eficiencia
EFFLUENT (biocon).
[1] SLURRY that has been removed from a
BIOGAS PLANT.
[2] Liquid sewage after having passed
through any stage
in its purification.
F - effluent
S - efluente
EMISSIVITY (sol).
The ratio of RADIANT ENERGY emitted by a
body to that
emitted by a perfect BLACKBODY. A
perfect
blackbody has an
emissivity of one; a perfect REFLECTOR,
an emissivity of
zero.
F - emissivite
S - emisividad
EMITTANCE (sol) (meas).
A rating of the ability of a
material to give
off heat as RADIANT ENERGY.
F - emittance
S - emitancia
ENERGY (gen). The
capacity of a body to do work; POWER in
action.
F - energie
S - energia
ENERGY CAPABILITY OF AN ELECTRICITY-PRODUCING DEVICE (gen)
(meas).
The maximum amount of electricity that an
electricity-producing device may produce under the best
conditions during a given period.
ENERGY capability is
determined by the
mechanical EFFICIENCY of the device.
F - capacite
energetique d'un dispositif produisant du
courant
S - capacidad
energetica de un aparato productor de
electricidad
ENERGY CONSERVATION (gen).
Practices and measures that
increase the
EFFICIENCY with which ENERGY is used or
produced.
F - conservation
de l'energie
S - conservacion
de energia
ENERGY CONSUMPTION (gen).
The amount of ENERGY consumed in
the form in which
it is obtained by the user. This term
excludes electrical
generation and distribution losses.
It also is called
net energy consumption.
F - consommation
d'energie
S - consumo de
energia
ENERGY CONVERSION
ENERGY CONVERSION (gen).
The act of changing ENERGY from
one form to another
(e.g., WIND ENERGY to mechanical
energy).
ENERGY
CONVERSION OF PRACTICAL, RENEWABLE
ENERGY
SYSTEMS - Maximum Efficiency
Wind Generator 40%
Mechanical
Water Turbine 68-93%
Electrical
Steam Power Plant 40%
Mechanical
Windmill 20-30%
Mechanical
Waterwheel 70-85%
Solar
Flat Collector 40-60%
Thermal
Concentrator 80-90%
(Heat)
Chemical
Wood Combustion Burner
Thermal
85% maximum
(Heat)
Chemical
Battery 80% (Storage)
Electrical
Chemical
Biogas Digester 40-60%
Chemical
F -
conversion de l'energie
S -
conversion de energia
ENERGY PATTERN FACTOR (wind).
The ratio of the available
ENERGY in all of
the winds in a particular location over
a certain period of
time to the energy that would be
available if the
WIND SPEED over that period of time
were constant at
the mean wind speed over that period of
time.
F - coefficient
de diagramme energetique
S - factor
energetico del viento
ENERGY PRODUCTS (gen).
Fuels that can be used to produce
ENERGY.
Also, the by-products that result when fuels
are
produced.
F - combustibles
energetiques
S - productos
energeticos
ENERGY STORAGE (gen) (meas).
The ability to convert ENERGY
into other forms,
such as heat or a chemical reaction,
so that it can be
retrieved for later use. Also the
development,
design, construction, and operation of
devices for storing
energy until needed. The technology
includes devices such
as batteries, pumped storage for
hydroelectric
generation and compressed gas.
F - stockage de
l'energie
S -
almacenamiento de energia
ENHANCEMENT (sol).
Increasing the amount of sunlight
transmitted through
the GLAZING in a SOLAR COLLECTOR
through the use of
a REFLECTOR.
F - renforcement
S -
intensificacion
EQUINOX
RENEWABLE ENERGY STORAGE
Storage
Storage Efficien-
Major Loss
(*) (**)
Medium cy (%)
Characteristics
A B
SOLAR
Water
75-90 Leaks
(therma] 2
1
(Heat)
&
physical)
Earth
varies Leaks
(thermal) 1
1
Rock 60-80
Leaks (thermal)
2 2
Salt
Hy- 75-95
Material Break-
3 3
drates down
WIND/WATER
Pumped 50-70
Evaporation
1 2
(Mechanical)
Water
Friction
Compressed 40-50
Leaks
2 2
Air
(com- Friction
pressed)
WIND/WATER
Battery
70-85
Internal 3
3
(Electrical)
Discharge
METHANE
Tank
Leaks
1 2
Tank
(com- 50-60
3 3
pressed)
ALCOHOL
Tank
Leaks
Evaporation
1
1
(*) A Relative
Cost 1.
Negligible
2.
Intermediate
(**) B Degree of
Mechanical Complexity 3.
Considerable
ENZYMATIC HYDROLYSIS (alc).
The use of ENZYMES to convert
STARCH into simple
sugars. This is a stage in the
production
of ETHANOL.
F -
saccharification enzymatique
S - hidrolisis
enzimica
ENZYMES (chem) (alc).
Organic substances that are produced
in the cells of
living organisms, and which cause specific
chemical
changes. Enzymes are produced by
BACTERIA
or FUNGI and are
used in the liquefication and SACCHARIFICATION
steps of ALCOHOL
production.
F - enzymes
S - enzimas
EOLIAN (wind). Of,
relating to, formed by, or deposited by
the wind or air
currents. (Syn:
Aeolian)
F - eolien,
eolienne
S - eolico
EQUINOX (sol).
Either of two times of year when the sun
passes over the
celestial equator and when the length of
day and night are
almost equal.
F - equinoxe
S - equinoccio
ETHANOL
ETHANOL (alc). A
Flammable organic compound (C[H.sub.3]C[H.sub.2]OH)
formed during sugar
FERMENTATION. It is also called
ethyl alcohol,
GRAIN ALCOHOL, or simply ALCOHOL.
F - ethanol
S - etanol
ETHYL ALCOHOL (alc).
(See: ETHANOL)
F - alcool
ethylique
S - alcohol etilico
EUTECTIC SALTS (heat).
Heat storing salts that melt at a
relatively low
temperature. They absorb large
quantities
of heat when they
do melt. Heat is released when the
salts freeze.
F - eutectiques
S - sales
eutecticos
EVACUATED TUBE COLLECTOR (sol).
A SOLAR COLLECTOR that
uses a vacuum to
insulate the ABSORBER PLATE. This
COLLECTOR is highly
EFFICIENT but very expensive.
F - capteur a
tube vide
S - colector con
tubo vaciado
EVAPORATIVE COOLING (refrig).
The exchange of heat from
air to a water
spray or wet surface through a reversible
THERMODYNAMIC
process. Air passing through the water
is
cooled as the water
evaporates. The process can be
reversed by
condensing the vapor on a cool surface.
F -
refroidissement par evaporation
S - enfriamiento
evaporante
EXCESS AIR (heat).
Air that passes through a COMBUSTION
ZONE in excess of
the quantity theoretically required
for complete
combustion.
F - exces d'air
S - aire excesivo
EXTRATERRESTRIAL SOLAR RADIATION (sol) (meas).
The amount
of SOLAR RADIATION
that would strike a surface if that
surface were
outside the Earth's atmosphere. (See
also:
CLEARNESS INDEX)
F - rayonnement
solaire extraterrestre
S - radiacion
solar extraterrestre
F
F (meas).
Abbreviation for FAHRENHEIT.
F - F
S - F
FAHRENHEIT (meas).
The temperature scale in which water
freezes at 32
[degrees] F and boils at 212 [degrees] F.
Temperatures of the
Fahrenheit scale
can be converted to equivalent temperatures
on the CELSIUS or
Centigrade scale by first subtracting
32 [degrees] from
the Fahrenheit temperature, then
multiplying the
result by 5/9 according to the formula:
(F -32) X 5/9 = C.
F - Fahrenheit
S - Fahrenheit
FALL WIND (wind). A
strong, cold, downhill wind.
F - vent
catabatique
S - racha de viento
FANTAIL (wind) (arc).
A small, secondary ROTOR set at a
right angle to the
main ROTOR of a WINDMILL to provide
the motive POWER to
turn the CAP to face the wind.
F - gouvernail
S - timon
FARM WINDMILL (wind).
A multi-BLADED WINDMILL that is
based on an Early
American design and is used primarily
for water pumping.
F - eolienne de
ferme
S - molino de
viento rural
<FIGURE>
10p54.gif (486x317)

FEATHER (wind).
Turning the SAILS or the ROTOR of a WIND
MACHINE out of the
wind to protect the device from
damage from high
WIND VELOCITIES.
F - mettre en
drapeau
S - poner en
bandolera
FEATHERING MECHANISM (wind) (impl).
A mechanism on a
WINDMILL that
automatically turns the BLADES out of the
wind when winds are
too strong. This slows the windmill,
protecting it from
damage in high winds.
F - mecanisme de
mise en drapeau
S - mecanismo de
puesta en bandolera
FEED (gen).
See: FEEDSTOCK)
F - alimentation
S - alimento
FEEDSTOCK (gen). The
raw ORGANIC MATTER, such as grain,
fruit, DUNG, or
other BIOMASS, used as the INFLUENT in
the FERMENTATION or
DIGESTION processes.
F - charge
d'alimentation
S - materia prima
organica
FARM WINDMILL
FIRE BRICK
FENESTRATION (sol).
An opening in a building that admits
light and/or air.
F - fenestration
S - ventanaje
FERMENT (biocon). A
transformation or DECOMPOSITION of
ORGANIC MATTER by
the catalytic effect of ENZYMATIC
action.
To cause or undergo the action of
FERMENTATION.
F - fermenter
S - fermentar
FERMENTABLE SUGAR (alc).
(See: MONOSACCHARIDE)
F - sucre
fermentable
S - azucar
fermentable
FERMENTATION (alc) (chem).
[1] A biological sequence of
ENZYMATIC reactions
that convert sugars to carbon dioxide
and ALCOHOL in the
absence of FREE OXYGEN. The term
generally refers to
metabolism in the absence of oxygen.
[2] The process by
which YEAST changes sugar to
ALCOHOL in the absence
of air. [3] The process of
chemical change in
ORGANIC MATTER brought about by
living organisms.
F - fermentation
S - fermentacion
FERMENTATION PERIOD (gen) (meas).
The length of time
required for a
substance to FERMENT.
F - duree de
fermentation
S - periodo de
fermentacion
FERMENTATION TANK (alc).
The container in which FERMENTATION
takes place in an
ETHANOL production operation.
F - cuve de
fermentation
S - tanque de
fermentacion
FERMENTER (gen).
(See: FERMENTATION TANK)
F - fermenteur
S - fermentador
FETCH AREA (wind).
The geographic area over which the wind
passes shortly
before reaching a WIND MACHINE. It is
considered in the
selection of a site for a wind-powered
device.
F - portee du
vent
S - extension
expuesta
FIRE BACK (constr).
A metal plate set in a CHIMNEY to control
the back DRAFT of
flames.
F - contre-feu
S - respaldo
refractario
FIREBOX (gen). The
area in a stove, oven, or PRODUCER
GAS GENERATOR in
which combustion occurs.
F - chambre de
combustion
S - caja
refractaria
FIRE BRICK (constr).
A type of brick with a high melting
point that is used
to line FLUES, CHIMNEYS, furnaces,
and fireplaces.
F - brique
refractaire
S - ladrillo refractario
FIXED-DOME DIGESTER
FIXED-DOME DIGESTER (biocon).
A BIOGAS DIGESTER in which
the gasholder is an
integral part of the digester,
rather than a
FLOATING GAS CAP. This type of digester
is
usually used to
produce fertilizer. METHANE is considered
a by-product.
F - digesteur a
dome fixe
S - digestor de
sombrerete fijo
FLAT BLACK PAINT (sol).
A nonglossy black paint with a
relatively high
ABSORPTANCE.
F - peinture
noire mate
S - pintura negra
uniforme
FLAT-PLATE SOLAR COLLECTOR (sol).
A device that uses an
ABSORBER PLATE to
COLLECT SOLAR RADIATION without
assistance of
devices to concentrate the sun's rays.
F - capteur
solaire a panneau plan
S - colector
solar de placa lisa
FLOAT (hydr). The
BUCKET of a WATER WHEEL.
F - aube
S - paleta [1]
FLOATING GAS CAP (biocon).
A lid over a BIOGAS DIGESTER
that rises or falls
with the production of METHANE.
F - cloche a gaz
flottante
S - sombrerete
movible
<FIGURE>
10p56.gif (540x540)

FOCUSING COLLECTOR
FLOW (gen). The
volume of a substance passing a point per
unit time (e.g.,
meters per second, gallons per hour,
etc.)
F - debit
S - flujo
FLOW DESIGN (hydr) (meas).
The FLOW rate at which a
TURBINE is designed
to operate.
F - debit nominal
S - diseno de
flujo
FLUE (const). A
passageway in a CHIMNEY that vents gases
produced during
combustion. The flue opening can be
regulated to
control the DRAFT in the oven or stove,
thus changing the
rate of combustion.
F - carneau
S - conducto de
humos
FLUE GAS DRYING (heat).
THERMAL drying using gases in a
FLUE as the source
of heat.
F - sechage au
gaz de carneau
S - secado por
gases del conducto
FLUID (gen). Any
substance that FLOWS, such as a liquid or
gas.
Fluids differ from solids in that they
cannot
resist changes in
their shape when acted upon by a
force.
F - fluide
S - fluido
FLUIDIZED BED GASSIFIER (prod).
A type of PRODUCER GAS
GENERATOR in which
air FLOWS upward through a bed of
suitably-sized fuel
particles fast enough to buoy the
particles and give
them an appearance of great agitation.
The fuel particles
generally are small. This type
of combustion
reduces the sulphur-dioxide emissions when
coal is burned.
F - gazogene a
lit fluidise
S - gasificador
en lecho fluidizado
FLUME (hydr). [1] A
HEAD RACE in the form of a trough or
CHANNEL that
carries water to a WATER WHEEL. [2] A
waterway, usually
made of wood and often supported on a
trestle, that
conveys water to be used for POWER,
transportation,
etc.
F - [1] coursier;
[2] canal d'amenee
S - canaleta
FLYWHEEL (gen) (impl).
A rotating element attached to the
shaft of a machine
to maintain uniform angular velocity
and revolutions per
minute.
F - volant
S - volante
FOCUSING COLLECTOR (sol).
A type of SOLAR COLLECTOR that
focuses the sun's
rays on a sinqle point.
F - capteur a
concentration [2]
S - colector
enfocante
FOLD-UP REFLECTOR
FOLD-UP REFLECTOR (sol).
A portable type of folding mirror
used in SOLAR
COOKERS to reflect sunlight.
F - reflecteur
pliant
S - reflector
plegable
FOOT-POUND (gen) (meas).
The amount of ENERGY required to
lift one pound of a
substance one foot.
F - pied-livre
S - libra-pie
FORCED CONVECTION (heat).
The use of a pump or blower to
control the FLOW of
heat into a heated FLUID (e.g. circulating
warm air in a room
or dwelling with a pump or
blower).
F - convection
forcee
S - conveccion
forzada
FOSSIL FUELS (fos).
Nonrenewable, naturally-occurring
fuels from ORGANIC
MATTER. These include coal, crude
oil, and natural
gas.
F - combustibles
fossiles
S - combustibles
fosiles
FRACTIONATING COLUMN (alc).
A vertical tube or column
attached to an
ALCOHOL STILL that is usually filled with
packing or
intersected with plates. An internal
REFLUX
results in a
separation between the high and low boiling
fractions inside
the column. Those with the lowest
boiling
point DISTILL
out. (See also: DISTILLATION COLUMN)
F - colonne de
fractionnement
S - columna de
fraccionar
FRESNEL LENS
FRANCIS TURBINE (hydr).
A WATER TURBINE that operates on a
low or medium HEAD
and is often installed in large
HYDROELECTRIC
plants. Water enters the turbine
radially
and leaves axially.
F - turbine de
Francis
S - turbina
Francis
<FIGURE>
10p58.gif (486x486)

FREE OXYGEN (bio).
Oxygen in the atmosphere, which can be
extracted at no
cost. Conversely, oxygen extracted at a
cost would cause
the substance from which the oxygen
molecules were
taken to DECOMPOSE.
F - oxygene libre
S - oxigeno libre
FRESNEL COLLECTOR (sol).
A type of SOLAR COLLECTOR
consisting of a
concentric series of rings with
reflecting
surfaces. These rings focus SOLAR
RADIATION
onto an ABSORBER
PLATE.
F - capteur a
lentille de Fresnel
S - colector
Fresnel
FRESNEL LENS (sol).
A type of lens built up from a number
of narrow
concentric segments. It is used in
SOLAR
CONCENTRATORS.
F - lentille de
Fresnel
S - lente de
Fresnel
<FIGURE>
10p59.gif (486x486)

FRICTION
FRICTION (gen).
Surface resistance to relative motion,
which slows down
movement and causes heat.
F - frottement
S - friccion
FRICTION HEAD (hydr).
HEAD or ENERGY lost due to FRICTION
created by the
contact between a moving stream of water
and the conduit
through which it is moving. In pipes,
the friction head
is also caused by bends in the pipelines,
changes in the pipe
diameter, valves, and
couplings.
F - perte
frictionnelle
S - perdida de
carga por rozamiento
FRUCTOSE(alc) (chem).
A FERMENTABLE sugar commonly found
in fruit.
Fructose can be used as a FEEDSTOCK in
ETHANOL
production.
F - fructose
S - fructosa
FUEL EFFICIENCY (heat) (meas).
The ratio of heat produced
by a fuel for doing
work to the available heat of the
fuel.
Fuel EFFICIENCY is determined by the
nonheat-forming
materials in the
fuel and the nonwork-producing heat
that is developed
by the fuel.
F - rendement du
combustible
S - eficiencia
del combustible
FUELWOOD (heat). Any
type of wood that can be used to fuel
a fire.
F - bois de
chauffe
S - lena
FULL SAIL (wind) (arc).
A COMMON SAIL with the cloth fully
spread.
F - aile deployee
S - aspa
completamente estirada
FUNGUS (bio). One of
numerous plants in the division of
Thallophyta
characterized by a lack of chlorophyll,
including YEAST,
molds, and mushrooms. Fungi do not
require FREE OXYGEN
to survive. (Plural:
fungi)
F - champignon
S - hongo
FURLING (wind).
Rollinq up and tying back SAILS of a
WINDMILL to keep
the ROTOR from turning.
F - ferlage
S - aferramiento
FURLING SPEED (wind).
(See: CUT-OUT SPEED)
F - vitesse de
ferlage
S - velocidad
maxima admisible
G
GASAHOL (alc). A
gasoline substitute or supplement derived
from 10 percent
ETHANOL and 90 percent unleaded
gasoline.
(Syn:
gasohol)
F - carburol
S - gasohol
GAS CAP (biocon).
(See: GASHOLDER)
F - cloche a gaz
S - tapa de gas
GAS DIGESTION (biocon).
The second stage of BIOGAS generation,
during which
METHANE ([CH.sub.4]) is produced.
F - digestion de
gaz
S - digestion de
gas
GASHOLDER (biocon). (1)
A container for holding the BIOGAS
produced in a
DIGESTER. The size of the holder
depends
on the rates of gas
production and gas use. (See also:
FLOATING GAS CAP)
F - gazometre
S - gasometro
GASIFICATION (prod).
The conversion of wood or coal to
COMBUSTIBLE GAS
without leaving a combustible residue.
F - gazeification
S - gasificacion
GASIFIER (prod). A
special type of furnace in which the
air supply to the
COMBUSTION ZONE is carefully metered.
This promotes the
production of COMBUSTIBLE GASES as
wood or coal are
burned.
F - gazogene
S - gasificador
GAS PRODUCTION RATE (biocon) (meas).
The quantity of
METHANE generated
per unit of time. It generally is
expressed as cubic
feet/day or cubic meters/day. The
figure should be
quoted under standard conditions of
temperature and
pressure.
F - taux de
production du gaz
S - tasa de
produccion de gas
GAS SCRUBBER (gen).
(See: SCRUBBING)
F - epurateur de
gaz
S - lavagases
GAS STORAGE CAPACITY (biocon).
The maximum amount of
METHANE that a
BIOGAS DIGESTER is able to store. The
amount generally is
expressed in cubic feet or cubic
meters.
F - capacite de
stockage de gaz
S - capacidad de
almacenamiento de gas
GAS TURBINE
GAS TURBINE (auto).
An ALTERNATIVE COMBUSTION ENGINE in
which a gas, under
pressure or formed by combustion, is
directed against
the BLADES of a TURBINE. The ENERGY in
the expanding gas
is thereby converted into useful
mechanical energy.
F - turbine a gaz
S - turbina de
gas
GEAR RATIO (gen) (meas).
The number of revolutions required
of one gear to turn
another gear, which generally
is of a different
size.
F -
demultiplication
S - relacion de
los engranajes
GENERATOR (elec) (impl).
A device that converts mechanical
ENERGY into
electrical energy.
F - generateur
S - generador
GENGAS (prod).
(See: PRODUCER GAS)
F - gaz pauvre de
gazogene
S - gengas
GEOPRESSURED RESERVOIR (geo).
A GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR consisting
of porous sands
that contain water or BRINE at
high temperatures
and pressure.
F - reservoir
sous geopression
S - tanque de
presion geotermica
GEOTHERMAL (geo). Of
or relating to the heat of the
Earth's interior.
F - geothermique
S - geotermico
GEOTHERMAL FIELD (geo).
A geographical region with known
GEOTHERMAL POWER
sources that might be tapped to produce
ENERGY.
F - zone
geothermique
S - zona
geotermica
GEOTHERMAL POWER (geo).
ENERGY obtained from GEOTHERMAL
sources.
Geothermal power is tapped in three
ways: by
using hot water,
steam, or DRY STEAM. Each may be used
to drive a TURBINE.
F - energie
geothermique
S - energia
geotermica
GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR (geo).
A water reserve created near a
HOT DRY ROCK
RESERVOIR to develop a potential GEOTHERMAL
POWER site.
F - reservoir
geothermique
S - tanque
geotermico
GEOTHERMAL STEAM (geo).
Steam drawn from sources within
the Earth.
F - vapeur
geothermique
S - vapor
geotermico
GEYSER (geo).
Natural steam or hot water spouts in active
GEOTHERMAL regions.
F - geyser
S - geiser
GRAVITY CONVECTION
GIN POLE (wind). A
long board or pipe used to improve the
leverage in lifting
a TOWER for a WINDMILL.
F - fleche de
levage
S - mastil grua
GLAZING (impl) (sol).
A transparent sheet that admits sunlight
to a SOLAR
COLLECTOR and then inhibits the escape
of heat.
Commonly used glazing materials include
ACETATE,
acrylic,
fiber-reinforced plastics, and glass.
F - vitrification
S - vidriado
GLOBAL RADIATION (sol).
The combination of DIFFUSED RADIATION,
DIRECT RADIATION,
and REFLECTED RADIATION. (See:
SOLAR RADIATION)
F - rayonnement
global
S - radiacion
global
GLUCOSE (chem) (alc).
The most common sugar, which is
derived from STARCH
during the ETHANOL production
process.
F - glucose
S - glucosa
GOBAR GAS (biocon).
(See: BIOGAS)
F - bio-gaz
S - gas gobar
GOVERNOR (gen) (impl).
A device that regulates the speed
of an engine or
other device under varying conditions of
load and
pressure. Also a device for regulating
the FLOW
or pressure of a
FLUID passing through a device.
F - regulateur
S - regulador
GRAIN ALCOHOL (alc).
ETHANOL made from grain by
DISTILLATION.
F - alcool de
grains
S - alcohol de
granos
GRAM CALORIE (gen).
The amount of ENERGY required to raise
one gram of water
one degree CELSIUS.
F - calorie [2]
S - caloria-gramo
GRAMLAXMI GAS (biocon).
(See: BIOGAS)
F - bio-gaz
S - gas gramlaxmi
GRATE (impl) (heat).
A frame of metal bars that holds
fuel above the
floor of a firebox. It usually is used
in
a boiler, GASIFIER,
fireplace, or stove.
F - grille
S - parilla
GRAVITY CONVECTION heat).
(See: NATURAL CONVECTION)
F - convection
par pesanteur
S - conveccion
por gravedad
GUIDE VANES
GUIDE VANES (hydr) (impl).
Surfaces that direct water to
the appropriate
parts of TURBINE BLADES or BUCKETS so as
to increase POWER
output.
F - aubes
directrices
S - alabe
director
GUSSET (constr) (wind).
A triangular metal brace for
reinforcing a
corner or angle. It is commonly used in
TOWER construction.
F - gousset
S - esquinero
GUST (wind). A
sudden, brief increase in WIND VELOCITY
that is then
followed by calmer air.
F - rafale
S - rafaga
GUYED TOWER (impl) (wind).
A WINDMILL TOWER that is
supported by GUY
WIRES.
F - pylone
haubanne
S - torre
atirantada
<FIGURE>
10p64.gif (393x393)
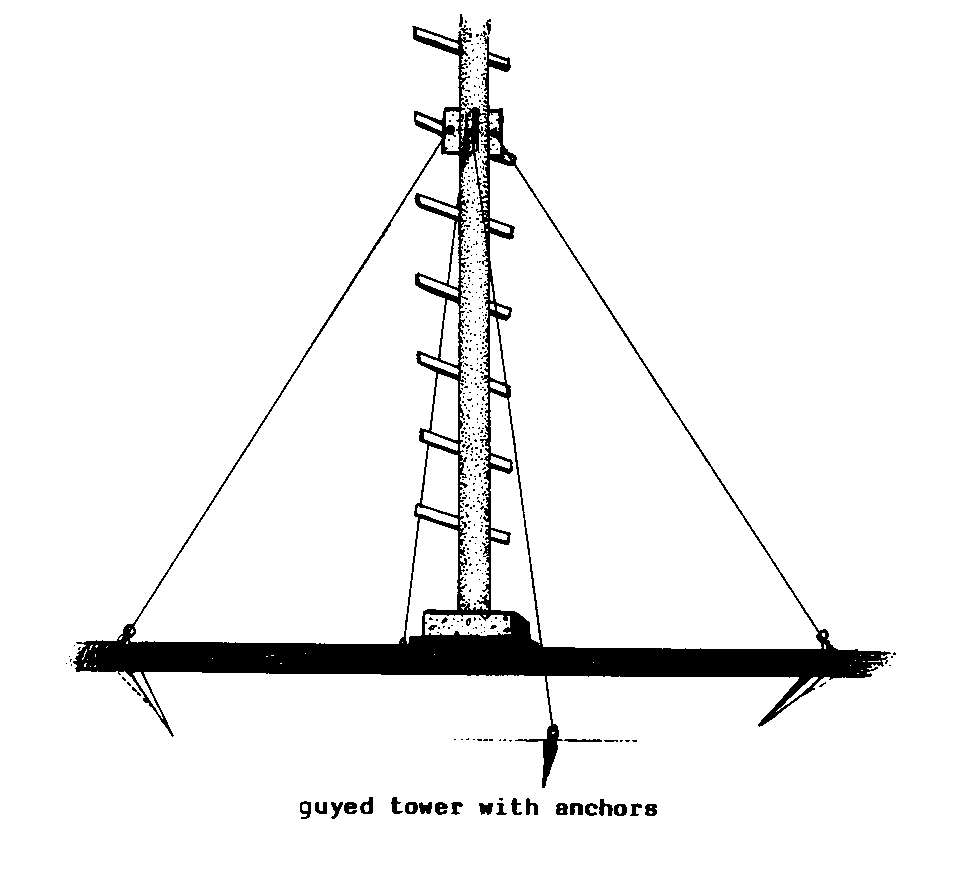
GUY WIRE (wind) (impl).
A cable that stabilizes a structure
and keeps it in
position. For example, wires
attached to a
WINDMILL TOWER so that it cannot move or
shake from the
force of the wind.
F - hauban
S - retenida de
alambre
H
HARNESS (ani). The
gear or tackle, other than a YOKE, used
on draft animals to
pull a vehicle or drive an implement.
It differs from a
yoke, which joins together draft
animals.
F - harnais
S - arnes
<FIGURE>
10p65.gif (486x486)
HEAD (hydr) (meas).
[1] The vertical distance from the
point where water
enters an intake to the point where
the water leaves a
HYDROPOWER device. It is generally
measured in feet or
meters. The product of the head
times the FLOW is a
measurement of potential POWER. [2]
The vertical
distance a liquid must be pumped from its
source to its point
of use or storage.
F - chute d'eau
[1]-[2]
S - altura
<FIGURE>
10p66.gif (600x600)
HEADER (sol). The
pipe that runs across the top of an
ABSORBER PLATE to
gather or distribute HEAT TRANSFER
FLUID from or to
the grid pipes that run across the
absorber
surface. Some headers run along the
bottom of
the absorber plate.
F - entree-sortie
S - tubo colector
HEADRACE
HEADRACE (hydr). A
CANAL or conduit that feeds water into
a mill, WATER
WHEEL, or TURBINE.
F - bief d'amont
S - canal de
llegada
HEAD WATER (hydr).
The water upstream of a DAM or a
HYDROPOWER plant.
F - eau d'amont
S - aguas arriba
HEAT CAPACITY (heat) (meas).
The amount of heat required
to raise by one
degree the temperature of a unit mass of
a substance.
F - capacite
thermique
S - capacidad
calorifica
HEAT ENERGY (heat).
ENERGY in the form of heat.
F - energie
thermique
S - energia
calorifica
HEAT TRANSFER FLUID
HEAT EXCHANGER (heat) (impl).
A device, such as a coiled
copper tube
immersed in a tank of water which is used
to transfer heat
from one FLUID to another through a
separating wall.
A CONDENSER is one type of heat
exchanger.
F - echangeur de
chaleur
S -
termopermutador
HEAT GAIN (heat).
The increase of heat in a space resulting
from DIRECT
RADIATION and from the heat given off by
such other sources
as THERMAL MASS, a stove, a fireplace,
humans, or animals.
F - apport de
chaleur
S - ganancia
calorifica
HEATING VALUE (heat) (meas).
The amount of heat produced
by the complete
combustion of a specific amount of
fuel.
This is a measure of FUEL EFFICIENCY.
F - pouvoir
calorifique
S - valor
calorifico
HEAT LOSS (heat). An
unwanted decrease in the amount of
heat contained in a
space. Heat is usually lost through
CONVECTION.
F - perte de
chaleur
S - perdida
calorifica
HEAT PUMP (heat) (impl).
A mechanical device that transfers
heat from a heat
source to a HEAT SINK. This process
causes the source
to cool and the sink to become
warmer.
F - pompe a
chaleur
S - bomba
calorifica
HEAT RATE TRANSFER COEFFICIENT (heat) (meas).
The rate at
which heat is
transferred per hour, per unit surface,
per degree of
temperature difference.
F - coefficient
de transmission de chaleur
S - coeficiente
de transferencia del consumo
calorifico
HEAT-REFLECTIVE GLASS (sol).
A type of glass designed to
reflect SOLAR
RADIATION.
F - verre a
pouvoir reflechissant thermique
S - vidrio
reflector de calor
HEAT SINK (sol). A
body that is capable of accepting and
storing heat.
It therefore may also act as a heat
source.
F - puits de
chaleur
S - sumidor de
calor
HEAT TAX (heat).
Referring to the HEAT ENERGY that becomes
unavailable for
further use whenever ENERGY is converted
from one form to
another.
F - chaleur
perdue
S - gravamen
calorifico
HEAT TRANSFER FLUID (sol).
(See: HEAT TRANSFER MEDIUM)
F - fluide
caloporteur
S - fluido de
termotransferencia
HEAT TRANSFER MEDIUM
HEAT TRANSFER MEDIUM (sol).
The FLUID that is heated in a
SOLAR COLLECTOR for
conducting heat to another place or
substance.
F - caloporteur
S - medio de
termotransferencia
HELICAL SAIL WINDMILL (wind).
The name for a particular
type of
HORIZONTAL-AXIS, SAIL ROTOR WINDMILL.
It usually
is used for
low-lift water pumping.
F - eolienne a
ailes helicoidales
S - molino con
aspas helicoidales
HELIO-ELECTRICAL PROCESS (sol).
A process by which PHOTOVOLTAIC
MODULES convert
SOLAR ENERGY into electricity.
F - processus
helioelectrique
S - proceso
helioelectrico
HELIOSTAT (sol) (impl).
A solar-focusing instrument consisting
of a mirror mounted
on an AXIS that is moved by
clockwork.
The heliostat reflects sunbeams in one
direction,
usually to a
central ABSORBER located in a TOWER.
F - heliostat
S - heliostato
HELIOTHERMAL (sol).
[1] A process that uses SOLAR
RADIATION to
produce heat. [2] A device that absorbs
RADIATION on a
blackened surface and converts it into
heat.
F -
heliothermique
S - heliotermico
HELIOTHERMAL PROCESS (sol).
A process by which SOLAR
ENERGY is used to
provide THERMAL ENERGY for space
heating, space
cooling, and domestic water heating.
F - processus
heliothermique
S - proceso
heliotermico
HELIOTHERMOMETER (sol) (meas).
An instrument that measures
heat from the sun.
F -
heliothermometre
S -
heliotermometro
HELIOTROPIC (sol) (impl).
Turning toward light. It
describes devices
that TRACK the sun, following its
movement across the
sky.
F - heliotropique
S - heliotropico
HORIZONTAL AIR MILL (wind) (arc).
(See: HORIZONTAL-AXIS
WINDMILL)
F - moulin a vent
a arbre horizontal
S - molino de
aire horizontal
HORIZONTAL AXIS SAIL ROTOR (wind).
A WIND MACHINE with
cloth sails in
which the WIND SHAFT is situated on a
horizontal plane.
F - eolienne a
ailes en toile sur axe horizontal
S - rotor de eje
horizontal
HUMUS
HORIZONTAL AXIS WINDMILL (wind).
A WINDMILL driven by a
ROTOR on a
horizontal WIND SHAFT.
F - eolienne a
arbre horizontal
S - molino de eje
horizontal
HORIZONTAL WATERMILL (hydr).
A WATERMILL driven by a
horizontal wheel
mounted on a vertical shaft. (Syn:
Greek Mill; Norse
Mill)
F - moulin a eau
horizontal
S - molino
hidraulico horizontal
HORIZONTAL WATER WHEEL (hydr).
(See: HORIZONTAL
WATERMILL)
F - roue
hydraulique horizontale
S - rueda
hidraulica horizontal
HORSEPOWER (gen). A
unit of POWER equal to 33,000 FOOT
POUNDS per minute,
550 foot pounds per second, or 746
WATTS.
F - cheval-vapeur
S - potencia util
HOT DRY ROCK (geo) A system for using GEOTHERMAL POWER.
A
hole is drilled and
the deep rock cracked. This may be
done hydraulically,
as is done in conventional oil
fields, or with
explosives. Water is injected into the
fractured rock,
allowed to heat, and then withdrawn as
steam for use as an
ENERGY source.
F - roche chaude
et seche
S - roca seca
caliente
HOT WATER RESERVOIR (geo).
(See: GEOTHERMAL RESERVOIR)
F - reservoir
d'eau chaude
S - tanque de
agua caliente
HOUR ANGLE (sol) (meas).
The angular displacement of the
sun east or west of
the local meridian due to the rotation
of the Earth on its
AXIS at 15 [degrees] per hour (morning
[+] afternoon [-]).
F - angle horaire
S - angulo hora
HUB EXTENSION (wind).
A piece of pipe that sticks out from
the front of the
hub of a ROTOR on a WINDMILL. It
provides
a place to attach
GUY WIRES to strengthen the
BLADES or SAILS.
F - rallonge de
moyeu
S - extension del
cubo
HUMIDIFIER (gen). A
mechanical means for increasing the
relative humidity
in an enclosed area by injecting water
vapor into the air.
F -
humidificateur
S - humidificador
HUMUS (biocon).
Well-decomposed organic soil material consisting
of the residues
from plant and animal matter
together with the
cell substances of soil organisms and
various inorganic
materials.
F - humus
S - humus
HYBRID GENERATOR
HYBRID GENERATOR (biocon).
A two-stage BIOGAS DIGESTER
design consisting
of a larger batch-fed, ACID-producing,
cold phase, and a
smaller CONTINUOUS-FEED, METHANE-producing,
heated phase.
Alternatively, any digester
that separates acid
and methane production.
F - generateur
hybride
S - generador
hibrido
HYBRID POWER SYSTEM (gen).
A system, such as one might
find within a home,
that derives its heating, lighting,
and other ENERGY
from several interconnected sources.
One or more of
these sources generally would come from
RENEWABLE ENERGY.
F - energie
heterogene, systeme d'
S - sistema de
energia hibrida
HYBRID SOLAR ENERGY SYSTEM (sol).
A heating or cooling
system that uses
both ACTIVE SOLAR HEATING and PASSIVE
SOLAR HEATING
methods in its design. At least one of
the
system's
significant THERMAL ENERGY FLOWS is by natural
means, and at least
one is by forced means.
F - energie
solaire heterogene, systeme d'
S - sistema de
energia solar hibrida
HYDRATE (chem). A
solid material resulting from the
combination under
pressure of a gas with water.
F - hydrate
S - hidrato
HYDRAULIC RAM (hydr) (impl).
A water pump that uses the
ENERGY of
descending water to raise a part of the water
to a height greater
than that of the source. It requires
no other power than
the energy from the descending
water.
F - belier
hydraulique
S - ariete
hidraulico
<FIGURE>
10p70.gif (600x600)
HYDROXYL
HYDRAULIC RETENTION TIME (biocon) (meas).
The number of
days an average
volume of SLURRY remains in a BIOGAS
DIGESTER.
F - duree de
retention hydraulique
S - periodo de
retention hidraulica
HYDROELECTRIC (hydr).
Relative to a system in which the
potential ENERGY of
falling water is harnessed by
releasing it from
DAMS or through a PENSTOCK downward
through WATER
TURBINES.
F -
hydro-electrique
S -
hidroelectrico
HYDROLOGIC CYCLE (hydr).
The cycle in which water passes
through different
states. It begins as atmospheric water
vapor.
It then becomes a liquid through
precipitation.
Next it flows along
the ground surface, where it is useful
as an energy
source. Finally, it returns to its
original form
through evaporation and transpiration.
F - cycle
hydrologique
S - ciclo
hidrologico
HYDROLOGY (hydr).
The science of water systems on or
beneath the Earth's
surface.
F - hydrologie
S - hidrologia
HYDROLYSIS (alc) (chem).
The chemical process that breaks
complex organic
molecules into simple molecules. For
example, STARCH and
CELLULOSE can be hydrolyzed by ACIDS
or ENZYMES to
produce simple sugars, which can be FERMENTED
to form ETHANOL.
F - hydrolyse
S - hidrolisis
HYDROMETER (impl) (meas).
An instrument used to determine
the density or
SPECIFIC GRAVITY of FLUIDS.
F - hydrometre
S - hidrometro
HYDROPOWER (hydr).
POWER produced by falling water.
The
term is used to
identify a type of electricity-generating
station or any
energy output in which the main mover
is driven by
FLOWing water.
F - puissance
hydraulique
S - potencia
hidraulica
HYDROPOWER SYSTEM (hydr).
A system in which the potential
ENERGY of FLOWing
water is used to create electricity or
to mechanically
drive machines, by impounding it behind
DAMS and then
diverting it through a CHANNEL to a WATER
TURBINE.
F - systeme de
puissance hydraulique
S - sistema de
potencia hidraulica
<FIGURE>
10p72.gif (600x600)
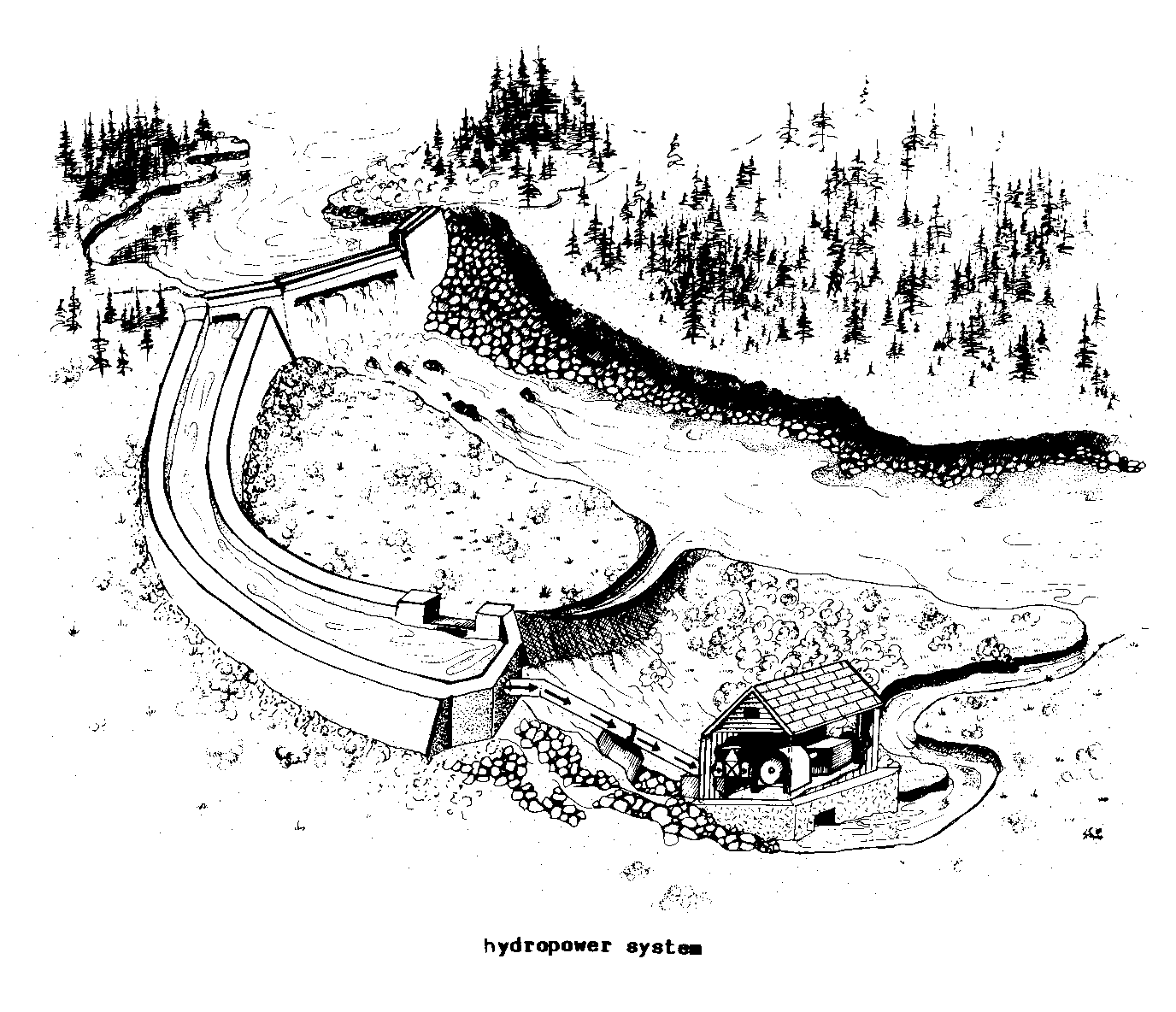
HYDROXYL (biocon). A
monovalent group consisting of a
hydrogen atom and
an oxygen atom linked together. Most
BASES contain
hydroxyl groups. (See also:
BASE)
F - hydroxyle
S - hidroxilo
HYDROPOWER SYSTEM
HYGROMETER
HYGROMETER (impl) (meas) (sol).
A device for measuring the
humidity of the
air. It is used in designing SOLAR
HEATING and SOLAR
COOLING systems.
F - hygrometre
S - higrometro
I
IMPERMEABLE DRY ROCK (geo).
Rock systems in GEOTHERMAL
regions where the
heat is contained almost entirely in
impermeable rock.
F - roche seche
impermeable
S - roca seca
impermeable
IMPULSE TURBINE (hydr).
A TURBINE driven by high velocity
JETS of water or
steam that are produced by forcing the
water or steam
through a nozzle.
F - turbine a
action
S - turbina de
impulsion
<FIGURE>
10p74.gif (486x486)
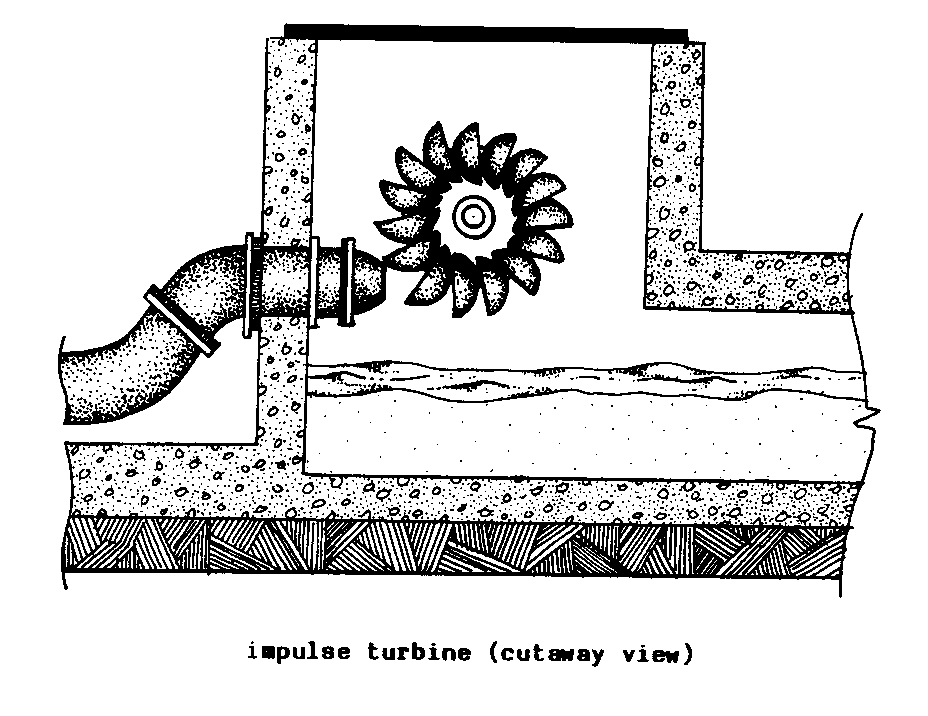
INCIDENT ANGLE (sol) (hydr).
[1] The angle between the
sun's rays and a
line perpendicular (normal) to the
irradiated
surface. The incident angle determines
both
the intensity of
the DIRECT RADIATION component striking
the surface and the
ability of the surface to reflect,
transmit, or ABSORB
the sun's rays. [2] In the case of
HYDROPOWER devices,
the angle between the water intake
and a line
perpendicular to the BUCKETS.
F - angle
d'incidence
S - angulo
incidente
INCIDENT RADIATION (sol) (meas).
The quantity of RADIANT
ENERGY striking a
surface per unit time and unit area.
F - rayonnement
incident
S - radiacion de
incidencia
INDIRECT SOLAR ENERGY
INDIAN-TYPE DIGESTER (biocon).
A BIOGAS DIGESTER primarily
designed to produce
METHANE. These digesters usually
have FLOATING GAS
CAPS.
F - digesteur
type indien
S - digestor de
tipo indio
<FIGURE>
10p75.gif (486x486)
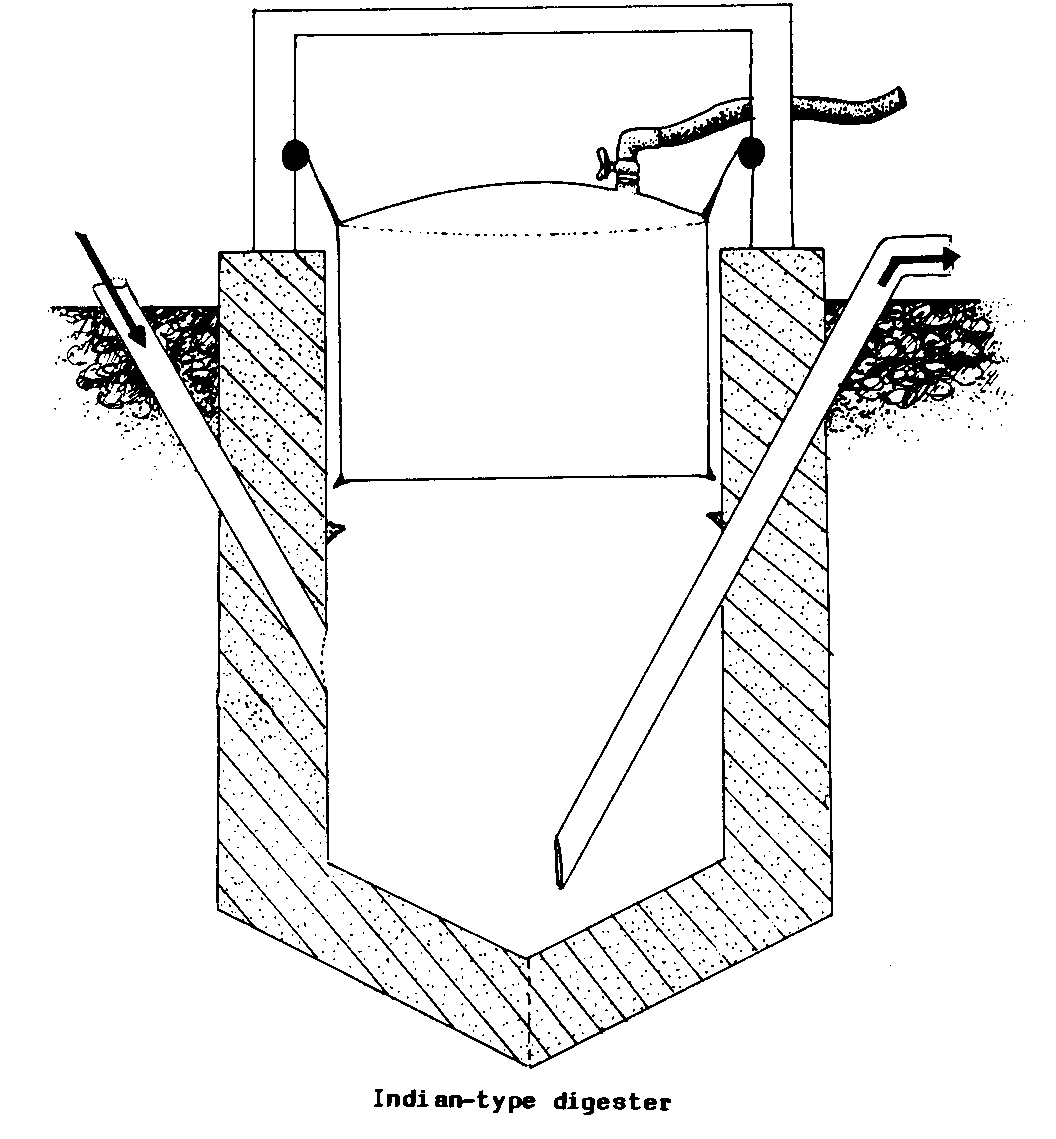
INDIRECT CONVERSION (sol).
The indirect use of SOLAR
ENERGY from such
sources as solar-produced winds,
thermal currents in
air and water, and wave action.
F - conversion
indirecte
S - conversion
indirecta
INDIRECT SOLAR ENERGY (sol).
A system in which SOLAR
ENERGY is COLLECTED
and used through mechanical means.
F - energie
solaire indirecte
S - energia solar
indirecta
INDIRECT SOLAR GAIN
INDIRECT SOLAR GAIN (sol) .
A PASSIVE SOLAR HEATING system
in which heat is
stored between the COLLECTING and the
distributing surfaces
(e.g., TROMBE WALL).
F - apport
solaire indirect
S - ganancia
solar indirecta
INDIRECT SOLAR HEATING (sol).
A method of solar heating in
which SOLAR
RADIATION is COLLECTED in FLAT PLATE or
CONCENTRATING
COLLECTORS that are mounted on a roof, a
wall, or apart from
a building. Pumps or fans are used
to circulate HEAT
TRANSFER FLUIDS through the collectors
and then back to a
heat storage medium.
F - chauffage
solaire indirect
S - calefaccion
solar indirecta
INDUCTION MOTOR (elec) (wind).
A common type of motor,
which, when
modified slightly and driven by the rotary
action of a
WINDMILL or TURBINE, provides ALTERNATING
CURRENT (ac).
F - moteur a
induction
S - motor de
induccion
INFILTRATION (heat).
The unchecked movement of outdoor air
into a building
through cracks around windows and doors
or in walls, roofs,
and floors. Infiltration generally
refers to cold air
during the winter and hot air during
the summer.
F - infiltration
S - infiltracion
INFLUENT (biocon).
BIOMASS mixed with water for use in a
BIOGAS DIGESTER.
F - affluent
S - influente
INFRARED RADIATION (sol).
Electromagnetic RADIATION from
the sun or a warm
body that has wavelengths longer than
the red end of the
visible spectrum. Infrared radiation
is experienced as
heat.
F - radiation
infrarouge
S - radiacion
infraroja
INOCULATION (biocon).
Adding a SEED of ANAEROBIC BACTERIA
to a BIOGAS
GENERATOR.
F - inoculation
S - inoculacion
INOCULUM (biocon). A
sample of partially DIGESTED SLURRY,
and its associated
BACTERIA, that is added at the start
of DIGESTION to a
BIOGAS DIGESTER. It provides sufficient
micro-organisms for
the digestion process to proceed
at a satisfactory
rate. Without this seeding, there
generally is a
prolonged wait before a digester begins
producing gas.
(Syn:
seed)
F - inoculum
S - inoculum
ISOLATED SOLAR GAIN
INSOLATION (sol).
The rate at which ENERGY from the sun
reaches the Earth's
surface. Insolation generally is
measured in
BTU/square feet (meters)/day.
F - insolation
S - insolacion
INSULATED STEAM COOKER (sol).
A small, insulated cooking
box in which steam
acts as the heating agent. Water
heated to steam by
a SOLAR COLLECTOR flows into the box,
condenses, and
drips back into the COLLECTOR.
F - rechaud a
vapeur isole
S - cocinilla
aislada de vapor
INTEGRATED HEATING (sol).
A method of SOLAR HEATING in
which SOLAR RADIATION
is intercepted and absorbed by a
massive exterior
wall or roof pond, which usually
doubles as a heat
storage container. Heat flows to the
rooms by
CONDUCTION, or natural CONVECTION. This
is a
form of PASSIVE
SOLAR HEATING.
F - chauffage integre
S - calefaccion
solar integrada
INTEGRATED SYSTEM (biocon).
A system in which the outputs
of one activity are
used as inputs in other related
activities.
For example, a BIOGAS system in which the
EFFLUENT is used as
a nutrient to enrich an aquaculture
environment.
In exchange, BIOMASS from the aquaculture
may be used as
INFLUENT to the DIGESTER.
F - systeme
integre
S - sistema
integrado
INVERTER (elec) (wind).
A device that converts DIRECT
CURRENT (dc) to
ALTERNATING CURRENT (ac). It often is
used with WIND
GENERATORS.
F - onduleur
S - invertidor
IRRIGATION WHEEL (hydr).
(See: NORIA)
F - roue
hydraulique d'irrigation
S - rueda de
irrigacion
ISOLATED SOLAR GAIN (sol).
A PASSIVE SOLAR HEATING system
in which heat is
collected in one area to be used in
another.
(See also:
SOLAR GREENHOUSE)
F - apport
solaire isole
S - ganancia
solar aislada
J
JACKET (prod) (impl).
An enclosure around a PRODUCER GAS
GENERATOR through
which cooling liquid flows. (See also:
WATER JACKET)
F - chemise d'eau
S - cubierta
JET (auto) (hydro).
A nozzle of a specific size that
limits the FLOW of
water to a TURBINE or the flow of
fuel in a
CARBURETOR.
F - gicleur
S - lanza
JET STREAM (wind).
Strong winds concentrated in a
relatively narrow,
shallow stream in the upper
troposphere.
F - jet-stream
S - manga de aire
JIB SAILS (wind) (arc).
Triangular COMMON SAILS, set on
radiating SPARS.
F- clinfoc
S- aspas
triangulares
JOULE (meas). A unit
of ENERGY or work equal to one WATT
per second or 0.737
foot pounds.
F- Joule
S- Joule
JOULE'S LAW (gen) (heat).
The law stating that: [1] The
rate at which heat
is produced by a steady current in
any part of an
electric circuit is jointly proportional
to the resistance
and to the square of the current. [2]
The internal ENERGY
of an ideal gas depends only on its
temperature
regardless of volume and pressure.
F - loi de Joule
S - ley de Joule
JUMPER (elec). A
length of wire, usually with clips on
each end, for
making temporary electrical connections.
F - fil volant
S - puente
K
KAPLAN TURBINE (hydr).
A propeller-type of WATER TURBINE
with variable pitch
BLADES that adjust automatically in
accordance with the
HEAD.
F - turbine de
Kaplan
S - turbina
Kaplan
<FIGURE>
10p79.gif (540x540)

KENAF (biocon). An
annual East Indian plant, which may be
used effectively in
BIOGAS production.
F - kenaf
S - hibiscus
cannabinus
KILN (heat). A high
temperature oven, furnace, or heated
enclosure used to
process a substance by burning,
firing, or
drying. Kilns often are described by
the
direction that air
passes through them (i.e., UPDRAFT or
DOWNDRAFT).
F - four
S - horno
KILOWATT (elec). A
unit of POWER equal to 1,000 WATTS or
to ENERGY
consumption at a rate of 1,000 JOULES per
second.
It is usually used as a measure of
electrical
energy.
Commonly abbreviated as kW.
F - kilowatt
S - kilovatios
KILOWATT HOUR
KILOWATT HOUR (elec) (meas).
A unit of POWER consumption
equal to the amount
of power multiplied by the amount of
time the power is
used. A 100-watt light bulb burning
for 10 hours uses
one kilowatt-hour of power.
F - kilowattheure
S -
kilovatio-hora
KINETIC ENERGY (gen).
The ENERGY that a body possesses by
virtue of its
motion.
F - energie
cinetique
S - energia
cinetica
KNOT (wind). A
measure of WIND SPEED equal to one nautical
mile per hour.
One knot equals 1.15 miles per hour.
F - noeud
S - nudo
L
LANGLEY (sol) (meas).
A unit of SOLAR RADIATION intensity,
equal to 1.0 gram
CALORIE per square centimeter.
F - langley
S - langley
LATITUDE (gen) (meas).
An angular position north or south
of the equator,
measured in degrees along a meridian of
a point.
F - latitude
S - latitud
LEADING EDGE (wind).
The vertical edge of a WINDMILL BLADE
that lies on the
side towards which the blade moves. The
opposite edge is
called the TRAILING EDGE.
F - arete avant
S - borde
anterior
LIFE-CYCLE COSTING (gen) (meas).
A method for estimating
the comparative
costs of ALTERNATIVE ENERGY or other
systems.
Life-cycle costing takes into consideration
such long-term
costs as ENERGY consumption, maintenance,
and repair.
F - evaluation du
cycle de vie
S - calculo del
coste de la vida util
LIFT (wind). The
aerodynamic force that "pulls" the BLADES
of a WINDMILL and
causes them to rotate.
F - portance
S - impulsion
LIFT COEFFICIENT (wind) (meas).
The ratio of LIFT forces
to FLOW forces.
F - coefficient
de portance
S - coeficiente
de impulsion
LIFT-TYPE DEVICES (wind).
WIND MACHINES that provide aerodynamic
LIFT in a wind
stream.
F - eoliennes a
portance
S - aparatos
impulsores
LIME (chem). A white
powder composed of calcium oxide that
forms a highly
ALKALINE solution when mixed with water.
It is used in
various ways, including as a means to
increase the pH
(POTENTIAL HYDROGEN) of MASH in ALCOHOL
STILLS or BIOGAS
DIGESTERS.
F - chaux
S - cal
LIME KILN (chem). A
KILN used to make LIME from coral or
limestone.
F - four a chaux
S - horno de cal
LIMEWATER
LIMEWATER (biocon) (chem).
A CALCIUM HYDROXIDE solution
often used as a gas
SCRUBBER.
F - eau de chaux
S - agua de cal
LINED FIREBOX (gen).
A firebox fitted with special insulating
material.
F - chambre de combustion
garnie
S - caja de fuego
revestida
LIQUID-BASED SOLAR HEATING SYSTEM (sol).
A SOLAR HEATING
system in which a
liquid HEAT TRANSFER MEDIUM is heated
in SOLAR
COLLECTORS. The liquid generally is
either
water or an
antifreeze solution.
F - chauffage
solaire a liquide, systeme de
S - sistema de
energia solar a base de liquidos
LIQUID SLURRY (biocon).
SLURRY comprising less than 10
percent solid
material.
F - boue liquide
S - fango liquido
LIQUID-TYPE COLLECTOR (sol).
(See: LIQUID-BASED SOLAR
HEATING SYSTEM)
F - capteur a
liquide
S - colector de
tipo liquido
LIVE CURB (wind) (arc).
The circular timber rim or wall
plate supporting a
WINDMILL CAP that revolves on ROLLERS
or WHEELS.
F - chemin de roulement
S - soporte movil
LOAD (elec) (meas).
The output of one or several electric
machines or
transformers. Load also denotes the
POWER
carried by a
particular circuit.
F - charge
S - carga
LOADING RATE (biocon) (meas).
The amount of BIOMASS added
to a DIGESTER over
a specific period of time.
F - taux de
charge
S - velocidad de
carga
LOLLY AXIS (wind).
(See: YAW AXIS)
F - axe de lacet
S - eje de
relingar
LORENA STOVE (biocon).
An inexpensive, yet efficient, cook
stove made of a
sand, clay, and water mixture known as
"lorena."
F - cuisiniere
lorena
S - estufa lorena
<FIGURE>
10p83.gif (486x486)
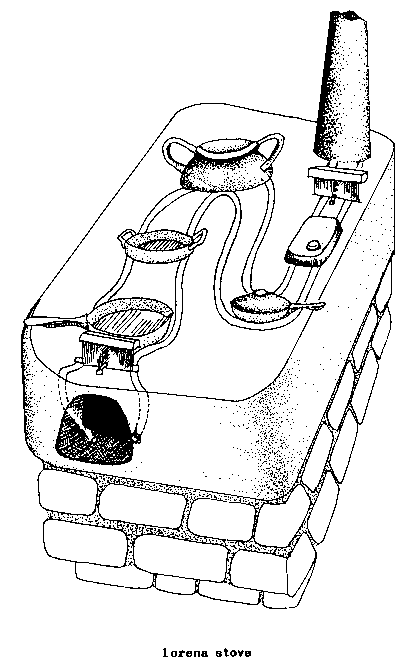
LOW HEAD TURBINE (hydr).
A WATER TURBINE that is designed
to function with a
low HEAD.
F - turbine pour
chutes faibles
S - turbina de
poco desnivel
LUFF
LUFF (wind). To turn
the BLADES of a WINDMILL into the
wind so they will
rotate.
F - lofer
S - cenir el
viento
M
MAGNESITE BRICK (constr) (sol).
A masonry brick to which
magnesium or
similar material has been added to darken
the color of the
brick and increase its THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY
and ABSORPTANCE.
F - brique a la
magnesite
S - ladrillo de magnesita
MAGNETO (elec). A
small, permanent-magnet, electric
GENERATOR capable
of producing periodic high voltage
impulses.
F - magneto
S - magneto
MAGNOUS EFFECT (wind).
An effect whereby a spinning CYLINDER
exposed to the wind
produces a horizontal force.
This effect has
been used to enable experimental WIND
MACHINES to POWER
small boats.
F - effet magnus
S - efecto de
fuerza horizontal
MALT (alc). Sprouted
grain that contains ENZYMES to convert
STARCH to
sugar. Special varieties of barley are
frequently used to
produce malt.
F - malt
S - malta
MANOMETER (biocon) (meas).
A device used to measure gas
pressure.
It may be used to monitor gas pressure in a
BIOGAS DIGESTER.
F - manometre
S - manometro
MANTLE (biocon) (impl).
A cloth MEMBRANE in which gases
are collected and
burned to create light through
incandescence.
F - manchon a
incandescence
S - manteleta
MARSH GAS (biocon).
METHANE. Decaying ORGANIC MATTER
at
the bottom of a
marsh or pond will produce bubbles of
methane gas when
stirred.
F - gaz des
marais
S - gas de los
pantanos
MASH (alc). A
mixture of water and crushed grains or other
FEEDSTOCKS that can
be FERMENTED to produce ETHANOL.
F - mout
S - mezcla
MASH COMPOSITION (alc).
The materials making up the MASH
in an ALCOHOL
STILL.
F - composition
du mout
S - malta
empastada
METHANE
MASONITE (constr).
Trademark name for a thin board made
of compressed wood
fibers. It is useful as a backing for
SOLAR REFLECTORS.
F - masonite
S - masonite
MAXIMUM FLOW RATE (hydr) (meas).
The maximum amount of
water that can FLOW
past a point during a given period
of time.
This measurement is used to evaluate the
HYDROPOWER
potential of a
site.
F - debit maximum
S - velocidad
maxima de flujo
MEADOW MILL (hydr).
A small, untended WATERMILL used for
drainage.
F - moulinet de
campagne
S - molino de
pradera
MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE (gen) (meas).
The factor by which a
machine multiplies
any applied force.
F - effet
mecanique
S - rendimiento
mecanico
MECHANICAL TURBULENCE (wind).
Erratic air movement caused
by such
obstructions as trees or buildings.
F - turbulence
mecanique
S - turbulencia
mecanica
MEGAWATT (elec) (meas).
One million WATTS.
F - megawatt
S - megavatio
MEMBRANE (alc). A
sheet polymer or thin biological tissue
capable of
separating liquid solutions. Membranes
are
sometimes used in
the ALCOHOL DISTILLATION process.
F - membrane
S - membrana
MERIDIONAL WIND (wind).
The wind or wind component along
the local meridian.
F - vent meridien
S - viento
meridional
MESOPHYLLIC BACTERIA (biocon).
BACTERIA that thrive best
at temperatures of
70-104 [degrees] F (21-40 [degrees] C) and are useful in
producing BIOGAS.
F - bacteries
mesophyliennes
S - bacteria
mesofilica
METHANATION (biocon).
A process of converting to METHANE
the carbon monoxide
and carbon dioxide present in synthetic
gas.
F - methanisation
S - metanacion
METHANE (biocon) (chem).
An odorless, colorless gas (C[H.sub.4]),
nearly insoluble in
water, which burns with a pale,
faintly luminous
flame to produce water and carbon
dioxide (or carbon
monoxide if oxygen is deficient).
(See also:
MARSH GAS) (Syn:
BIOGAS)
F - methane
S - metano
METHANE CONVERSION
METHANE CONVERSION (biocon).
The production of METHANE
through
BIOCONVERSION.
F - conversion du
methane
S - conversion de
metano
METHANE DIGESTER (biocon).
A device that converts BIOMASS
into METHANE and
Fertilizer through biological activity.
(See also:
BIOGAS DIGESTER)
F - digesteur au
methane
S - digestor de
metano
METHANE GAS (biocon) (chem).
(See: METHANE)
F - gaz de methane
S - gas de metano
METHANE GENERATION (biocon).
(See: BIOGAS DIGESTER)
F - production du
methane
S - produccion de
metano
METHANE PLANT (biocon).
(See: BIOGAS DIGESTER; METHANE)
F - generateur a
methane
S - instalacion de
metano
METHANOGENIC BACTERIA (bio) (biocon).
BACTERIA that generate
METHANE (i.e.,
those that are responsible for the
"second
step" of DIGESTION). (See
also: ANAEROBIC
DIGESTION)
F - bacteries methanogenes
S - bacteria
metanogenica
METHANOL (alc). A
light, VOLATILE, flammable, poisonous
liquid ALCOHOL
(C[H.sub.3]OH) formed in the DESTRUCTIVE DISTILLATION
of wood or made
synthetically. METHANOL is
used especially as
a solvent, antifreeze, or DENATURANT
for ETHANOL, and in
the synthesis of other chemicals. It
is also used
increasingly as a fuel. (Syn:
methyl
alcohol or wood
alcohol)
F - methanol
S - metanol
METHYL ALCOHOL (alc).
(See: METHANOL)
F - alcool
methylique
S - alcohol
metilico
MICROFLORA MICRO-ORGANISMS (bio) (biocon).
The microscopic
organisms, chiefly
BACTERIA in this context, that
are responsible for
ANAEROBIC DIGESTION.
F -
micro-organismes de la flore microbienne
S -
microorganismos de microflora
MICROHYDRO (hydr).
Small-scale, water-powered systems that
may be used to
produce mechanical POWER or less than 100
KILOWATTS of
electricity. They commonly are used for
homes, farms, or
small industries.
F -
microcentrales hydrauliques
S - microhidro
<FIGURE>
10p87.gif (600x600)
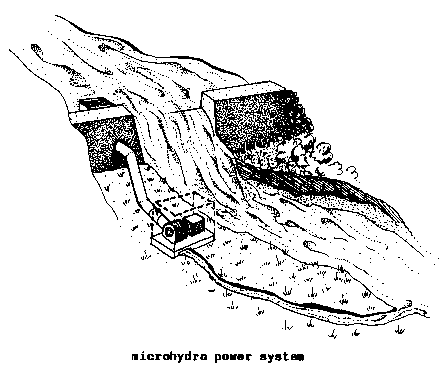
MIXING TANK
MILL (gen) (hydr) (wind).
A device to grind grain and
cereals.
Also used colloquially to describe a
WINDMILL,
WATER WHEEL, or
WATER MILL.
F - moulin
S - molino
MILL RACE (hydr). A
CHANNEL that carries water to a WATER
WHEEL.
F - bief de
moulin
S - caz
MINIHYDRO (hydr).
HYDROPOWER units that produce 100-1000
KILOWATTS.
F - minicentrales
hydrauliques
S - minihidro
MINIMUM FLOW RATE (hydr) (meas).
The least amount of water
that will FLOW past
a given point at any time. This
measurement is used
to help evaluate the HYDROPOWER
potential of a
site.
F - debit minimum
S - velocidad
minime de flujo
MISCIBLE (chem).
Capable of being mixed in any proportion.
F - miscible
S - miscible
MIXING TANK (biocon) (impl).
A chamber in which BIOMASS is
mixed with water to
form SLURRY for a BIOGAS DIGESTER.
F - reservoir de
melange
S - cuba de
mezcla
MOLECULAR SIEVE
MOLECULAR SIEVE (alc).
A STILL COLUMN that separates
molecules by
selectively ADSORPING them on the basis of
size.
F - tamis
moleculaire
S - criba por
accion molecular
MONOSACCHARIDE (alc).
SUGAR derived from STARCH and
CELLULOSE that can
be converted to ETHANOL.
F -
monosaccharide
S - monosacarido
MOUNTAIN AND VALLEY WINDS (wind).
A system of daily winds
prevailing in calm,
clear weather along the width of a
valley.
The winds blow uphill and upvalley by day
and
downhill and
downvalley by night.
F - vents des
monts et des vallees
S - vientos de
las montanas y aldeas
MULTIBLADE WINDMILL (wind).
A WINDMILL that has a large
number of
BLADES. It generally is used to pump
water.
F - eolienne a ailes
multiples
S - molino de
multiaspas
MULTIVANE WINDMILL (wind).
A WINDMILL having more than one
TAIL.
F - eolienne a
empennages multiples
S - molino de
multiples puntas
N
NACELLE (wind). The
portion of a wind electric conversion
machine that houses
the electricity generating
equipment.
F - carter
S - barquilla
NATURAL CONVECTION (heat).
The natural CONVECTION of heat
through the FLUID
in a body that occurs when warm, less
dense fluid rises
and cold, dense fluid sinks under the
influence of
gravity. (Syn:
gravity convection)
F - convection
naturelle
S - conveccion
natural
NET AREA (sol) (meas).
The area of the opening of a SOLAR
COLLECTOR, through
which SOLAR RADIATION may pass.
F - fenetre
d'entree
S - superficie
neta
NET ENERGY CONSUMPTION (gen) (meas).
(See:
ENERGY
CONSUMPTION)
F - consommation
nette d'energie
S - consumo neto
de energia
NIGHT SKY RADIATION (sol).
A method of cooling through
RADIANT ENERGY
exchange. Relatively warm surfaces are
exposed directly to
the colder night sky to which they
radiate the heat
they collected during the day.
F - rayonnement
diffus nocturne
S - radiacion del
cielo nocturno
NIGHT SOIL (bio).
Human excreta with or without flush
water, which may be
used as FEEDSTOCK for a BIOGAS
DIGESTER.
F - vidanges
S - defecaciones
humanas
NOCTURNAL RADIATION (sol).
(See: NIGHT SKY RADIATION)
F - rayonnement
nocturne
S - radiaciones
nocturnas
NORIA (hydr) (arc).
A vertical WATER WHEEL that is turned
by water
current. Containers attached to its rim
LIFT
water for
irrigation.
F - noria
S - noria
O
OCEAN THERMAL GRADIENTS (oceans).
The temperature difference
between deep and
surface water in the ocean. These
temperature
variations may be used as an ALTERNATIVE
ENERGY SOURCE.
F - gradients de
temperature oceaniques
S -
termogradientes oceanicos
OCEAN THERMAL POWER (ocean).
ENERGY acquired from differences
in temperatures at
different depths in the ocean.
F - energie
thermique des mers
S - termopotencia
oceanica
OCEAN TIDAL POWER (ocean).
The production of electricity
by harnessing ocean
tidal movements through the use of
adjustable-BLADE
WATER TURBINES or other devices.
F - energie
maremotrice
S - energia
oceanica
OFFSHORE WINDS (wind).
Winds blowing seaward from the
coast.
F - vents de
terre
S - vientos
terrales
OHM'S LAW (elec).
The law stating that for any circuit the
electric current is
proportional to the voltage and
inversely
proportional to the resistance.
F - loi d'ohm
S - ley de ohmio
ONSHORE WINDS (wind).
Winds blowing shoreward from the
sea.
F - vents du large
S - vientos del
mar
OPERATING FLOW (hydr) (meas).
The FLOW rate needed by a
HYDROPOWER device
to operate at its rated LOAD level.
F - debit nominal
S - flujo de
operacion
ORGANIC MATTER (gen).
Materials of animal or vegetable
origin.
F - matieres
organiques
S - materia
organica
ORGANIC WASTE (bio).
Residues derived from living organisms.
Organic wastes may
be used as FEEDSTOCK for BIOGAS
DIGESTERS.
(See also:
BIOMASS)
F - dechets
organiques
S - desperdicios
organicos
OVERSHOT WATER WHEEL
ORIENTATION (sol).
The arrangement of windows on a building
or solar device
along a given AXIS to face in a
direction best
suited to absorb SOLAR RADIATION. This
is
an essential
element in planning PASSIVE SOLAR HEATING
systems for homes
and other buildings.
F - exposition
S - orientacion
OSMOSIS (gen). The
process by which a solvent is DIFFUSED
through a
semipermeable MEMBRANE into a more
CONCENTRATED
solution.
F - osmose
S - osmosis
OVERFLOW WEIR (hydr).
(See: WEIR)
F - deversoir de
trop-plein
S - vertedero de
superficie
OVERSHOT WATER WHEEL (hydr).
A WATER WHEEL powered by a
HEADRACE that
discharges over the outer circumference of
the wheel.
(Syn:
overshot gravity wheel)
F - roue en
dessus
S - rueda
hidraulica de admision superior
<FIGURE>
10p91.gif (486x486)
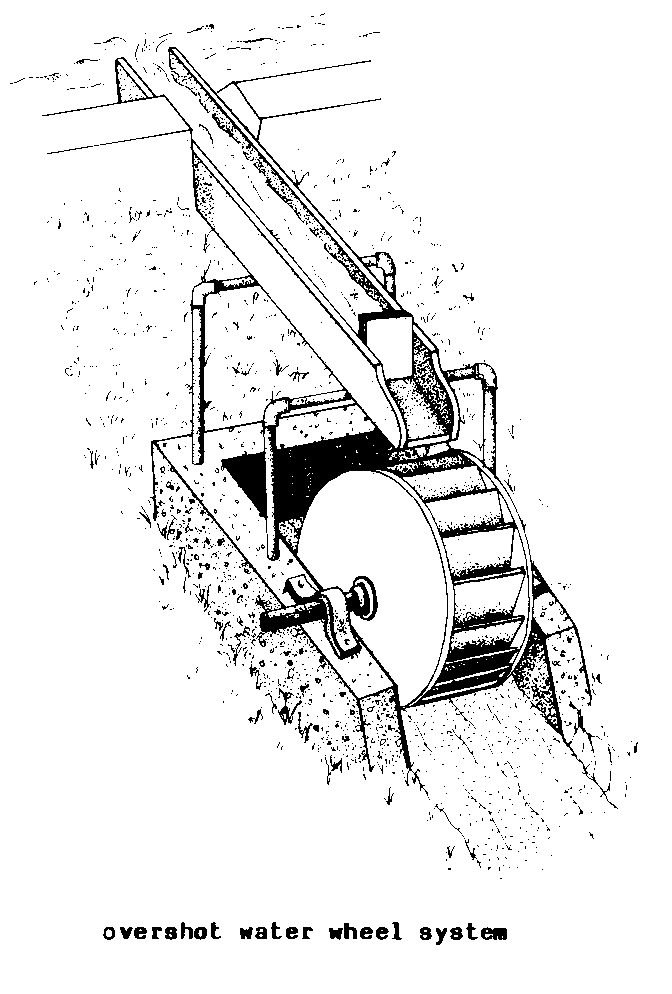
P
PACKED COLUMN (alc).
A type of STILL COLUMN or pipe that
is used in ALCOHOL
DISTILLATION. It is filled with such
material as metal
filings, plastic, or glass beads.
Packed columns
increase ALCOHOL yields by providing continuous
redistillation of
the ALCOHOL VAPOR as it moves
up the still
column.
F - colonne
garnie
S - columna
compacta
PANEMONE (wind). A
VERTICAL-AXIS WIND MACHINE, generally
a DRAG-TYPE WIND
MACHINE, that can react to winds from
any direction.
F - panemone
S - molino de eje
vertical
PARABOLA (sol). The geometrically-curved shape used in the
design of SOLAR
COOKERS to focus sunlight on a single
point.
A parabola is based on a family of quadratic
curves.
F - parabole
S - parabola
PARABOLIC CONCENTRATING COOKER (sol).
A SOLAR COOKER that
uses a PARABOLIC
DISH to focus sunlight.
F - cuiseur
solaire a miroir concave
S - cocina
parabolica concentrante
PARABOLIC DISH (sol).
A SOLAR ENERGY device shaped like a
dish or bowl, with
the characteristics of a PARABOLA. It
focuses sunlight on
a point or a very small area.
F - parabolique
solaire
S - plato
parabolico
PARABOLIC MIRROR (sol).
A device with a large, shiny,
curved surface that
focuses SOLAR RADIATION on a
specific point,
such as a cooking vessel, for heating or
boiling.
F - miroir
parabolique
S - espejo
parabolico
PASCAL'S LAW (gen).
The law stating that pressure applied
to a confined FLUID
at any point is transmitted throughout
the fluid in all
directions. The pressure acts upon
every part of the
confining vessel at right angles to
its interior
surfaces, acting equally upon equal areas.
F - loi de Pascal
S - ley de Pascal
PASSIVE SOLAR DESIGN (sol).
An architectural design that
makes use of the
structural elements of a building to
heat or cool spaces
in the building.
F - systeme
solaire passif
S - diseno solar
pasivo
PELTON WHEEL
PASSIVE SOLAR HEATING (sol).
The SOLAR HEATING of a building
by use of
architectural design, without the aid of
mechanical
equipment.
F - chauffage
solaire passif
S - calefaccion
solar pasiva
PATENT SAIL (wind) (arc).
A SAIL fitted with SHUTTERS
that are controlled
automatically.
F - aile a volets
S - aspa patente
PATHOGENIC ORGANISM (bio).
(See: PATHOGENS)
F - organisme
pathogene
S - organismos
patogenicos
PATHOGENS (bio).
Harmful micro-organisms, such as BACTERIA
and viruses.
Pathogens may be found in human, animal,
and other wastes,
and help spread disease.
F - microbes
pathogenes
S - patogenos
PEAK WATT (sol) (meas) (elec).
Unit used for the performance
rating of
PHOTOVOLTAIC CONVERTERS. A system rated
at one peak watt
will deliver one WATT at the specified
working voltage
under peak SOLAR IRRADIATION.
F - watt-crete
S - vatio maximo
PEAT (bio) (biocon).
Partially decomposed ORGANIC MATTER
formed in marshes
and swamps. Dried peat is useful as a
fuel.
F - tourbe
S - turba
PEBBLE BED (sol). A
large bin of uniformly-sized pebbles
that is used to
store heat in SOLAR HEATING or SOLAR
COOLING
systems. A pebble bed is one type of
HEAT SINK.
F - lit de galets
S - lecho de
gravilla
PEDAL POWER (gen).
Mechanical or electrical POWER generated
by the use of a
bicycle-gearing apparatus. Pedal
power may be used
for buffing, lathing, grinding grain
or meat, operating
a potter's wheel, driving a small
GENERATOR, turning
a sharpening stone, operating a corn
sheller, and other
applications.
F - energie par
pedalier
S - potencia
generada por pedal
PEDAL-POWER UNIT (impl).
(See: PEDAL POWER; DYNAPOD)
F - appareil a
entrainement par pedales
S - unidad de
potencia-pedal
PELTON WHEEL (hydr).
An IMPULSE WATER TURBINE in which the
pressure of the
water supply is concentrated through a
few stationary
nozzles. The JETS of water strike the
BUCKETS, which are
mounted on the RUNNER. Pelton wheels
usually are limited
to installations with HEADS that
exceed 500 feet, or
about 160 meters. (Syn:
Pelton
turbine)
F - roue Pelton
S - rueda Pelton
<FIGURE>
10p94a.gif (486x486)
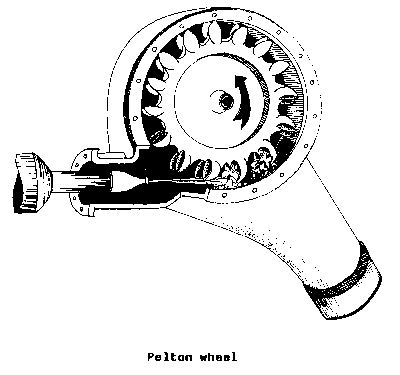
PENSTOCK
PENSTOCK (hydr). A
water conduit from a DAM to a
TURBINE or WATER
WHEEL. (See also:
CHANNEL)
F - conduite
forcee
S - paradera de
caz
<FIGURE>
10p94b.gif (486x486)

PHOTOVOLTAIC CELL
pH (chem) (meas).
Potential hydrogen. The symbol
that
denotes a
measurement of the effective hydrogen ion
CONCENTRATION.
On a scale of 0 to 14, 7 represents
neutrality.
Numbers less then 7 indicate increasing
ACIDITY.
Numbers greater than 7 indicate increasing
ALKALINITY of a
solution.
F - pH
S - pH
PHOTOMETER (sol) (meas).
A device that measures the
intensity of light.
F - photometre
S - fotometro
PHOTOVOLTAIC ARRAY (sol). A number of PHOTOVOLTAIC MODULES
that are
electrically connected in a series and/or in
parallel so as to
provide the desired POWER and
voltage.
The modules are mounted on a sturdy
framework
that generally
faces the equator. The array may be
tailored to the
requirements of a particular application
and location.
Such an array is valuable because it can
generate
electricity from sunlight without the use of
moving mechanical
parts.
F - chapelet de
photopiles
S - conjunto
fotovoltaico
<FIGURE>
10p95.gif (437x437)

PHOTOVOLTAIC CELL (sol).
A SOLAR ENERGY device that
changes light into
electrical ENERGY. The cell is a
small square or
circular wafer made of treated SILICON
or other
semiconductor material.
F - cellule
photovoltaique
S - celula
fotovoltaica
PHOTOVOLTAIC CONVERTER
PHOTOVOLTAIC CONVERTER (sol).
(See: PHOTOVOLTAIC CELL)
F - convertisseur
photovoltaique
S - convertidor
fotovoltaico
PHOTOVOLTAIC MODULE (sol).
The basic building block of a
PHOTOVOLTAIC ARRAY,
which consists of a number of
interconnected
SOLAR CELLS.
F - module
photovoltaique
S - modulo
fotovoltaico
PHOTOVOLTAIC PANEL (sol).
(Syn: PHOTOVOLTAIC MODULE)
F - panneau
photovoltaique
S - panel
fotovoltaico
PHOTOVOLTAIC PROCESS (sol).
A process by which light rays
are converted
directly into electrical ENERGY.
F - conversion
photovoltaique
S - proceso
fotovoltaico
PITCH (wind) (meas).
The angle between the BLADE surface
and the ANGLE OF
ATTACK in a WINDMILL.
F - pas
S - paso
PITCH-BACK WATER WHEEL (hydr).
An OVERSHOT WATER WHEEL in
which the trough
carrying water to the wheel is modified
to discharge onto
the near side of the wheel, thus
reversing the
normal direction of rotation.
F - roue
hydraulique a jet inverse
S - rueda
hidraulica de engranaje
PIT KILN (heat). A
KILN made from a hole that is dug in
the ground.
F - four en terre
S - horno de foso
PLUG FLOW GENERATOR (biocon) (impl).
A BIOGAS DIGESTER
with no mechanical
agitation through which the SLURRY
passes along in
more or less discrete "plugs," creating
a cycle of
"first in-first out." The
EFFLUENT is then
theoretically
composed only of older slurry. The plug
flow design differs
from traditional designs, in which
all slurry is
purposely mixed together in a single pit
or tank.
F - generateur a
effet bouchon
S - generador de
flujo
POLL ENDS (arc) (wind).
(See: CANISTER)
F - bouts de mats
S - puntas
POLYSACCHARIDE (chem).
(See: STARCH)
F -
polysaccharide
S - polisacarido
POLYURETHANE FOAM (constr).
A very lightweight plastic or
other synthetic
insulating material.
F - mousse de
polyurethanne
S - espuma de
poliuretano
POUNDS PER SQUARE INCH
POLYVINYL ACETATE (chem) (sol).
A clear plastic made of
CELLULOSE ACETATE
and used as GLAZING on SOLAR
COLLECTORS.
F - acetate de
polyvinyle
S - acetato de
polivinilo
PONCELET WHEEL (hydr).
An UNDERSHOT WATER WHEEL made with
curved metal
BLADES.
F - roue Poncelet
S - rueda hidraulica Poncelet
<FIGURE>
10p97.gif (437x437)
POST MILL (wind) (arc).
This is the earliest type of
European WINDMILL.
The body of the windmill is balanced
on a large post and
trestle. The entire body revolves to
turn the BLADES
into the wind.
F - moulin pivot
S - molino de
poste
<FIGURE>
10p98.gif (437x437)
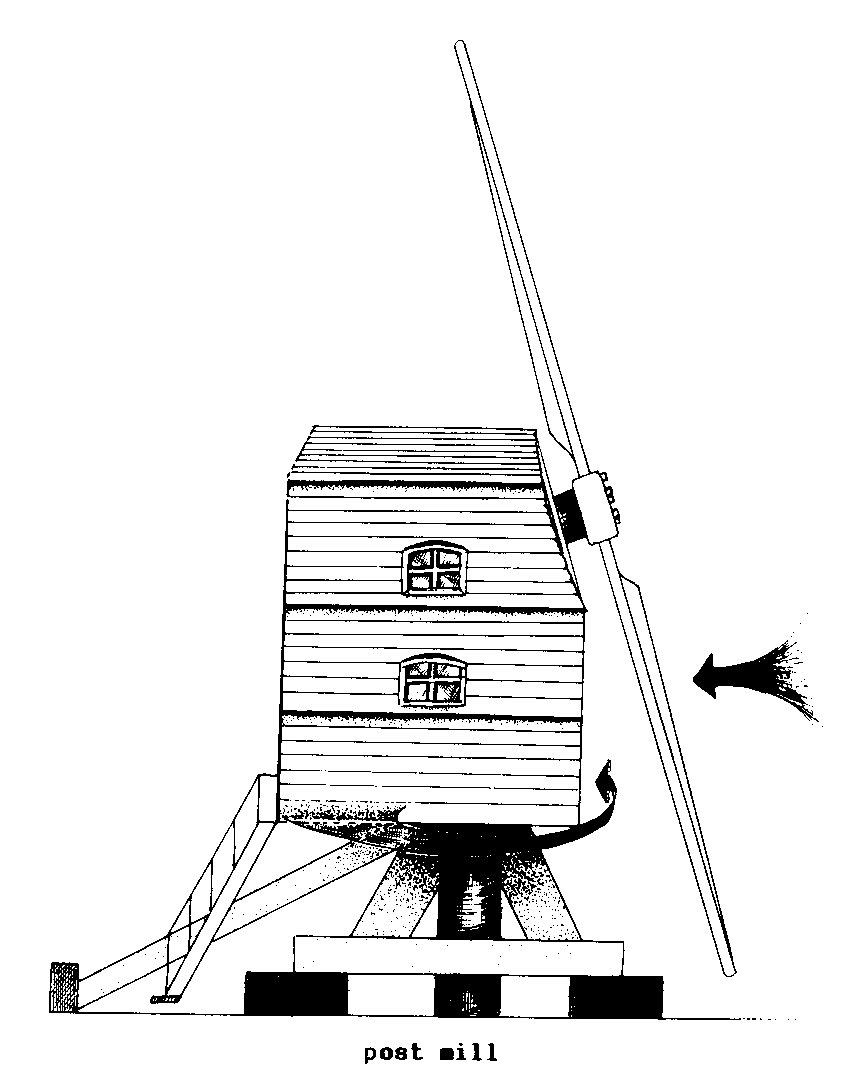
POTENTIAL HYDROGEN (chem) (meas).
(See: pH)
F - potentiel
d'hydrogene
S - potencial de
hidrogeno
POUNDS PER SQUARE INCH (meas).
A measurement of gas pressure.
Commonly
abbreviated as psi.
F - livres par
pouce carre
S -
libras/[pulgada.sup.2]
POWER
POWER (gen). The
rate at which ENERGY is consumed or
produced.
F - puissance
S - potencia
POWER COEFFICIENT (wind) (meas).
The ratio of the POWER
extracted by a WIND
MACHINE ROTOR to the power available
in a wind stream.
F - coefficient
de puissance
S - coeficiente
de potencia
POWER DENSITY (wind) (meas).
The amount of POWER per unit
of a
cross-sectional area of a wind stream.
F - puissance
volumique
S - densidad de
potencia
PRODUCER GAS
PRECULTURE (alc). A
method for reducing the time and
increasing the
EFFICIENCY of FERMENTATION. The
preculture
process involves
CONCENTRATING the ALCOHOL-producing
YEAST before
introducing it into the FERMENTATION
TANK.
F - preculture
S - precultivo
PREPARED ORGANIC WASTE (biocon).
BIOMASS mixed with water
for use in a BIOGAS
DIGESTER. (Syn:
SLURRY)
F - dechets
organiques prepares
S - desperdicio
organico preparado
PREVAILING WIND (wind).
The direction from which the wind
blows most often.
This is an important consideration in
selecting a site
for a WINDMILL.
F - vent dominant
S - viento
dominante
PRODUCER GAS (prod).
A combination of COMBUSTIBLE GASES
created through the
combustion of wood or coal in a
controlled-air
environment. Producer gas may be used
to
drive gasoline or
diesel engines.
F - gaz de
gazogene
S - gas pobre
PRODUCER GAS GENERATOR
PRODUCER GAS GENERATOR (gen).
A furnace in which COMBUSTIBLE
GASES are produced
for use as a fuel.
F - gazogene
S - generador de
gas pobre
<FIGURE>
10p99.gif (486x486)
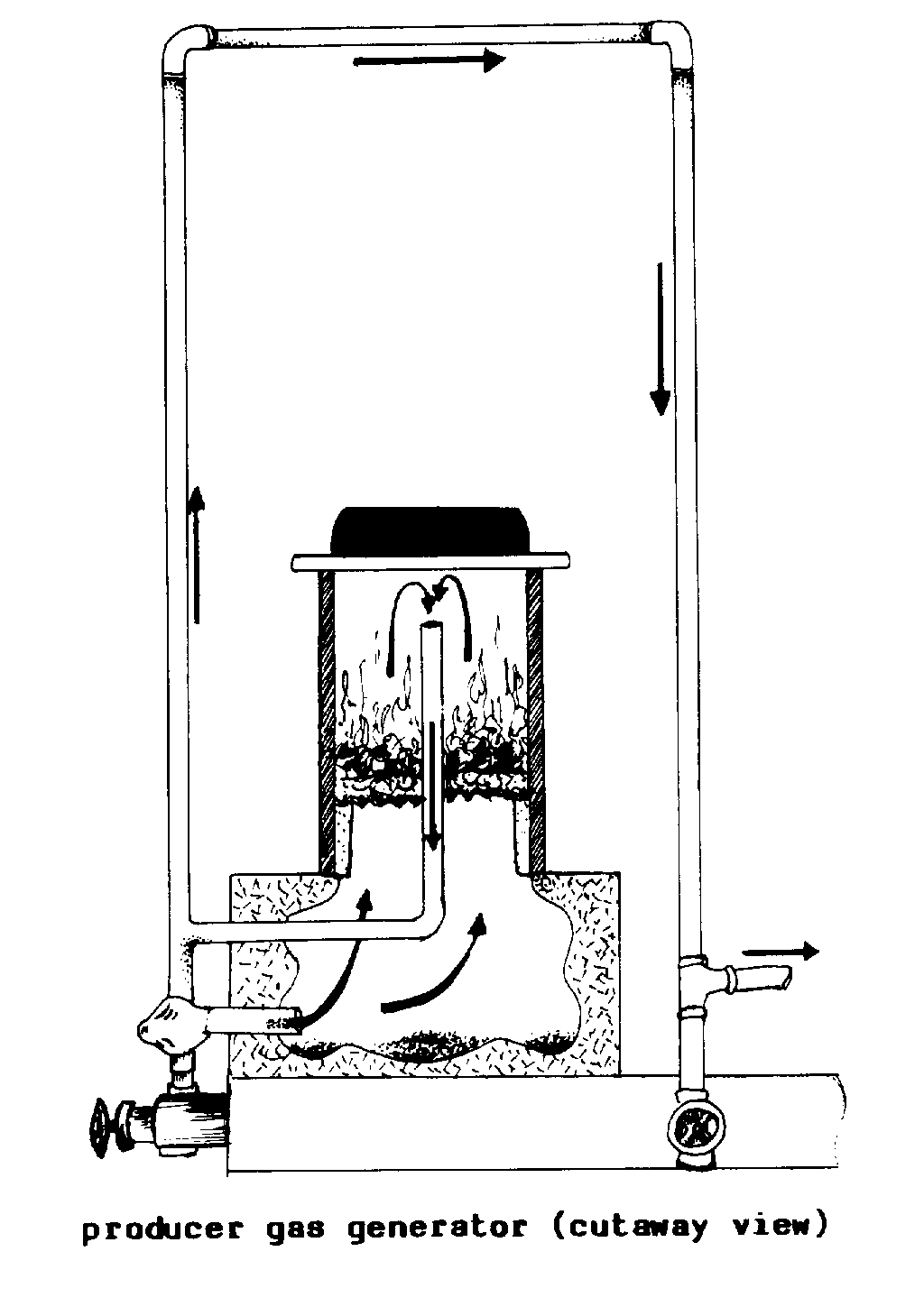
PROOF (alc) (meas).
A unit measurement of the strength of
ALCOHOL.
The proof is twice the percentage of the
alcohol
in the liquid.
Alcohol that is 90 proof contains 45
percent
alcohol. (See also:
PROOF-GALLON)
F - degre en
alcool
S - graduacion
normal
PROOF-GALLON (alc) (meas).
A standard U.S. gallon of a
mixture that is 50
percent ALCOHOL and 50 percent water
(i.e., that is 100
proof). An alcohol/water mixture that
contains a
different ratio of each may be translated
into proof-gallons
by moving the decimal point of the
proof two places to
the left and multiplying by the
total number of
gallons of the mixture.
F - proof-gallon
S - proof-gallon
PSI (meas).
Abbreviation for POUNDS PER SQUARE INCH.
F - psi
S -
lb/[pulg.sup.2]
PYRANOMETER (meas) (sol).
A device that measures total
GLOBAL RADIATION.
F - pyranometre
S - piranometro
PYROHELIOMETER (meas) (sol).
An instrument that measures
SOLAR RADIATION
from the sun, or from a small portion of
the sky that
surrounds the sun.
F -
pyroheliometre
S -
piroheliometro
PYROLYSIS (chem).
The DECOMPOSITION of a substance
subjected to very
high heat.
F - pyrolyse
S - pirolisis
Q
QUAD (meas). One
quadrillion BTUs. It is expressed as
either [10.sup.15]
or 1,000,000,000,000,000 BTus. A quad
is
used to measure any
large unit of energy such as wood,
gasoline, coal,
etc. For example, a quad can be used to
describe the amount
of THERMAL ENERGY that is potentially
available from
burning a certain acreage of trees in
WOODSTOVES.
F - quad
S - cuad
QUARTERING (wind).
The action of turning a WINDMILL broadside
to the WIND.
F - larguage
S - venteo
R
RACE (hydr). An
AQUEDUCT or CHANNEL that carries water to
and from the place
where it is used to drive a HYDROPOWER
device.
F - chenal
S - canal de
trabajo
RADIAL FLOW (hydr).
A type of HYDROPOWER device in which
the water flows out
radially from the power shaft. (See
also: FRANCIS
TURBINE)
F - ecoulement
radial
S - flujo radial
RADIANT ENERGY (sol).
ENERGY in the form of electromagnetic
waves that travels
outward in all directions from
its source.
F - energie
rayonnante
S - energia
radiante
RADIANT PANELS (sol).
SOLAR COLLECTORS with integral passages
for the FLOW of
HEAT TRANSFER FLUID. Heat from the
fluid is conducted
into a room or building by THERMAL
RADIATION.
F - panneaux
rayonnants
S - paneles
radiantes
RADIATION (sol).
Electromagnetic waves that directly
transport ENERGY
through space. Sunlight is a form of
radiation.
F - rayonnement
S - radiacion
RATED POWER CAPACITY (wind) (meas).
The expected POWER
output of a WIND
MACHINE. It is equal to either the
maximum power of
the machine or to an output at some
WIND SPEED less
than the maximum speed, but at which
GOVERNING controls
start to reduce the power.
F - puissance
nominale
S - capacidad de
potencia tasada
RATED WIND SPEED (meas) (wind).
The WIND SPEED at which a
WIND MACHINE
delivers its RATED POWER CAPACITY.
F - vitesse
nominale du vent
S - velocidad
eolica tasada
RATE LIMITING STEP (biocon). Whichever stage in the
ANAERIOBIC
process that is
slowest. Since each step
in the digestion
process requires the preceeding one to
be completed before
it can begin, the overall gas production
rate is limited by
the slowest step.
F - stage
limitant la cadence
S - etapa de
velocidad limitadora
RECTIFIER
RAW SLUDGE (biocon).
Fresh, undried, uncomposted EFFLUENT
from a
DIGESTER. Also residue in the same
condition from
the bottom of a
digester.
F - boues brutes
S - cienos sin
tratar
RAYLEIGH DISTRIBUTION (wind).
Standard WIND SPEED DISTRIBUTION
that is useful in
wind site analysis. It is a
probability density
function that allows one to model
the wind speed
distribution based on a single input
parameter.
(See also:
WEIBULL DISTRIBUTION)
F - distribution
de Rayleigh
S - distribucion
de Rayleigh
REACTION TURBINE (hydr).
A WATER TURBINE that uses the
mass or weight of
water hitting the RUNNER as opposed to
being driven by the
velocity of the water.
F - turbine a
reaction
S - turbina a
reaccion
REACTION WATER WHEEL (hydr).
A WATER WHEEL that uses the
mass or weight of water falling onto it
rather than the
FLOW.
F - roue
hydraulique a reaction
S - rueda
hidraulica reactiva
RECIPROCATING ENGINE (hydr).
A device that converts the
potential ENERGY in
a FLUID to mechanical energy by
expanding the FLUID
against a piston.
F - moteur a
pistons
S - maquina
alternativa
RECIPROCATING PUMP (wind).
A type of water pump commonly
used with
WINDMILLS. Motion and pressure are
applied to
the water by a
piston moving up and down in a CYLINDER.
The piston is
powered by the WINDMILL.
F - pompe
alternative
S - bomba
aspirante e impelente
RECLAIMED OIL (heat).
(See: USED OIL)
F - huile de
recuperation
S - aceite
recuperado
RECOVERED ENERGY (gen).
Heat or other ENERGY that normally
would be lost
during a process, but instead is captured
and reused.
For example, FLUE gases may be used for
drying purposes.
F - energie
recuperee
S - energia
recobrada
RECTIFIER [1] (alc) (impl).
A second column on an ALCOHOL
STILL that is used
to further remove water from the
ALCOHOL VAPOR, thus
increasing the PROOF of the alcohol.
This increase in
CONCENTRATION is achieved by the
repeated
interaction of the rising vapor with the liquid
DISTILLATE.
[2] (elec).
A device that converts ALTERNATING
CURRENT (ac) into
DIRECT CURRENT (dc).
F - [1] colonne
de rectification; [2] redresseur
S - [1]
rectificadora; [2] rectificador
RECTIFYING COLUMN
RECTIFYING COLUMN (alc) (impl).
[See: RECTIFIER (alc)]
F - colonne de
rectification
S - columna de
rectificar
REDUCING SUGAR (alc).
(See: MONOSACCHARIDE)
F - sucre
reducteur
S - azucar
reductora
REEFING (wind).
Rolling and tying down a portion of a
WINDMILL SAIL to
reduce the area exposed to the wind.
F - prendre les
ris
S - recoger las
velas
REFLECTANCE (sol).
The ratio of RADIATION reflected from a
surface to that
incident on the surface. [See also:
REFLECTIVITY (2)].
F - facteur de
reflexion
S - reflectancia
REFLECTED RADIATION (sol).
SOLAR RADIATION that has been
reflected from such
surfaces as the ground or buildings,
and which
ultimately becomes INCIDENT RADIATION.
F - rayonnement
reflechi
S - radiacion
reflejada
REFLECTIVITY (sol) (meas).
[1] The ability to reflect
SOLAR RADIATION,
which is possessed to some degree by
all materials.
It is called the ALBEDO in atmospheric
references.
[2] The ratio of RADIANT ENERGY reflected by
a body to that
falling upon it.
F - pouvoir
reflecteur
S - reflectividad
REFLECTOMETER (sol) (meas).
A PHOTOMETER or other electronic
device that
measures REFLECTANCE or RADIANT
ENERGY.
F - reflectometre
S - reflectometro
REFLECTOR (sol). A
device that can be used to reflect and
focus SOLAR
RADIATION.
F - reflecteur
S - reflector
REFLECTOR BACKING (sol).
The material used on the rear
part of a SOLAR
REFLECTOR. (See also:
MASONITE)
F - renfort de
reflecteur
S - revestimiento
reflector
REFLECTOR COOKER (sol).
(See: REFLECTOR-TYPE SOLAR
COOKER)
F - cuiseur a
reflecteur
S - hornillo
reflector
RETURN TIME
REFLECTOR-TYPE SOLAR COOKER (sol).
A SOLAR COOKER in which
a REFLECTOR
concentrates the sun's rays on a cooking
device.
F - cuiseur
solaire a reflecteur
S - hornillo
solar reflector
REFLUX (alc). Liquid
ALCOHOL that is condensed in a
DISTILLATION
COLUMN, and then reintroduced into the
column to increase
its CONCENTRATION.
F - reflux
S - reflujo
REFRIGERANT (refrig).
A VOLATILE substance that can be
used as a working
FLUID in a cooling system.
F - refrigerant
S - refrigerante
REFRIGERATION (refrig).
The act or process of making or
keeping something
cool or cold. It especially applies to
the use of
artificial means for cooling.
F - refrigeration
S - refrigeracion
RENEWABLE ENERGY (gen).
ENERGY produced from regenerative
or virtually
inexhaustible resources such as BIOMASS,
SOLAR RADIATION,
the wind, water, or heat from the
Earth's interior.
F - energie
renouvelable
S - energia
renovable
RENEWABLE RESOURCES (gen).
(See: RENEWABLE ENERGY)
F - ressources
renouvelables
S - recursos
renovables
RESISTANCE VALUE (constr) (meas).
A rating of a substance's
thermal resistance
to summer HEAT GAIN or
winter heat
loss. It is used as a measure of
insulation
efficiency.
(Syn:
R-VALUE) (See also: U-VALUE)
F - resistance
thermique
S - valor de
resistencia
RETORT (alc) (gen). [1]
A vessel in which substances are
subjected to heat
for the purpose of DISTILLATION or
DECOMPOSITION.
A retort is distinguished from a STILL in
that it is more
often used for the treatment of solid or
semisolid
substances. [2] A closed container used
in
CHARCOAL production
in which COMBUSTIBLE GASES are
captured and made
into liquids, generally through
CONDENSATION.
F - cornue
S - retorta
RETROFITTING (sol).
The installation of SOLAR HEATING or
SOLAR COOLING
systems in existing structures.
F - readaptation
S - modificacion
retroactiva
RETURN TIME (wind) (meas).
The length of time during which
low winds prevent a
WINDMILL from reaching its CUT-IN
SPEED or START-UP
SPEED. The "down time" or
time period
when the wind is
too low to enable a WINDMILL to reach
its cut-in speed or
start-up speed.
F - temps mort
S - tiempo de
restablecimiento
REYNOLDS' NUMBER
REYNOLDS' NUMBER (meas) (sol) (wind).
The ratio of
material forces to
VISCOUS forces in any FLUID FLOW. The
Reynolds' number is
determined through the following
equation:
(PVD)/U where:
P
(rho) = density
V =
velocity
D =
length of flow distance
U
(mu) = viscosity.
F - nombre de
Reynolds
S - numero de
Reynolds
RICE HUSK STOVE (biocon).
A stove designed to use rice
husks as its
primary fuel.
F - poele a
paille de riz
S - estufa de
cascaras de arroz
RIGGING (wind) (impl).
Collectively, all the ropes and
cords used to
support the mast of the WINDMILL, and to
FURL or unfurl the
SAILS.
F - haubanage
S - cordaje
RIPARIAN RIGHTS (hydr).
The right of a landowner to the
water on or
bordering his or her property, including the
right to prevent
diversion or misuse of upstream water.
F - droits de
riverainete
S - derechos
riberenos
RISER (alc). A tube
that penetrates a plate in a STILL
COLUMN, allowing
ALCOHOL VAPORS to move up the column. A
perforated cap or
cup is placed on top of each riser to
distribute the
vapor into the column section and to
prevent water from
dripping into the riser.
F - colonne
montante
S - tubo de
subida
RIVER GENERATOR (elec) (hydr).
A HYDROELECTRIC GENERATOR
that gets its power
from a river or other FLOWING water.
F - generateur
riverain
S - generador
fluvial
ROCKBED (sol). A
heat storage container filled with rocks
or pebbles that is
used in SOLAR HEATING and SOLAR COOLING
systems.
F - lit de
pierres
S - fondo de roca
ROCKBED COOLING SYSTEM (sol).
A passive air-conditioning
system that
circulates a building's air through a bed of
rocks that has
cooled during the night or early morning.
F -
refroidissement par lit de pierres, systeme de
S - sistema de enfriamiento
con lecho de roca
R-VALUE
ROCKER ARM (wind) (impl).
A support mechanism that rotates
on a shaft at one
end while moving up and down at the
other.
It is used to convert the rotating motion of
a
WINDMILL to an
up-and-down motion, usually for pumping.
F - culbuteur
S - balancin
ROLLER REEFING SAIL (wind) (arc).
A ROTOR BLADE that is
fitted with canvas
strips (SAILS) wound on ROLLERS. The
rollers are used
for REEFING the sails.
F - aile a
rouleaux de prise de ris
S - aspa con
rodillos
ROLLERS (wind) (arc).
BEARINGS between the CURB and the
CAP of a TOWER MILL
or SMOCK MILL. The rollers allow the
top of the MILL to
turn into the wind.
F - rouleaux
S - rodillos
ROTOR (wind). The
assembly of SAILS or BLADES that rotate
about an AXIS
created by the WIND SHAFT of a WINDMILL.
F - rotor
S - rotor
ROTOR SHAFT (wind).
(See: WIND SHAFT)
F - arbre de
rotor
S - eje del rotor
RUNG (hydr) (wind).
[1] The BLADES of a WATER WHEEL.
[2]
The transverse iron
rods that hold the SAIL CLOTHS in a
WINDMILL.
F - [1] palette;
[2] barreau
S - paleta
RUNNER (hydr). The
TURBINE wheel.
F - roue de
turbine
S - rueda movil
<FIGURE>
10p107.gif (486x486)
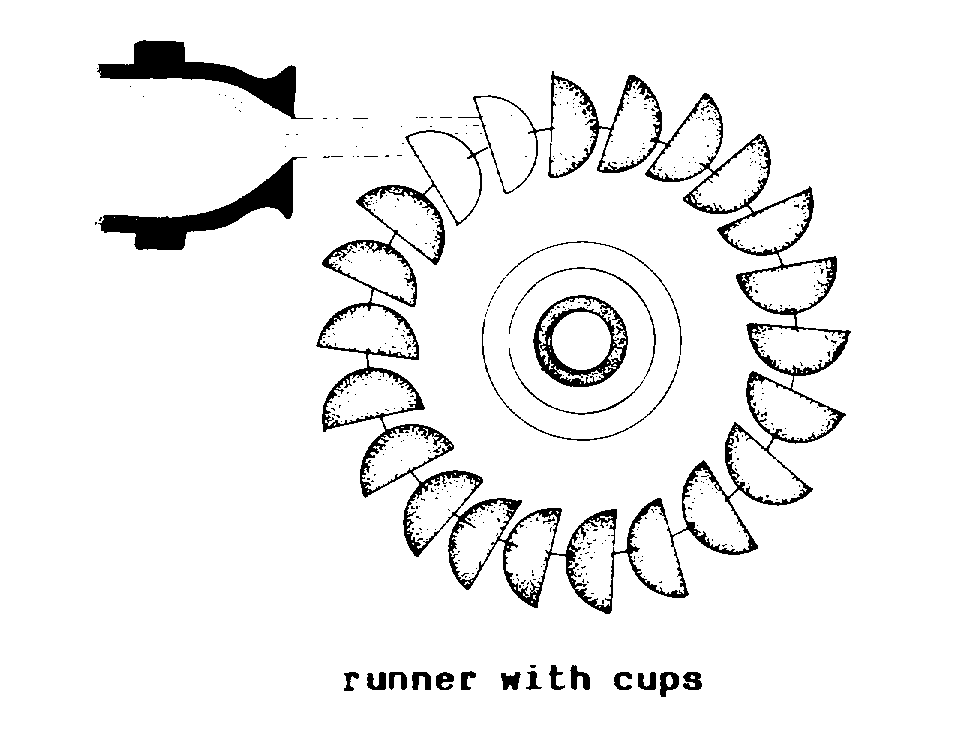
R-VALUE (meas).
(See: RESISTANCE VALUE)
F - resistance
thermique
S - valor R
S
SACCHARIFICATION (alc).
A conversion process using ACIDS,
BASES, or ENZYMES
in which CARBOHYDRATES are broken down
into FERMENTABLE
SUGARS. (See also:
FERMENTATION)
F -
saccharification
S -
sacarificacion
SAIL (wind). A piece
of cloth attached between each of the
SPARS of a WINDMILL
for the purpose of catching the
wind.
Also used to define windmill sails collectively.
F - aile
S - vela
SAIL BACK (wind) (arc).
A single SPAR that replaces the
STOCK and WHIP in
WINDMILLS that are fitted with iron
crosses instead of
POLL ENDS.
F - bras d'aile
S - barra del
aspa
SAILCLOTH (wind).
Very strong cotton or canvas that may
be used for SAILS
on WINDMILLS.
F - toile a voile
S - lona
SAILWING WINDMILL (wind).
A WINDMILL that has a small
number of cloth
SAILS. Sailwing windmills are usually
simple designs, and
are most commonly used for water
pumping.
F - moulin a
volants
S - molino de
viento con vela de lona
SALT (chem). A
product formed by the neutralization of
an ACID by a BASE.
F - sel
S - sal
SANITATION/DIGESTER SYSTEM (biocon).
A BIOGAS system that
combines METHANE
production with facilities to dispose
of human
excreta. This also is an effective way
to
eliminate dangerous
PATHOGENS.
F - systeme
sanitaire/digesteur
S - sistema de
saneamiento/digestor
SAVONIUS ROTOR (wind).
A WIND MACHINE with a VERTICAL
AXIS, often made
from split oil drums. It is a DRAG-TYPE
device with
relatively low EFFICIENCY, but with
high starting
TORQUE.
F - rotor de
Savonius
S - rotor
Savonius
<FIGURE>
10p109.gif (600x600)
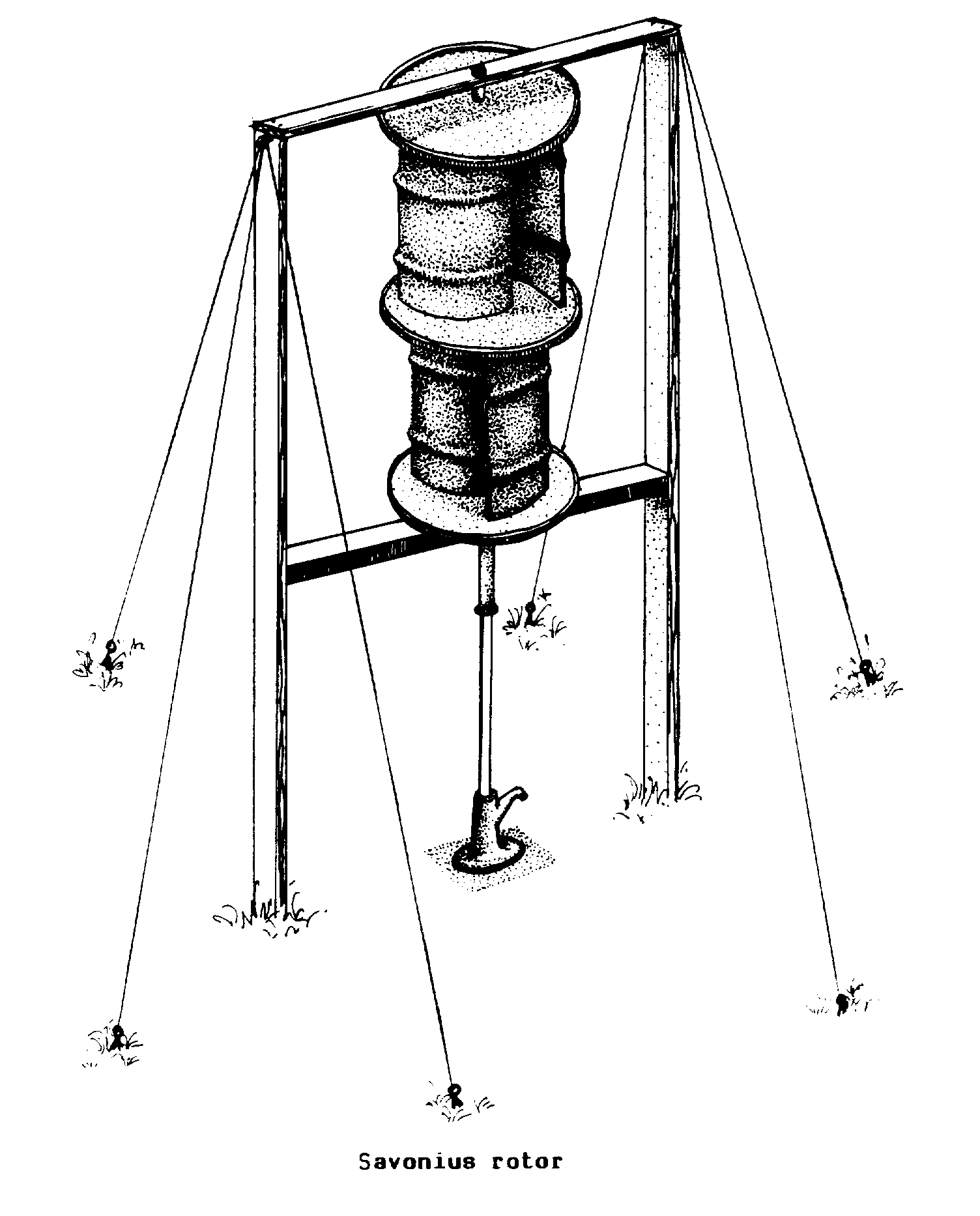
SCOOP WHEEL
SAWDUST STOVE (biocon).
A stove designed to use sawdust as
its primary fuel.
F - poele a
sciure de bois
S - estufa de
aserrin
<FIGURE>
10p110.gif (486x486)

SCOOP WHEEL (wind) (arc).
A vertical, cast-iron wheel with
wooden BLADES or
scoops that lift water from one level
to another.
Scoop wheels usually are driven by
WINDMILLS.
F - roue a godets
S - rueda de
cangilones
SCRUBBING
SCRUBBING (biocon).
[1] Removing unwanted gases from
BIOGAS or PRODUCER
GAS. [2] The process of removing an
undesirable, and
usually corrosive, component or components
from a COMBUSTIBLE
GAS mixture. This is done by
passing the mixture
upwards and counter to a stream of
liquid that is
capable of selectively ADSORBING the
undesirable
components. Gases can also be scrubbed
by
passing them
through iron filings.
F - epuration
S - proceso de
lavado
SHADING COEFFICIENT
SCUM (biocon). In
BIOGAS DIGESTION, a mixture of coarse,
fibrous material floating
on the surface of the SLURRY.
The accumulation of
scum may inhibit METHANE production.
F - ecume
S - nata espumosa
SCUM CONTROL DEVICE (biocon) (impl).
A mechanism, usually
some type of
STIRRING device, that is used to break up
the layer of SCUM
that rises to the surface in a BIOGAS
DIGESTER.
F - dispositif
pour le controle de l'ecume
S - aparato
controlador de la nata
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS (gen).
The law stating that
ENERGY FLOWS from a
higher CONCENTRATION to a lower
concentration.
F - seconde loi
de la thermodynamique
S - segunda ley
termodinamica
SEED (biocon).
(See: INOCULUM)
F - germe
S - semilla
SELECTIVE SURFACE (sol).
A specially adapted surface coating
for a COLLECTOR
that has high SOLAR RADIATION
ABSORPTANCE and low
THERMAL EMITTANCE. It is used on the
surface of ABSORBER
PLATES to increase collector
EFFICIENCY.
F - vitrage
selectif
S - superficie
selectiva
SELF-SUPPORTING TOWER (wind).
A TOWER, usually made of
steel, which
supports a WINDMILL without the use of GUY
WIRES.
F - pylone
autoporteur
S - torre
autoportante
SENSIBLE HEAT (heat).
That heat, which, when added or
subtracted, results
only in a temperature change (as
opposed to a chemical
or other reaction).
F - chaleur
sensible
S - calefaccion
termosensible
SENSIBLE HEAT STORAGE (heat).
A heat storage medium in
which the addition
or removal of heat results only in a
temperature change
(as opposed to a chemical or other
reaction).
The storage medium often consists of water or
gravel.
F - stockage de
chaleur sensible
S - almacenaje
termosensible
SHADING COEFFICIENT (sol) (meas).
A method for determining
reductions in solar
HEAT GAIN caused by certain kinds of
GLAZING.
It is determined by dividing the solar heat
gain through a
sheet of glazing under specific conditions
by the solar gain
through a single-color DOUBLE-GLAZING
under the same
conditions. The lower the number,
the greater the
reduction in solar heat gain.
F - coefficient
de vitrage
S - coeficiente
de sombra
SHEAR
SHEAR (wind).
Variations in horizontal WIND SPEED due to
the distance of the
wind from the ground. The higher
the wind is above
the ground, the faster it moves
because of the
reduced friction.
F - cisaillement
S - gradiente
transversal de la velocidad del viento
SHOT CURB (wind) (arc).
(See: LIVE CURB)
F - chemin de
roulement
S - reborde movil
SHROUD (wind) (arc) (hydr).
[1] A structure used to concentrate
or deflect a stream
of wind. [2] A deep rim
partially enclosing
the BUCKETS in OVERSHOT WATER WHEELS
or BREAST WHEELS.
F - [1] carenage;
[2] bache
S - refuerzo
SHROUDED WINDMILL (wind) (arc).
A WINDMILL with a funnel-like
structure around
the outside edge of the SWEPT AREA
that forces wind
from a larger area to pass through the
BLADES.
F - eolienne
carenee
S - molino de
viento reforzado
SHUTTERS (wind) (arc).
Pivoting slats that are used
instead of SAILCLOTH
in SPRING SAILS and PATENT SAILS.
F - volets
S - hojas
basculantes
SIEVE PLATE (alc). A
component of an ALCOHOL STILL
COLUMN.
It is one of a series of perforated plates
that
is used to promote
the contact of liquid with vapor in
the column.
F - plateau
perfore
S - placa
perforada
SILICON SOLAR CELL (sol).
A SOLAR CELL made with the
crystalline element
SILICON as part of its conductor.
F - cellule
solaire a la silicone
S - celula solar
de silicio
SILVICULTURAL BIOMASS (biocon).
BIOMASS from trees.
F - biomasse de
sylviculture
S - biomasa de
silvicultura
SINGLE-AXIS TRACKING COLLECTOR (sol).
A SOLAR COLLECTOR
that follows the
path of the sun on only one AXIS.
F - capteur a
poursuite du soleil autour d'un seul axe
S - colector de
seguimiento monoaxial
SINGLE SHUTTERED (wind) (arc).
A SAIL having SHUTTERS on
only one side of
the WHIP.
F - a obturation
simple
S - aspa de
monohoja
SMOCK MILL
SITE SELECTION (gen).
The process of locating the best
available site to
build or place a WlND MACHINE,
HYDROPOWER device,
or SOLAR POWER device.
F - choix du site
S - seleccion del
emplazamiento
SKY DOME (sol). The
sky above the horizon in all
directions, as seen
from a particular area.
F - dome du ciel
S - domo aereo
SKYLIGHT (sol). A
roof opening that is covered with
GLAZING and that
allows sunlight to enter a house or
room.
F - lucarne
S - tragaluz
SKYSCRAPERS (wind) (arc).
(See: AIR BRAKES)
F - freins a vent
S - rascacielos
SLOPE (hydr) (meas).
A CHANNEL FLOW calculation equal to
the number of feet
a surface "drops" or inclines
downward per 1,000
feet of horizontal distance; also
expressed in meters
of drop per kilometer.
F - pente
S - pendiente
SLUDGE (biocon).
Solid material that collects at the
bottom of a
DIGESTER.
F - boues
S - sedimentos
SLUDGE GAS (biocon).
An alternative name used for BIOGAS,
particularly when
the gas is produced by sewage.
F - gaz de
vidange
S - gas de lodo
SLUICE (hydr). A
manmade CHANNEL or waterway to conduct
water to a
HYDROPOWER device. It generally has one
or
more adjustable
gates to regulate the FLOW of water.
F - canal a
vannes
S - esclusa
SLUICEWAY (hydr).
(See: SLUICE)
F - chenal
d'ecluse
S - saetin
SLURRY (biocon). The
semisolid material in a BIOGAS
DIGESTER consisting
of BIOMASS mixed with water.
F - boue
S - fango
SMOCK MILL (wind) (arc).
The timber-framed counterpart to
the TOWER
MILL. The smock mill frame generally is
covered with
boarding to protect it from the weather.
F - moulin a
calotte pivotante
S - molino a la
holandesa
SMOKE CHAMBER
SMOKE CHAMBER (heat).
The section in a fireplace FLUE that
is directly above
the DAMPER.
F - conduite de
fumee
S - camara de
humo
SODIUM CARBONATE (biocon).
A BASE used to control pH
(POTENTIAL
HYDROGEN). It is useful in maintaining
the pH
balance in a BIOGAS
DIGESTER, and to a somewhat lesser
degree in ALCOHOL
STILLS.
F - carbonate de
sodium
S - carbonato de
sodio
SOLAR ABSORBER (sol).
A sheet of material, usually copper,
aluminum, or steel
that forms the surface of a SOLAR
COLLECTOR.
It collects and retains SOLAR RADIATION,
which is passed to
a HEAT TRANSFER MEDIUM.
F - absorbeur
solaire
S - absorbente
solar
SOLAR ABSORPTION (sol).
The absorption of SOLAR RADIATION
by a material.
F - absorption
solaire
S - absorcion solar
SOLAR ALTITUDE (sol).
The sun's angle above the horizon,
as measured in a
vertical plane.
F- hauteur du
soleil
S- altura solar
SOLAR ARCHITECTURE (sol).
(See: PASSIVE SOLAR DESIGN)
F - architecture
solaire
S - arquitectura
solar
SOLAR ARRAY (sol). A
group of SOLAR COLLECTORS or
PHOTOVOLTAIC
MODULES.
F - panneau
solaire
S - conjunto
solar
SOLAR AZIMUTH (sol).
The horizontal angle between the sun
and due south in
the northern hemisphere, or between the
sun and due north
in the southern hemisphere. (Syn:
bearing angle)
F - azimut du
soleil
S - azimut solar
SOLAR BATTERY (sol).
A BATTERY that is charged through
PHOTOVOLTAIC CELLS.
F - pile solaire
S - bateria solar
SOLAR CABINET DRYER (sol).
(See: SOLAR CROP DRYER)
F - chambre de
sechage solaire
S - secador solar
de gabinete
SOLAR CELL (sol).
(See: PHOTOVOLTAIC CELL)
F - cellule
solaire
S - celula solar
SOLAR DECLINATION
SOLAR COATING (sol).
FLAT BLACK PAINT or some other
ABSORPTIVE
substance that is applied to the ABSORBER
PLATE of a SOLAR
COLLECTOR to help it absorb, rather
than reflect,
sunlight.
F - couche
antireflet
S - revestimiento
solar
SOLAR COLLECTOR (sol).
A device that gathers and accumulates
SOLAR RADIATION to
produce heat. Nearly all solar
collectors have a
layer of GLAZING on top to trap heat
that has passed
into the collector. Beneath the glazing
is a solar ABSORBER
PLATE, which transfers heat to a
HEAT TRANSFER
MEDIUM. The medium may be air, water,
an
antifreeze
solution, or other substance(s).
F - capteur
solaire
S - colector de
radiacion solar
SOLAR COLLECTOR CONNECTIONS (sol).
Inlets and outlets
leading to and from
SOLAR COLLECTORS and connecting the
collectors with
related apparatus. In the case of water
tanks that run
water through collectors, there will be
an outlet near the
bottom of the tank and an inlet near
the top of the
tank. Likewise, there will be an inlet
near the bottom of
the collector and an outlet near the
top of the
collector.
F - raccordements
pour capteurs
S - conexiones
del colector solar
SOLAR COLLECTOR EFFICIENCY (sol) (meas).
The total SOLAR
RADIATION that is
incident on a COLLECTOR during a
specific time
period.
F - rendement
radiatif
S - rendimiento
del colector solar
SOLAR CONCENTRATOR (sol).
The part of a SOLAR COLLECTOR
that focuses
sunlight onto an ABSORBER surface.
F - concentrateur
solaire
S - concentrador
solar
SOLAR COOKER (sol).
A general term for the many types of
SOLAR-POWERED
cooking devices.
F - cuiseur
solaire
S - cocina por
calor solar
SOLAR COOLING (sol).
A SOLAR SYSTEM used to lower the
temperature in a
room or a device.
F -
refroidissement solaire
S - enfriamiento
solar
SOLAR CROP DRYER (sol).
An apparatus that uses SOLAR
RADIATION to dry
rice, grain, fruit, vegetables, or
other foods.
F - sechoir
solaire pour recoltes
S - secador solar
para alimentos
SOLAR CROP DRYER (sol).
An apparatus that uses SOLAR
RADIATION to dry
rice, grain, fruit, vegetables, or
other foods.
F - sechoir
solaire pour recoltes
S - secador solar
para alimentos
SOLAR DECLINATION (sol).
The angle of the sun north or
south of the
equatorial plane. It is plus if north
of
the plane, and
minus if south of the plane.
F - declinaison
solaire
S - declinacion
solar
SOLAR DISH
SOLAR DISH (sol).
(See: PARABOLIC DISH)
F - miroir
solaire
S - reflector
parabolico
SOLAR DISTILLATE (sol).
The product resulting from SOLAR
DISTILLATION.
F - distillat
solaire
S - destilado
solar
SOLAR DISTILLATION (sol).
A process in which SOLAR ENERGY
is trapped and used
to evaporate impure or salty water.
The water vapor
CONDENSES as distilled water that can be
used for drinking
or for other uses.
F - distillation
solaire
S - destilacion
solar
SOLAR DRYER (sol).
Any device that uses SOLAR RADIATION to
remove moisture
from a substance. (See also:
SOLAR CROP
DRYER)
F - sechoir
solaire
S - secador solar
SOLAR DRYING (sol).
(See: SOLAR DRYER)
F - sechage par
energie solaire
S - secado por
energia solar
SOLAR ELECTRICITY (sol).
Electricity that is produced from
SOLAR ENERGY
sources. (See also:
PHOTOVOLTAIC PROCESS;
PHOTOVOLTAIC CELL)
F - electricite
solaire
S - electricidad
solar
SOLAR ENERGY (sol).
The electromagnetic RADIATION generated
by the sun.
Solar energy may be converted to useful
forms of ENERGY
through the PHOTOVOLTAIC PROCESS, THERMAL
CONVERSION, or
through high temperature concentrators
and
COLLECTORS. Solar energy initially is
usually
captured in the
form of heat, and is therefore best used
for a variety of
heating purposes. This may be done
through the use of
SOLAR COLLECTORS and SOLAR COOKERS.
SOLAR RADIATION may
also be converted directly into
electrical energy
through the use of PHOTOVOLTAIC CELLS.
F - energie
solaire
S - energia solar
SOLAR EYEBALL (sol).
A type of SOLAR CONCENTRATING COLLECTOR
that uses a FRESNEL
LENS to focus SOLAR RADIATION
on a PHOTOVOLTAIC
CELL.
F - bulbe solaire
S - foco solar
SOLAR FURNACE (sol).
A SOLAR CONCENTRATOR used to produce
very
high
temperatures. Also
a solar device used to
obtain high
temperatures by focusing the sun's rays onto
a small receiver.
F - four solaire
S - horno solar
SOLAR IRRADIANCE
SOLAR GAIN (sol).
The part of a building's heat supply, or
an additional load
for cooling, that is provided by
SOLAR RADIATION
that strikes the building or passes into
it through windows.
it through windows.
F - apport
solaire
S - ganancia por
la energia solar
SOLAR GRAIN DRYER (sol).
(See: SOLAR CROP DRYER)
F - sechoir
solaire pour cereales
S - secador solar
de granos
SOLAR GREENHOUSE (sol).
Specific greenhouse designs that
take into account
basic principles of PASSIVE SOLAR
HEATING.
Increasingly, solar greenhouses are being
attached to
dwellings. Excess heat from the
greenhouse
passes into the
dwelling through air CONVECTION and
THERMAL CONDUCTANCE
from a mutual wall.
F - serre solaire
S - invernadero
solar
<FIGURE>
10p117.gif (486x486)
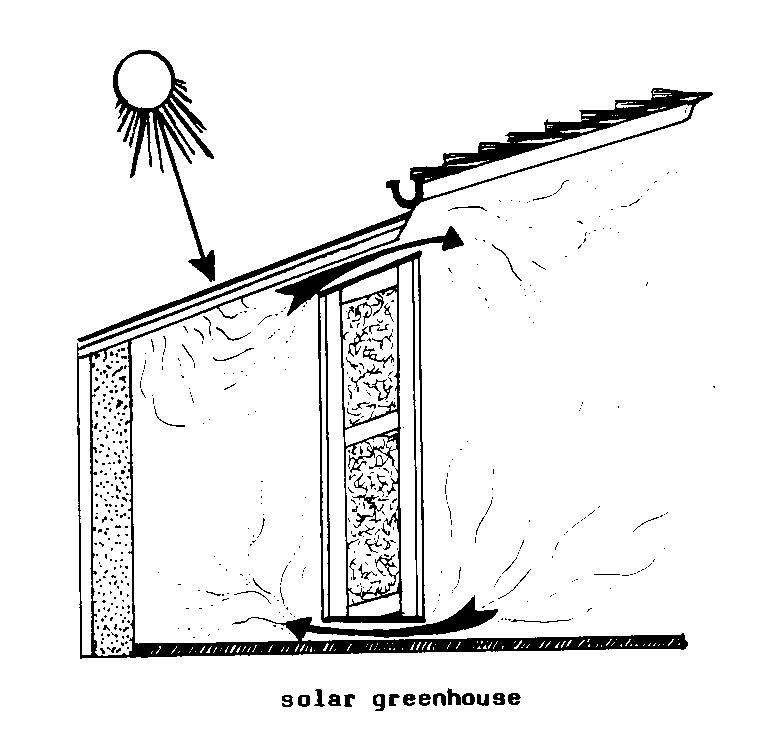
SOLAR HEATING (sol).
The use of a SOLAR SYSTEM to raise
the temperature in
a room or a device.
F - chauffage
solaire
S - calefaccion
solar
SOLAR IRRADIANCE (sol).
The total amount of SOLAR
RADIATION striking
a given area.
F - irradiation
solaire
S - irradiancia
solar
SOLAR OVER
SOLAR OVEN (sol). An
oven that relies on SOLAR RADIATION
as its source of
ENERGY.
F - four solaire
S - horno solar
SOLAR POND (sol). A
shallow body of salt water with a
black or dark
bottom. When incident SOLAR RADIATION
penetrates the
water, some of it is absorbed by the
water.
However, a large proportion of the radiation
reaches the bottom
of the pond. There it is absorbed,
heating the bottom
surface. The bottom surface in turn
heats the water
next to it, which then can be used as an
ENERGY source
through the use of HEAT EXCHANGERS. The
pond's salinity
should increase with its depth.
F - bassin
solaire
S - charca solar
SOLAR POSITION (sol).
The location of the sun in the sky
during the EQUINOXES,
based on the latitude of the
observer.
Solar position is determined by the value of
the SOLAR ALTITUDE
and the SOLAR AZIMUTH.
F - position du
soleil
S - posicion
solar
SOLAR POWER (sol).
The rate at which SOLAR ENERGY falls on
an area.
The area is usually given in terms of the
whole
Earth.
F - puissance
solaire
S - potencia
solar
SOLAR PUMP (sol). A
pump that operates on SOLAR ENERGY,
either by a
PHOTOVOLTAIC process or by a thermal system
in which a FLUID
heated by the sun drives a TURBINE or
piston that powers
the pump.
F - pompe solaire
S - bomba solar
SOLAR RADIATION (sol).
RADIANT ENERGY received from the
sun, from both
direct exposure and diffuse or reflected
sunlight.
F - rayonnement solaire
S - radiacion
solar
SOLAR REFLECTOR (sol).
A device that reflects SOLAR
RADIATION.
F - reflecteur
solaire
S - reflector
solar
SOLAR REFRIGERATION (sol).
A process in which SOLAR
RADIATION is used
to provide HEAT ENERGY to activate a
cooling process.
F - refrigeration
solaire
S - refrigeracion
solar
SOLAR SALT (sol).
SALT obtained by SOLAR DISTILLATION of
salt water.
F - sel solaire
S - sal solar
SOLAR SYSTEM
SOLAR SHOWER (sol).
A shower bath that uses a SOLAR WATER
HEATER to provide
hot water.
F - douche
solaire
S - ducha solar
SOLAR SITE SELECTOR (sol) (meas).
A circular transparency,
similar to a map,
that is used to determine solar positions
and calculate
shading.
F - dispositif de
selection de l'emplacement solaire
S - selector del
emplazamiento solar
SOLAR SPACE HEATER (sol).
A SOLAR HEATING system that
heats FLUID on a
black metal surface that is under
GLAZING.
The heated fluid may be circulated during
the
day and stored at
night.
F - appareil de
chauffage solaire individuel
S - calentador
espacial solar
SOLAR SPECTRUM (sol).
The total distribution of electromagnetic
RADIATION emitted
from the sun. It is usually
listed minus those
wavelengths that are absorbed by the
atmosphere.
On Earth, this amounts to about 420 trillion
KILOWATT HOURS of
SOLAR POWER annually.
F - spectre
solaire
S - espectro
solar
SOLAR STEAM COOKER (sol).
(See: INSULATED STEAM COOKER)
F - autoclave
solaire
S - horno de
vapor solar
SOLAR STILL (sol). A
device used for SOLAR DISTILLATION.
F - alambic
solaire
S - alambique
solar
<FIGURE>
10p119.gif (486x486)
SOLAR SYSTEM (sol).
Any heating, cooling, or POWER system
that uses ENERGY
generated by the sun.
F - systeme
solaire
S - sistema solar
SOLAR WATER HEATER
SOLAR WATER HEATER (sol).
A water heater that depends on
RADIANT ENERGY from
the sun as its source of power.
F - chauffage-eau
solaire
S - calentador de
agua solar
<FIGURE>
10p120.gif (437x437)
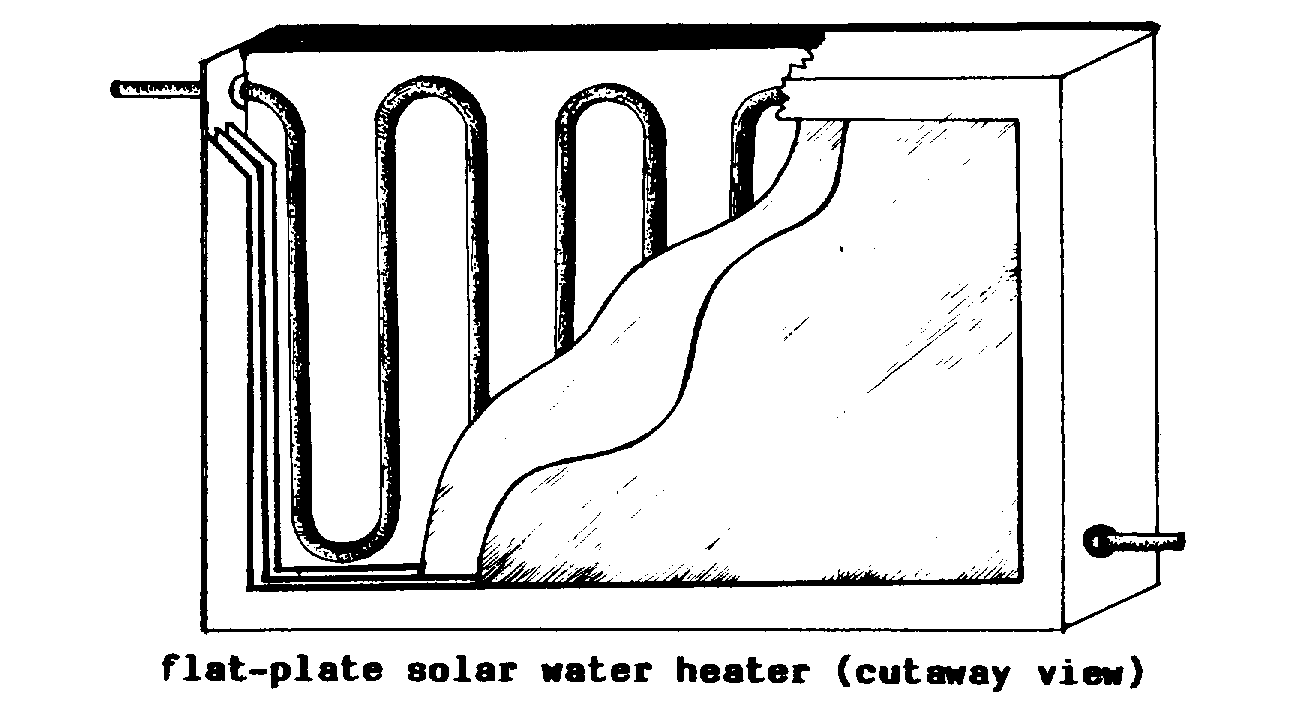
SOLIDITY (wind) (meas).
The ratio of the BLADE surface
area to the SWEPT
AREA of a ROTOR.
F - coefficient
de solidite
S - solidez
SOLIDS RETENTION TIME (biocon) (meas).
(See:
DETENTION
TIME)
F - temps de
retention des solides
S - periodo de
retencion de los solidos
SOLID WASTE (biocon).
Waste material in a solid state,
such as is found in
households, commercial activities,
municipal plants,
etc. Many solid wastes are useful in
BIOCONVERSION
processes.
F - dechets
solides
S - desperdicios
solidos
SOLUBILIZATION (biocon).
The first of three stages in the
ANAEROBIC DIGESTION
of ORGANIC MATTER, in which the complex
proteins,
CARBOHYDRATES, CELLULOSE, fats, and oils
are dissolved by
ENZYMES. This HYDROLYSIS transforms the
complex compounds
into simple amino ACIDS, simple
sugars, fatty
acids, and glycerol. The simple
compounds
are rendered into a
form that is dissolved easily and
can pass through
the cell walls of the acid-forming
BACTERIA to be
FERMENTED.
F -
solubilisation
S -
solubilizacion
SPARK ARRESTER (impl).
Screening, steel wool, or other
porous substance(s)
that is placed in the distribution
pipes from a BIOGAS
DIGESTER or PRODUCER GAS GENERATOR.
They prevent a
spark or flame from passing back up the
pipe and causing an
explosion.
F -
pare-etincelle
S - parachispas
SQUARE WAVE
SPARS (wind). The
frames extending from the WIND SHAFT of
a WIND MACHINE to
support the SAILS.
F - bras [1]
S - [1]
largueros; [2] varillaje
SPECIFIC GRAVITY (gen).
The ratio of the weight of a
given volume of a
substance to an equal volume of air or
water at a given
temperature and pressure. The specific
gravity, which may
be measured by a HYDROMETER, indicates
the CONCENTRATION
of a substance in a solution.
(See also:
PROOF).
F - densite
S - gravedad
especifica
SPECIFIC SPEED (hydr) (meas).
The speed at which a given
type of RUNNER in a
TURBINE would operate if it were
reduced
proportionately in size to produce one HORSE-POWER
under a one-foot
(30.48 centimeter) HEAD. This
speed or velocity
is expressed in revolutions per
minute.
It is used to determine the proper type of
turbine to install
at a HYDROELECTRIC POWER PLANT under
given conditions.
F - vitesse
specifique
S - velocidad
especifica
SPENT MASH (alc).
The semisolid MASH, without the ALCOHOL,
following
FERMENTATION and DISTILLATION.
F - residu de
distillation
S - vinazas
SPENT SLURRY (biocon).
(See: EFFLUENT)
F - boue epuisee
S - fango usado
SPILLWAY (hydr). A
passage over or around a CHANNEL or DAM
through which
excess water may escape.
F - deversoir
S - vertedero
SPILLWAY APRON (hydr).
(See: SPILLWAY)
F - chenal du
deversoir
S - paramento del
vertedero
SPILLWAY CHANNEL (hydr).
(See: SPILLWAY)
F - canal du
deversoir
S - canal
vertedor
SPRING SAIL (wind) (arc).
A WINDMILL BLADE fitted with
SHUTTERS that are
controlled by springs.
F - aile a
ressorts
S - aspa de
resorte
SQUARE WAVE (wind).
A type of ALTERNATING CURRENT (ac),
produced by
low-cost, solid-state INVERTERS, which may
be used for most,
but not all, ac appliances.
F - onde
rectangulaire
S - onda cuadrada
S-ROTOR
S-ROTOR (wind).
see: SAVONIUS ROTOR)
F - rotor de
Savonius
S - rotor S
STACK (constr). A
CHIMNEY or other passageway designed to
vent smoke from a
stove, oven, furnace, etc.
F - corps de
cheminee
S - canon
STACK EFFECT (heat).
The impulse of a heated gas to rise
through a vertical
passage, such as a CHIMNEY.
F - effet de
cheminee
S - efecto de
humero
STACK GAS (heat).
Gases resulting from combustion, which
pass up a CHIMNEY.
F - gaz de
cheminee
S - gases de la
chimenea
STAGNATION (sol).
The condition that may be reached in a
SOLAR COLLECTOR
when the sun is shining on the device
and no FLUID is
flowing through it. The resulting high
temperatures may
damage the COLLECTOR.
F - stagnation
S - estancacion
STARCH (alc) (chem).
A white, tasteless, solid CARBOHYDRATE
([C.sub.6][H.sub.10][O.sub.5]).
Starch is a major component of many
agricultural crops,
such as potatoes, grains, etc., that
are used to produce
GLUCOSE.
F - amidon
S - almidon
START-UP (biocon).
The process of adding INOCULUM to a
BIOGAS DIGESTER so
that the digester will begin to
function.
F - mise en
marche
S - puesta en
marcha
START-UP SPEED (wind) (meas).
The WIND VELOCITY at which a
WIND MACHINE begins
to rotate.
F - vitesse de
mise en marche
S - velocidad de
puesta en marcha
STATIC HEAD (hydr).
The vertical height from the surface
of a body of water
to the water outlet of the DISCHARGE
PIPE of a TURBINE.
F - hauteur
d'elevation
S - altura de
elevacion
STATIONARY PEDAL POWER UNIT (gen).
(See: PEDAL POWER)
F - appareil
stationnaire d'entrainement par pedales
S - unidad de
rendimiento del pedal inmovil
STEAM ENGINE (geo) (auto).
An engine in which the mechanical
force of steam is
used as a motive POWER to drive
machinery, etc.
F - moteur A
vapeur
S - motor de
vapor de agua
STOCK
STEAM GAS (geo).
Superheated steam that is used as an
ENERGY source.
Steam gas is usually obtained from
GEOTHERMAL sources.
F - vapeur
surchauffee
S - gas de agua
STEAM TURBINE (gen) (geo).
A TURBINE that is driven by
expanding steam or
gas rather then by the velocity or
weight of water.
F - turbine a
vapeur
S - turbina de
vapor
STILL (gen) (alc).
[1] An apparatus for DISTILLATION that
consists primarily
of a closed vessel in which the solution
to be distilled is
heated. It also includes mechanisms
to condense the
vapor that is produced. [2] An
ALCOHOL
distillation unit that consists of a container
to heat MASH, a
DISTILLATION COLUMN to separate the
water from the
alcohol, and a CONDENSER to convert
ALCOHOL VAPORS into
liquid.
F - alambic
S - alambique
STILLAGE (alc). A
mixture of non-FERMENTABLE SOLID WASTES
and water that
remains in a STILL after the ALCOHOL is
removed by
DISTILLATION. Stillage may be used as
an
animal feed.
F - residus de
distillation non-fermentable
S - residuos
STILL CAP (alc).
(See: BUBBLE CAP)
F - calotte de
barbotage
S - casquete de
alambique
STILL COLUMN(alc) (impl).
A component of an ALCOHOL STILL
that is used to
separate ALCOHOL from the MASH and
water.
The still column consists of SIEVE PLATES,
BUBBLE
CAPS, and a
DOWNCOMER.
F - colonne de
distillation
S - columna de
alambique
STIRLING ENGINE (auto).
An external combustion engine in
which air is
alternately heated and cooled to drive a
piston up and
down. Hydrogen is used instead of air
in
some newer
models. The Stirling engine may in some
cases
be nonpolluting and
more efficient than the internal
combustion engine.
F - moteur de
Stirling
S - motor
Stirling
STIRRING (biocon).
Agitating or mixing the SLURRY in a
BIOGAS
DIGESTER. Stirring helps prevent SCUM
buildup and
promotes METHANE
production.
F - vaguage
S - agitacion
STOCK (wind) (arc).
[1] A bar that is used to support a
WINDMILL SAIL.
[2] A tapered SPAR that passes through
the POLL END of a
windmill, supporting a pair of sails.
(Syn:
sailstock)
F - fut
S - barra
STORAGE
STORAGE (gen).
(See: ENERGY STORAGE)
F - stockage
S - almacenado
STORAGE CAPACITY (gen).
The total amount of ENERGY that a
system is capable
of holding for use at a later time.
(See also:
ENERGY STORAGE)
F - capacite de
stockage
S - capacidad de
almacenado
STRATIFICATION (sol).
In SOLAR HEATING, temperature variations
that occur in a
substance or an area. The highest
temperatures are
found higher up and cooler temperatures
are found lower
down.
F -
stratification
S -
estratificacion
STRIKING GEAR (wind) (arc).
The mechanism used with PATENT
SAILS to apply
pressure to SHUTTERS. It consists of a
striking rod that
passes through the length of the WIND
SHAFT.
The rod is operated by an endless chain upon
which weights are
hung. The number of weights is
determined
by the force of the
wind.
F - embrayage
S - engranaje de
contacto
STRIPPING COLUMN (alc).
The section of the STILL COLUMN in
which the ALCOHOL
CONCENTRATION in the DISTILLATE is
increased and the
starting solution is decreased. (Syn:
beer column)
F - colonne a
desessencier
S - columna de
destilacion
SUBMERGED WEIR (hydr).
An underwater obstruction that
diverts water into
a CHANNEL.
F - barrage
immerge
S - vertedero
sumergido
SUBSTRATE (bio) (biocon).
[1] The particular FEEDSTOCK
component that is
used by bacteria to promote their
growth and
metabolism. The component often is one
particular
compound. [2] ORGANIC MATTER that is
used to
generate METHANE in
a BIOGAS DIGESTER. (See:
SLURRY)
F - substrat
S - subestrato
SUCROSE (alc) (chem).
A FERMENTABLE SUGAR ([C.sub.12][H.sub.22][O.sub.11]) that
is commonly found
in nature.
F - sucrose
S - sucrosa
SUCTION ANEMOMETER (wind) (meas).
A device that measures
WIND VELOCITY
according to the degree of exhaust caused
when the wind is
blown through or across a tube.
F - anemometre a
aspiration
S - anemometro de
succion
SUN BASKET
SULFURIC ACID (alc) (chem).
A strong ACID that is used to
increase the
acidity, and thus lower the pH (POTENTIAL
HYDROGEN), in an
ALCOHOL STILL.
F - acide
sulfurique
S - acido
sulfurico
SUN ANGLE CALCULATOR (sol) (meas).
A set of transparent
curves and overlays
that tells where the sun is in the
sky and that gives
other SOLAR ALTITUDES. (See:
SOLAR
SITE SELECTOR)
F - calculateur
d'angle solaire
S - calculador
del angulo solar
SUN BASKET (sol). A
SOLAR COOKER in the shape of a deep
PARABOLA.
This cooker may be a woven basket lined with
a
reflective
material.
F - panier
solaire
S - cesto solar
<FIGURE>
10p125.gif (486x486)
SUN EFFECT
SUN EFFECT (sol) (meas).
The amount of heat from the sun
that tends to heat
an enclosed space.
F - effet solaire
S - efecto solar
SUN-TEMPERING (sol).
A heating system that involves a
significant daytime
SOLAR GAIN and an effective
distribution
system, but which generally lacks a STORAGE
function.
F - dispositif de
repartition de l'energie solaire
S - atemperacion
solar
SUN-TRACKING DEVICE (sol) (impl).
A device attached to a
SOLAR COLLECTOR
that automatically turns the face of the
collector towards
the sun.
F - dispositif de
poursuite du soleil
S - dispositivo
de seguimiento solar
SUPERNATANT (biocon).
The liquid portion of the SLURRY
that floats above
the SLUDGE in a BIOGAS DIGESTER.
F - fraction
surnageante
S - sobrenatatil
SWASH PLATE (wind).
A disk set obliquely on a rotating
AXIS.
It acts as a CAM to convert rotational
movement
into up-and-down
movement.
F - plateau
oscillant
S - plato oscilante
SWEEP (wind) (arc).
(See: SAIL)
F - balayage
S - barrer
SWEPT AREA (wind) (meas).
The area in a plane that is
perpendicular to
the wind through which a WINDMILL's
BLADES pass.
The area is defined by the circumference of
the circle formed
by the rotating blades, and is one
factor in
determining the amount of WIND POWER available
from the wind.
F - zone balayee
S - area barrida
SWING POT (wind) (arc).
A pivoting bearing that is
sometimes used to
support the WIND SHAFT of a WINDMILL.
F - palier
pivotant
S - cojinete
pivotante
SWORD POINT (wind) (arc).
The amount that a SAILCLOTH is
rolled up or REEFED
to reduce its exposure to the wind.
This term refers to
the pointed end on a reefed SAIL.
(See also:
REEFING)
F - prise de ris
S - punto de
recogida
SYNCHRONOUS INVERTER (elec) (wind).
An electronic device
that can be used
with a WIND GENERATOR, to convert
DIRECT CURRENT (dc)
to ALTERNATING CURRENT (ac), but
which must be
powered by another ac source.
F - inverseur
synchrone
S - convertidor
sincronico
T
TABOR SURFACE (sol).
A black nickel SELECTIVE SURFACE
coating that
typically absorbs 90 percent of the incoming
SOLAR RADIATION but
which radiates only about 10
percent as much
radiation as would be emitted by a coat
of FLAT BLACK
PAINT.
F - surface de
tabor
S - superficie
tabor
TAIL (wind). A flat
piece of sheet metal that is attached
to the extension of
the WINDSHAFT of a WINDMILL. The
plane of the tail
is normally perpendicular to the wind
so the tail may
intercept changes in wind direction and
turn the ROTOR
around to face the wind. (Syn:
vane)
F - empennage
S - punta del
aspa
TAIL POLE (wind) (arc).
The projecting SPAR used to turn a
WINDMILL that is
not equipped with automatic WINDING
gear.
F - barre de
queue
S - saliente del
aspa
TAILRACE (hydr). The
discharging CHANNEL of a HYDROPOWER
system.
It is that section of a RACE that is downstream
of a hydropower
device.
F - bief d'aval
S - canal de
descarga
TAILWATER (hydr).
Water passing back into a discharging
CHANNEL after being
applied to a HYDROPOWER device.
F - eau d'aval
S - agua de
descarga
TAILWATER LEVEL (hydr) (meas).
The depth of the TAILWATER
as measured at a
reference point on its surface.
F - niveau de
l'eau d'aval
S - nivel de la
descarga
TAILWINDED (wind).
The condition when a WINDMILL is caught
by a sudden change
in wind direction, which exerts
pressure on the
wrong side of the SAIL assembly.
F - a vent
arriere
S - con viento de
cola
THERMAL (gen).
Having to do with the use or production of
heat.
Also any reaction caused by heat.
F - thermique
S - termico
THERMAL ADMITTANCE (heat) (meas).
The total amount of BTUs
that a square foot
(929 square centimenters) of a surface
will admit in one
hour.
F - admittance
thermique
S - admision
termica
THERMAL COLLECTOR
THERMAL COLLECTOR (sol).
(See: COLLECTOR)
F - capteur
thermique
S - colector
termico
THERMAL CONDUCTANCE (heat) (meas).
The amount of heat that
will pass through a
given amount of material in a given
amount of time, and
with a unit temperature difference
maintained between
the surfaces of the material under
uniform and steady
conditions.
F - conductance
thermique
S -
termoconductancia
THERMAL CONDUCTION (heat).
Heat transfer by direct contact
from one substance
to another of a lower temperature.
F - transmission
de chaleur
S -
termotransmision
THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY (heat) (meas).
The ability of a
material to conduct
heat. It is commonly measured in
units of THERMAL
CONDUCTANCE.
F - conductivite
thermique
S -
termoconductibilidad
THERMAL EFFICIENCY (heat) (meas).
A percentage that indicates
the available heat
that is converted to useful
purposes.
Thermal efficiency is used to evaluate
wood-conserving
stoves and numerous
other devices.
F - rendement
thermique
S - termorendimiento
THERMAL ENERGY (heat).
ENERGY from heat.
F - energie
thermique
S - termoenergia
THERMAL LAG (meas).
The time required for the temperature
of an area to reach
that of an adjacent area, either by
heating or
cooling. For example, the time required
for
indoor air
temperature to reach the cooler outside air
temperature when
there is no additional heat added to
the house; or the
time required for the inside surface
of a TROMBE WALL to
reach the temperature of the outside
surface, which is
exposed to the sun.
F - retard
thermique
S - retardo
termico
THERMAL MASS (gen).
Material or mass of sufficient size
and density to
store heat. Thermal mass walls are
often
used in buildings
that use PASSIVE SOLAR HEATING
techniques and
NIGHT SKY RADIATION. (See also:
TROMBE
WALL)
F - masse
thermique
S - masa termica
THERMAL POWER (gen).
Any type of ENERGY generated or
developed through
the use of HEAT ENERGY.
F - puissance
thermique
S - termopotencia
TIDAL POWER
THERMAL WINDS (wind).
Winds that are caused by the heating
of the ground by
SOLAR RADIATION.
F - vents
thermiques
S - vientos
termicos
THERMOCOUPLE (meas) (impl).
A device used to measure temperature.
It is based on the
principle that an electrical
current is produced
when two dissimilar wires are
joined together and
the junction is heated. Thermocouples
are often used to
measure temperatures at different
levels in BIOGAS
DIGESTERS, WOOD STOVES, KILNS,
or other devices
where use of a conventional thermometer
would be difficult.
F - thermocouple
S - termopar
THERMOPHILLIC BACTERIA (biocon).
BACTERIA that grow best
in a temperature
range between 122-131 [degrees] F (50-55 [degrees] C).
F - bacteries
thermophiles
S - bacteria
termofilica
THERMOSYPHON (sol).
A CLOSED LOOP SYSTEM in which water
automatically
circulates between a SOLAR COLLECTOR and a
water storage tank
above it. A solar collector based on
the THERMOSYPHON
PRINCIPLE uses the natural difference
in density between
the warmer and cooler portions of a
liquid.
F - thermosiphon
S - termosifon
THERMOSYPHON CIRCULATION (sol).
(See: THERMOSYPHON
PRINCIPLE)
F - circulation de
thermosiphon
S - circulacion
por termosifon
THERMOSYPHON EFFECT (sol).
(See: THERMOSYPHON)
F - effet
thermosiphon
S - efecto de
termosifon
THERMOSYPHON PRINCIPLE (gen) (sol).
The tendency of heated
liquids to
rise. In a SOLAR WATER HEATER, this
principle
is used to lift
water from a SOLAR COLLECTOR to a storage
tank above it
without the use of a pump.
F - principe du
thermosiphon
S - principio de
termosifon
THIN STILLAGE (biocon).
The water soluble fraction of
FERMENTED MASH plus
the mash water.
F - residu dilue
de distillation
S - residuos
liquidos
TIDAL ENERGY (ocean).
The KINETIC ENERGY existing in the
tides by virtue of
the moving mass of water.
F - energie des
marees
S - energia
mareal
TIDAL POWER (ocean).
Mechanical POWER generated by the
rise and fall of
ocean tides, which may be converted
into electricity.
F - puissance
maremotrice
S - fuerza mareal
TILT ANGLE
TILT ANGLE (sol).
The angle at which a SOLAR COLLECTOR is
tilted upward from
the horizon for maximum solar exposure
and maximum heat
collection.
F - angle
d'inclination
S - angulo de
inclinacion
TIME LAG (sol) (meas).
(See: THERMAL LAG)
F - retard
S - tiempo de
retardo
TIP SPEED (wind) (meas).
The speed of the outer end or tip
of a BLADE of a
WINDMILL ROTOR. This speed may be
faster
than the rotation
rate of the WIND SHAFT, and may be
faster or slower
than the actual WIND SPEED.
F - vitesse
peripherique
S - velocidad de
giro de las aspas
TIP SPEED RATIO (wind) (meas).
The quotient of the TIP
SPEED and the
actual WIND SPEED.
F - quotient de
vitesse peripherique
S - relacion de
las velocidades de giro
TORQUE (gen). Any
force that acts to produce rotation.
The
measured ability of
a rotating part, such as a gear or
shaft.
F - couple
S - par
TOTAL ENERGY HOUSE (gen).
A house that is heated, cooled,
and
receives its cooking and lighting POWER,
completely
from ALTERNATIVE
ENERGY SOURCES.
F - maison a
energie integrale
S - casa
energetica total
TOTAL SOLIDS (biocon) (meas).
The proportion in weight of
solids in a sample
of SLURRY or other EFFLUENT (e.g.
MASH).
F - fraction
solide
S - solidos
totales
TOWER (wind). The
main supporting structure of a WIND
MACHINE.
Towers are usually made of wood or steel,
and
are suitably braced
to withstand the stress to which
they are subjected.
F - pylone
S - torre
TOWER MILL (wind) (arc).
A WINDMILL made of masonry or
brickwork, and
usually fitted with a REVOLVING CAP.
F - eolienne sur
pylone
S - molino de
torre
TOXIN (bio) (biocon).
A material that inhibits the growth
and metabolism of
or kills micro-organisms, often by
interfering with
the normal chemical or biochemical
processes.
A toxin may cause a BIOGAS DIGESTER to stop
producing gas.
F - toxine
S - toxina
TREADLE POWER
TRACKED PHOTOVOLTAIC ARRAY (sol).
A PHOTOVOLTAIC ARRAY
that follows the
path of the sun across the sky.
F - dispositif
photovoltaique a poursuite solaire
S - conjunto
fotovoltaico de seguimiento
TRACKING (sol).
Referring to adjustments that cause a
SOLAR COOKER or a
SOLAR COLLECTOR to "track" or follow
the sun's path across
the sky. Tracking is done either
automatically or
manually.
F - poursuite du
soleil
S - seguimiento
TRACKING CONTROL (sol) (impl).
(See: AUTOMATIC TRACKING)
F - controle de
la poursuite
S - control del
seguimiento
TRAILING EDGE (wind).
The edge of a WINDMILL BLADE that
lies on the side
opposite the direction of rotation.
F - arete arriere
S - borde
posterior
TRANSDUCER (gen). A
device that converts ENERGY from one
form into another
(e.g., PHOTOVOLTAIC CELL).
F - transducteur
S - transductor
TRANSFER MEDIUM (sol).
A substance that carries heat From
a SOLAR COLLECTOR
to a storage area or from a storage
area to be warmed
in a collector. Transfer mediums are
usually either air,
water, or antifreeze solutions.
F - agent de
transfert
S - medio de
transferencia
TRANSMITTANCE (sol) (meas).
The ratio of the RADIANT
ENERGY transmitted
through a substance to the total
radiant energy
falling on its surface. Transmittance
is
always affected by
the thickness and composition of the
substance, as well
as by the INCIDENT ANGLE.
F - facteur de
transmission
S - transmision
TRASH RACK (hydr). A
protective "screen" made of vertical
bars that catches
leaves, grass, and debris, keeping
clear the intake of a HYDROPOWER device.
F - grille
pare-bois
S - parrilla
colectora
TREADLE MECHANISM (gen).
(See: TREADLE POWER)
F - mecanisme a
pedale
S - mecanismo de
pedal
TREADLE POWER (gen).
A use of foot POWER in which an
up-and-down motion
of the foot on a pedal produces a
rotating motion on
a machine.
F - puissance de
pedale
S - energia
producida por pedal
TREATED EFFLUENT
TREATED EFFLUENT (biocon).
Discharge from a BIOGAS DIGESTER
that has been
rendered harmless by reducing the
number of PATHOGENS
in it. The treatment often consists
of either drying or
COMPOSTING the EFFLUENT.
F - effluent
traite
S - efluente
tratado
TROMBE WALL (constr) (heat) (sol).
A masonry wall located
directly inside
windows that face the equator. The wall
functions
simultaneously as a structural element of the
building and as a
SOLAR COLLECTOR and HEAT STORAGE
unit.
(See also:
THERMAL MASS)
F - mur de trombe
S - pared de
trombe
<FIGURE>
10p132.gif (587x587)
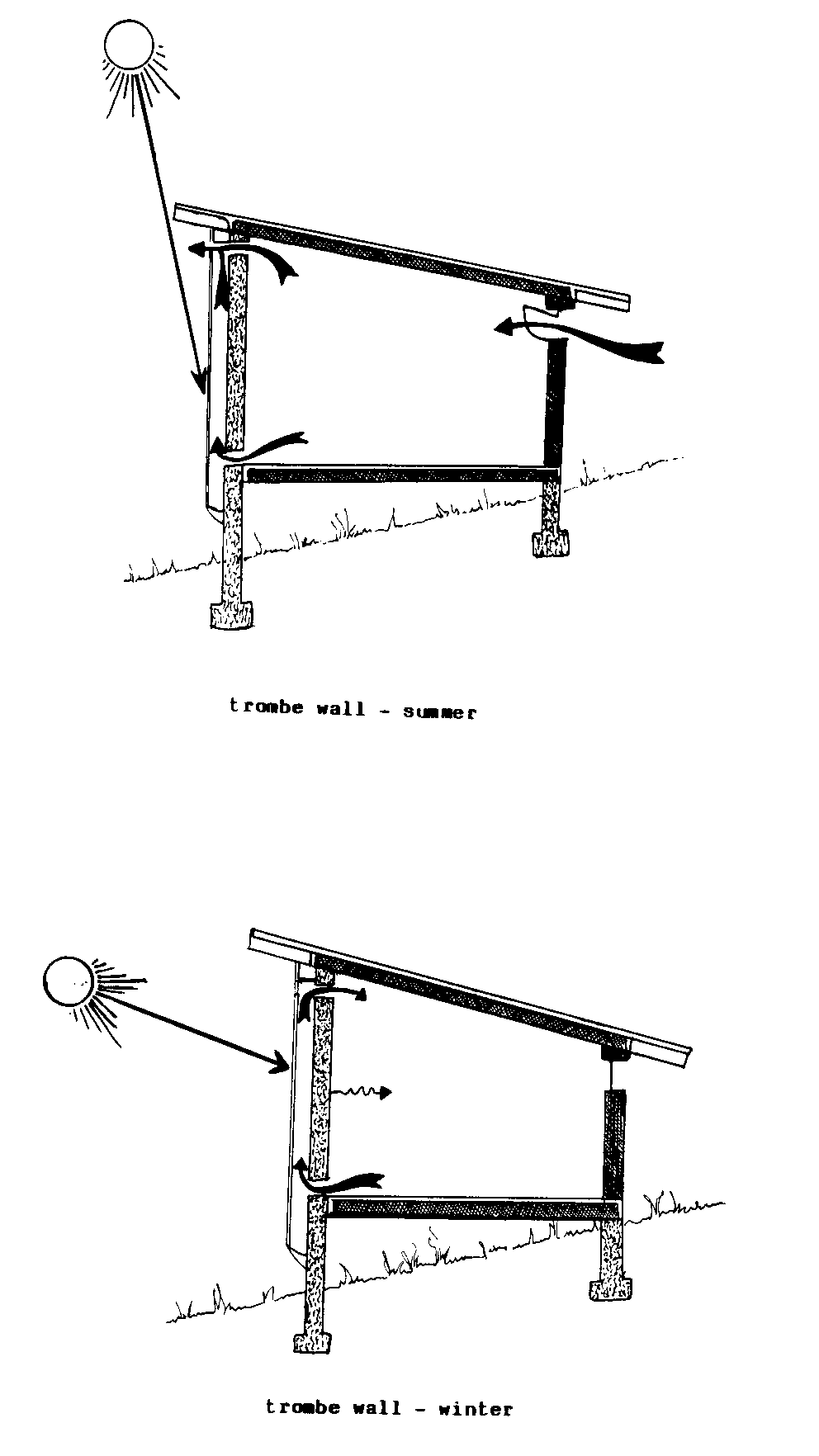
TRUNION (impl) (wind).
A pin or pivot that is mounted on
BEARINGS to rotate
or turn something. It usually is used
as a WINDMILL
component. (See also:
TURNTABLE)
F - tourillon
S - munon
TURBULENCE
TUBE-IN-PLATE ABSORBER (sol).
A metal ABSORBER PLATE with
passages through
which HEAT TRANSFER FLUID flows.
F - absorbeur a
tubes internes
S - absorbedor
con placa de tubos
TUBE-TYPE COLLECTOR (sol).
A COLLECTOR in which the
TRANSFER MEDIUM
FLOWS through metal tubes fastened to an
ABSORBER PLATE.
F - capteur a
tubes solidaires
S - colector con
tubos
TURBINE (gen). A
device that converts the ENERGY in a
stream of FLUID
into mechanical energy. By passing the
stream through a
system of fixed and/or moving BLADES, a
drive shaft is
rotated.
F - turbine
S - turbina
TURBINE WHEEL (hydr).
The part of a WATER TURBINE that is
attached to a drive
shaft, and which holds the BLADES or
CUPS that cause the
wheel to rotate when struck by a
stream of steam or
water. The wheel rotates the shaft to
produce mechanical
or electrical POWER. (Syn:
RUNNER)
F - roue de
turbine
S - rueda turbina
TURBULENCE (wind).
Irregular motion and GUSTS in the WIND
SPEED.
(See also:
MECHANICAL TURBULENCE)
F - turbulence
S - turbulencia
TURGO IMPULSE TURBINE
TURGO IMPULSE TURBINE (hydr).
An improved version of the
PELTON WHEEL in
which the JET is set at an angle to the
face of the
RUNNER. Water strikes the front of the
BUCKETS and
discharges at the opposite side.
F - turbine a
impulsion turgo
S - turbina de
impulsion turgo
<FIGURE>
10p134.gif (437x540)
TURNAROUND EFFICIENCY (gen) (meas).
The resulting
EFFICIENCY when
ENERGY is converted from one form to
another and then
changed back again into its original
form or state.
F - rendement
aller-retour
S - eficiencia
resultante
TURNTABLE (wind). A
rotating platform on which the ROTOR,
ROTOR SHAFT, and
TAIL of a WINDMILL may move to orient
the BLADES or SAILS
into the wind.
F - plaque
tournante
S - plataforma
giratoria
U
ULTRA-VIOLET RADIATION (sol).
Electromagnetic RADIATION,
usually from the
sun, that consists of wavelengths that
are shorter than
the violet end of the visible spectrum.
F - rayons
ultra-violet
S - radiacion
ultravioleta
UNDERSHOT WATER WHEEL (hydr).
A WATER WHEEL driven by
water that strikes
the underside of the wheel.
F - roue en
dessous
S - rueda
hidraulica de admision inferior
<FIGURE>
10p135.gif (353x486)
UNDIGESTED SOLIDS (biocon).
Heterogenous BIOMASS, contained
in either the
SLURRY or EFFLUENT, which has not
DECOMPOSED in a
BIOGAS DIGESTER.
F - solides
non-digeres
S - solidos sin
digerir
UNGLAZED COLLECTOR (sol).
A COLLECTOR without a cover.
F - capteur
non-vitre
S - colector no
vidriado
UPDRAFT (prod) (gen).
[1] Referring to a PRODUCER GAS
GENERATOR in which
the air-gas mixture flows upward to
the engine.
[2] Any cooking or heating device (e.g., a
KILN) in which air
for CONVECTION or combustion flows
upward through the
device.
F - tirage vers
le haut
S - corriente
aerea ascendente
UPLONG
UPLONG (wind) (arc).
A longitudinal bar in the BACKSTAY of
a SAIL.
F - barre
longitudinale
S - varilla
longitudinal
UPWIND (wind). [1]
On the same side as the direction from
which the wind is
blowing (i.e. , in the path of the
oncoming
wind). [2] A type of WINDMILL in which
the
ROTOR remains
between the oncoming wind and the TOWER.
F - vent de proue
S - viento
contrario
<FIGURE>
10p136.gif (353x353)
USED OIL (heat).
Automotive or other lubrication oil,
which is "used
up" or no longer useful for its original
purpose.
If mixed with water at a ratio of five to
one,
and then dripped
onto a heated metal sheet, used oil
will burst into
flames. This makes it useful as a fuel.
(Syn:
waste oil)
F - huile epuisee
S - aceite usado
U-VALUE
USEFUL ENERGY GAIN (sol).
The ENERGY absorbed by a SOLAR
COLLECTOR that is
not lost to the surrounding atmosphere
and which may be
used for space or water heating.
F - gain
energetique utile
S - ganancia de
energia util
USEFUL SOLAR HEAT (sol).
Heat delivered by a SOLAR COLLECTOR
that can be applied
for cooking, heating, or
other purposes.
F - chaleur
solaire utile
S - calor solar
util
USEFUL WATER CAPACITY (hydr) (meas).
The volume of water
that a reservoir
can hold and usefully exploit, and
which lies between the
lowest and highest levels normally
contained in the
reservoir.
F - capacite
utile en eau
S - capacidad
aprovechable de agua
U-VALUE (heat) (meas).
The amount of heat that FLOWS in or
out of a substance
under constant conditions, in one
hour, when there is a one degree difference
in temperature
between the air
inside and outside the building.
U-value is the
inverse of RESISTANCE-VALUE.
F - valeur U
S - valor U
V
VACUUM DISTILLATION (gen).
DISTILLATION under reduced
pressure.
This lowers the boiling point of the
distilled
material so that it
will not crack or decompose.
F - distillation
sous vide
S -
vacuodestilacion
VALVE ASSEMBLY (gen).
The assembled parts of a valve.
F - garniture de
soupape
S - montaje de
valvula
VANE [1] (hydr) (See:
GUIDE VANE); [2] (wind) (See:
TAIL)
F - aube
S - aspa
VAPOR LOCK (auto). A
blockage in a fuel line that is
caused when the
fuel vaporizes.
F - tampon de
vapeur
S - obstruccion
por vapor
VAPOR PRESSURE (chem) (meas).
The pressure of a vapor
while in contact
with its solid or liquid form. This is
also referred to as
saturated vapor pressure. The
pressure rises with
any increase in temperature.
F - tension de
vapeur
S - presion del
vapor
VERTICAL-AXIS WATER WHEEL (hydr).
A WATER WHEEL that
drives a vertical
axis instead of the more common
horizontal axis
F - roue
hydraulique a axe vertical
S - rueda
hidraulica de eje vertical
VERTICAL-AXIS WIND MACHINE (wind).
A WIND MACHINE in which
the WINDSHAFT is on
a vertical axis. This type of device
may accept wind
from any direction. (See also:
DARRIEUS
ROTOR; SAVONIUS
ROTOR)
F - eolienne axe
vertical
S - generador
eolico de eje vertical
VIOLET CELL (sol). A
type of SILICON SOLAR CELL that is
more effective than
conventional PHOTOVOLTAIC CELLS in
converting sunlight
to electricity from the violet and
ULTRA-VIOLET range
of the light spectrum.
F - cellule
violette
S - celula
violeta
VISCOSITY (chem).
The resistance to FLOW or change of
shape due to
molecular cohesion and internal friction in
FLUIDS.
Viscosity varies inversely with temperature.
F - viscosite
S - viscosidad
VOLATILE ACIDS
VOLATILE (gen) (refrig).
[1] Easily burned, unstable, or
explosive.
[2] Liquids that are readily evaporated at a
relatively low
temperature.
F - volatile
S - volatil
VOLATILE ACIDS (biocon).
Fatty ACIDS of a low molecular
weight.
These acids are very SOLUBLE.
F - acides
volatiles
S - acidos
volatiles
W - X
WASTE CONVERSION TO ENERGY (biocon).
(See:
BIOCONVERSION)
F - conversion
des dechets en energie
S - conversion
energetica de desperdicios
WASTE HEAT (heat).
Heat that is left after useful ENERGY
generation.
F - chaleur
perdue [1]
S - calor perdido
WATER-AIR HEAT EXCHANGER (heat).
A HEAT EXCHANGER in which
FLUIDS may either
be heated or cooled by water or air.
F - echangeur de
chaleur eau/air
S -
termopermutador de agua-aire
WATER BED (sol).
Shallow plastic bags that are filled with
water and placed on
roofs of homes or buildings. In
cooler climates,
the bags collect SOLAR ENERGY during
the day, and
radiate heat to the building during the day
and radiate this
heat to the sky at night, thus cooling
the building.
In warmer climates, panels are placed over
the bags during the
day and removed at night so the bags
can draw off heat
from the building and keep it cool.
F - lit d'eau
S - lecho de agua
WATER CHUTE (hydr).
A steep CHANNEL by which water
descends in
force. Water chutes are used to create
or
increase the HEAD
for a HYDROPOWER system.
F - chute d'eau
S - caida de agua
WATER HYACINTHS (biocon).
A type of water plant with a
high carbon
content, which makes it very useful as
FEEDSTOCK for
BIOGAS production.
F - eichornia
S - jacinto de
agua
WATER JACKET (auto) (prod).
A casing or compartment
containing water
that is placed around all or part of a
device to keep it
cool, as around the cylinders or
cylinder head of an
internal combustion engine.
F - chemise a eau
S - envuelta de
agua
WATER MILL (hydr). A
MILL driven by a WATER WHEEL.
F - moulin
hydraulique
S - molino
hidraulico
WATERPOWER (hydr).
The ENERGY in water as derived from its
weight or momentum,
and which may be used to drive
machinery, generate
electricity, or for other purposes.
(Syn:
HYDROPOWER)
F - energie
hydraulique
S - energia
hidraulica
W.E.C.S. OR WECS
WATER PUMPING WINDMILLS (wind).
(See: WIND-POWERED PUMP)
F - eoliennes de
pompage
S - molinos de
viento con bombas hidraulicas
WATER SEAL (biocon).
The part of a GASHOLDER designed to
prevent the
METHANE from mixing with air and becoming
potentially
explosive. It generally is created by
submerging a
portion of the holder in water.
F - joint
hydraulique
S - junta
hidraulica
WATERSHED (hydr).
[1] the divide or crestline dividing two
drainage
areas. [2] The area draining into a
river,
stream etc.
F - [1]
ligne de partage des eaux;
[2]
bassin
hydrographique
S - divisoria de
aguas
WATER TURBINE (hydr).
A device that converts the ENERGY
of falling water
into rotating mechanical energy. Water
turbines are
usually smaller than WATER WHEELS and
operate at the
higher speeds required to generate
electricity.
F - turbine
hydraulique
S - turbina
hidraulica
WATER WHEEL (hydr).
A wheel with BUCKETS or BLADES that
allow it to be
turned by the weight or velocity of
falling water or
by water moving underneath it.
F - roue
hydraulique
S - rueda hidraulica
WATT (elec) (meas).
The unit rate at which work is done in
an electrical
circuit. One watt equals one JOULE of
work
per second.
F - watt
S - vatio
WAVE POWER (ocean).
The production of electricity by
harnessing ocean
wave movements through the use of
specialized
TURBINES or other devices.
F - energie des
vagues
S - energia de
las olas
WEATHERED SAILS (wind) (arc).
SAILS with variable pitch
from the inner to
the outer edge.
F - ailes a
airage
S - velas
inclinadas
WEATHER STRIPPING (gen).
Narrow strips of rubber, felt,
metal or other
material that are used to conserve ENERGY
by preventing air
INFILTRATION around doors or windows.
F - bourrelets
d'etancheite
S - moldura
W.E.C.S. or WECS (wind).
(See: WIND ENERGY CONVERSION
SYSTEM)
F - S.C.E.E. ou
SCEE
S - S.C.E.E. o
SCEE
WEIBULL DISTRIBUTION
WEIBULL DISTRIBUTION (wind) (meas).
A probability density
function that
allows one to model the WIND SPEED DISTRIBUTION
for a given site,
based on certain input parameters.
A mathematical
application of the Weibull
probability density
function gives the wind speed distribution.
The Weibull
distribution is a two-parameter
function, whereas
the RAYLEIGH DISTRIBUTION is a simplified
Weibull that only
uses one parameter. (See also:
RAYLEIGH
DISTRIBUTION)
F - distribution
de Weibull
S - distribucion
de Weibull
WEIR (hydr). An
obstruction placed across a stream to
divert the water to
make it FLOW through a desired
CHANNEL, which may
be a notch or opening in the weir
itself.
A weir also is that part of a dam,
embankment,
CANAL, etc. that
contains gates, and over which surplus
water flows.
A calibrated rod can be placed before the
opening in a weir
to measure flow. Weirs are sometimes
set up exclusively
as flow-measuring devices. (Syn:
waterweir)
F - deversoir
S - presa de
aforo
<FIGURE>
10p142.gif (600x600)
WET-BULB TEMPERATURE (meas).
A measure of the relative
humidity in a
room. It is taken by a special
thermometer
whose bulb is kept
wet.
F - temperature
de bulbe humide
S - temperatura
de bola humeda
WIND ELECTRIC SYSTEM
WET SLURRY (biocon).
(See: LIQUID SLURRY)
F - boue humide
S - fango mojado
WET STEAM (geo).
Underground water that is hotter than the
boiling point, but
which remains liquid because of high
surrounding
pressures. Reservoirs of this
superheated
water may be
tapped, producing a mixture of water and
steam that flows to
the surface and which may provide
power for a TURBINE
or other machinery.
F - vapeur humide
S - vapor
saturado
WHEELS (wind) (arc).
(See: ROLLERS)
F - roues
S - muelas
WHIP (wind) (arc).
The principal longitudinal frame for
the individual
WINDMILL SAIL. It is strapped and
bolted
to the face of the
BLADE.
F - bras [2]
S - varillaje
WIND CONCENTRATOR (wind).
A device or structure that is
used to concentrate
a wind stream.
F - concentrateur
du vent
S - concentrador
de viento
<FIGURE>
10p143.gif (317x317)

WIND DIRECTION (wind).
The forward course along which the
wind is blowing.
F - direction du
vent
S - direccion del
viento
WIND ELECTRIC SYSTEM (wind).
A system in which a WINDMILL
is used to generate
electricity. A windmill can either
be used with an
ALTERNATOR or DYNAMO to provide electricity,
which is either
stored in batteries or used
directly to run
appliances.
F -
electricite eolienne, systeme de
S -
sistema electrogeno eolico
WIND ENERGY
WIND ENERGY (wind).
ENERGY that is tapped from the natural
movement of the
air. Wind energy is considered a form
of
SOLAR ENERGY
because wind is caused by variations in the
amount of heat that
the sun sends to different parts of
the earth.
It may be converted into electrical or
mechanical POWER
through the use of a WIND MACHINE.
F - energie du
vent
S - energia
eolica
WIND ENERGY CONVERSION SYSTEM (wind).
The conversion of
WIND ENERGY into
electrical, mechanical, or thermal
energy through the
use of WIND MACHINES. Commonly
abbreviated as
W.E.C.S. or WECS.
F - conversion de
l'energie eolienne, systeme de
S - sistema de
conversion de la energia eolica
WIND FURNACE (wind).
A WIND MACHINE that converts WIND
POWER into HEAT
ENERGY.
F - four eolien
S - horno eolico
WIND GAUGE (wind) (meas).
Any instrument that measures
WIND VELOCITY.
(Syn:
ANEMOMETER)
F - indicateur de
vent
S - anemometro
WIND GENERATOR (wind).
A type of WINDMILL that extracts
ENERGY from the
wind to produce electricity by driving a
GENERATOR.
It generally has two or three narrow BLADES
that turn at a high
speed, often using gearing to
multiply the number
of revolutions per minute up to a
range required by
the generator.
F - eolienne
generatrice
S - generador
eolico
<FIGURE>
10p144.gif (353x353)
WIND LOAD RATING
WINDING (wind) (arc).
The action of turning the WINDMILL
CAP into the
WIND. This is done either automatically
or
manually.
(Pronounced to rhyme with finding.)
F - virer
S - venteamiento
<FIGURE>
10p145.gif (486x285)
WIND LOAD RATING (wind) (meas).
A specification used to
indicate the
resistance of a WINDMILL TOWER to the force
of the wind.
F - puissance
eolienne nominale
S - clasificador
de la carga eolica
WIND MACHINE
WIND MACHINE (wind).
Any of several types of wind-driven
devices that are
used to extract useful POWER from the
wind.
F - eolienne
S - maquina
eolica
WIND MEASUREMENT (wind).
(See: BEAUFORT SCALE)
F - mesure du
vent
S - medicion
eolica
WINDMILL (wind). In
a strictly technical sense, only those
wind-powered
MACHINES that drive MILLS to grind grain.
However, the term
is generally used to describe WIND
MACHINES of all kinds.
A windmill is powered by wind
pressure, and
usually has a slowly turning ROTOR with
two or more BLADES
attached to it. The blades are turned
by the wind, thus
rotating the rotor and the WIND
SHAFT.
In this way, WIND ENERGY is
converted to
mechanical
energy. Some typical windmill
applications
include
water
pumping, milling or threshing, and
electricity
generation.
F - moulin a
vent, eolienne
S - molino de
viento
WIND POWER (wind) (meas).
Power available from the wind
that can be used by
various types of WIND MACHINES. It
can be expressed
as: P = E(.5)[DAV.sup.3], where:
A = SWEPT AREA in
square meters
V = WIND VELOCITY
in meters/sec
P = power in
KILOWATTS
D = air density in
kilograms/cubic meters
E = EFFICIENCY of
the device expressed as a percentage
F - puissance du
vent
S - potencia
eolica
WIND-POWERED PUMP (wind).
A water-lifting device driven by
a WIND MACHINE.
F - pompe a
energie eolienne
S - bomba de
aeromotor
WIND ROSE (wind) (meas).
A two-dimensional graph that
shows monthly or
yearly mean WIND SPEEDS as well as a
distribution of
wind speeds. It usually indicates the
speed and the
percentage of time that the wind blows
from eight to 16
different directions.
F - rose des
vents
S - rosa de los
vientos
WIND ROTOR (wind).
(See: ROTOR)
F - rotor
d'eolienne
S - rotor eolico
WIND SHAFT (wind).
The metal rod attached to and turned by
the ROTOR to
provide mechanical POWER.
F - arbre
d'eolienne
S - eje eolico
WIND SPEED (wind).
(See: WIND VELOCITY; BEAUFORT
SCALE)
F - vitesse du
vent
S - caudal del
viento
WORT
WIND SPEED DISTRIBUTION (wind) (meas).
A two-dimensional
graph that shows
the total time or the percentage of
time that the wind
blows at each WIND SPEED at a particular
location.
It differs from a WIND ROSE in that it
can give a grand
total of wind speeds, regardless of
their directions.
F - distribution
des vitesses du vent
S - distribucion
del canal del viento
WIND TURBINE (wind).
(See: WIND MACHINE)
F - turbine A
vent
S - turbina
eolica
WIND VELOCITY (wind) (meas).
The speed of air movement
measured in miles
per hour or meters per second. The
amount of POWER
available from the wind depends in part
on the WIND SPEED
or velocity. It is a peculiarity of
WIND POWER that the
ENERGY available increases as the
cube of the wind
velocity. Wind velocity may be measured
by an ANEMOMETER.
F - vitesse du vent
S - velocidad del
viento
WINKLER PROCESS (prod).
A FLUIDIZED BED GASIFIER process,
which produces a
low or medium BTU gas from a wide
variety of coals.
F - procede de
Winkler
S - proceso de
Winkler
WOOD ALCOHOL (alc).
(See: METHANOL)
F - alcool de
bois
S - alcohol
metilico
WOOD GAS (prod).
(See: PRODUCER GAS)
F - gaz de bois
S - gas metilico
WOOD STOVE (biocon).
A stove that uses wood and most wood
residues as fuel.
F - poele a bois
S - estufa de
lena
WORM (alc) (impl) (wind) (arc).
[1] A type of CONDENSER
used in ALCOHOL
STILLS. It is a coiled metal tube that
leads from the
still to a container holding cool water.
It increases the
rate of CONDENSATION and therefore the
purity of the
alcohol produced. [2] A cylindrical
gear
that supports a
helical thread. It frequently is used
in
WINDMILL WINDING
gears.
F - [1]
serpentin; [2] vis sans fin
S - tornillo sin
fin
WORT (alc). The liquid portion of MASH that has not yet
been inoculated
with YEAST. It is a brewing term that
describes the mash
when it is between the BREWING MASH
stage and the
FERMENTATION period.
F - avoi
S - mosto no
fermentado
Y
YAW AXIS (wind). The
vertical axis about which a HORIZONTAL
AXIS WINDMILL
rotates to align itself with the
wind.
F - axe de lacet
S - eje vertical
YEAST (alc) (bio). A
single-celled micro-organism that can
change simple
sugars into ETHANOL and carbon dioxide by
FERMENTATION.
Yeasts are one type of FUNGI.
F - levure
S - levadura
YOKE (ani) (impl). A
contrivance that joins together a
pair of draft
animals, especially oxen, and which generally
consists of a
crosspiece with bow-shaped pieces
that fit over the
shoulders of the animals.
F - joug
S - yugo
<FIGURE>
10p148.gif (486x486)

Z
ZERO TILL (agri). An
ENERGY-CONSERVING method of agriculture
that requires
little or no plowing or turning of
the soil.
F - labourage nul
S - cero arado
ZONAL WIND (wind).
Winds that blow approximately along the
local perallel of
the LATITUDE.
F - vent zonal
S - viento zonal
ZONE HEAT (heat). A
central heating system in which different
temperatures may be
maintained in two or more of
the areas being
heated.
F - chauffage par
zone
CONVERSION TABLES
MULTIPLY
BY
TO OBTAIN
acres
43,560 square feet
acres
4,047 square
meters
acres
1.562 X [10.sup.-3] square
miles
acres
0.004047 square
kilometers
acres
4840 square
yards
atmospheres
76.0 cms of
mercury
atmospheres
29.92 inches of
mercury
stmospheres
10,333 kgs/square
meter
atmospheres
14.70
pounds/square inch
British thermal units
0.2530
kilogram-calories
B.t.u.
777.5
foot-pounds
B.t.u.
3.927 X [10.sup.-4]
horsepower-hours
B.t.u.
1,054 joules
B.t.u.
107.5
kilogram-meters
B.t.u.
2.928 X [10.sup.-4]
kilowatt-hours
B.t.u./min.
0.02356 horsepower
B.t.u./min.
0.01757 kilowatts
B.t.u./min.
17.57 watts
calories
0.003968 B.t.u.
calories
3.08596
foot-pounds
calories
1.1622 X [10.sup.-6]
kilowatt-hours
centimeters
0.3937 inches
centimeters
0.01 meters
centimeters of mercury
0.1934
pounds/square inch
centimeters/second
1.969 feet/minute
centimeters/second
0.036
kilometer/hour
centimeters/second
0.6
meters/minute
centimeters/second
0.02237 miles/hour
cubic centimeters
[10.sup.-6] cubic
meters
cubic centimeters
6.102 X [10.sup.-2] cubic
inches
cubic centimeters
3.531 X [10.sup.-5] cubic feet
cubic centimeters
1.308 X [10.sup.-6] cubic
yards
cubic feet
1,728 cubic
inches
cubic feet
0.02832 cubic
meters
cubic feet
2.832 X [10.sup.4] cubic
centimeters
cubic feet
7.481 gallons
cubic feet
28.32 liters
cubic feet/minute
472.0 cubic
cms/second
cubic feet/minute
0.1247
gallons/second
cubic feet/minute
0.4720
liters/second
cubic feet/minute
62.4 pounds
water/min
cubic inches
5.787 X [10.sup.-4] cubic feet
cubic inches
1.639 X [10.sup.-5] cubic
meters
cubic inches
2.143 X [10.sup.-5] cubic
yards
cubic meters
35.31 cubic feet
cubic meters
264.2 gallons
cubic meters
[10.sup.3] liters
cubic yards
7.646 X [10.sup.5] cubic
centimeters
cubic yards
27.0 cubic feet
cubic yards
46,656 cubic
inches
cubic yards
0.7646 cubic
meters
cubic yards
202.0 gallons
cubic yards
764.6 liters
cubic yards/min.
0.45 cubic
feet/second
MULTIPLY
BY TO OBTAIN
cubic yards/min.
3.367
gallons/second
cubic yards/min.
12.74
liters/second
degrees (angle)
60 minutes
degrees (angle)
0.01745 radians
degrees (angle)
3,600 seconds
dynes
1.020 X [10.sup.-3] grams
dynes
2.248 X [10.sup.-6]
pounds
ergs
9.486 X [10.sup.11] B.t.u.
ergs
1
dyne-centimeters
ergs
7.376 X [10.sup.-8
foot-pounds
ergs
[10.sup.-7] joules
ergs
2.390 X [10.sup.-11]
kilogram-calories
ergs
1.020 X [10.sup.-8]
kilogram-meters
ergs/second
1.341 X [10.sup.-10] horsepower
ergs/second
[10.sup.-10] kilowatts
feet
30.48
centimeters
feet
0.3048 meters
feet/second
18.29
meters/minute
foot-pounds
1.286 X [10.sup.-3] B.t.u.
foot-pounds
1.356 X [10.sup.7] ergs
foot-pounds
5.050 X [10.sup.-7]
horsepower-hours
foot-pounds
3.241 X [10.sup.-4]
kilogram-calories
foot-pounds
0.1383
kilogram-meters
foot-pounds
3.766 X [10.sup.-7]
kilowatt-hours
foot-pounds/minute
1.286 X [10.sup.-3]
B.t.u./minute
foot-pounds/minute
0.01667
foot-pounds/second
foot-pounds/minute
3.241 X [10.sup.-4]
kg-calories/min
foot-pounds/minute
2.260 X [10.sup.-5] kilowatts
foot-pounds/second
7.172 X [10.sup.-2]
B.t.u./minute
foot-pounds/second
1.818 X [10.sup.-3] horsepower
foot-pounds/second
1.945 X [10.sup.-2]
kg-calories/min
foot-pounds/second
1.356 X [10.sup.-3] kilowatts
gallons
0.1337 cubic feet
gallons
231 cubic
inches
gallons
3.785 X [10.sup.-3] cubic
meters
gallons
3.785 liters
gallons/minute
2.228 X [10.sup.-3] cubic
feet/second
gallona/minute
0.06308
liters/second
grams
[10.sup.-3] kilograms
grams
[10.sup.3] miligrams
grams
0.03527 ounces
grams
0.03215 troy
ounces
grams/cubic centimeter
62.43 pounds/cubic
feet
grams centimeters
9.297 X [10.sup.-8] B.t.u.
horsepower
42.44
B.t.u./minute
horsepower
33,000
foot-pounds/minute
horsepower
550
foot-pounds/second
horsepower
10.70
kg-calories/min
harsepower
0.7457 kilowatts
horsepower
745.7 watts
horsepower
1.014
horsepower(metric)
horsepower-hours
2547 B.t.u.
horsepower-hours
1.98 X [10.sup.6]
foot-pounds
horsepower-hours
641.7
kilogram-calories
horsepower-hours
2.737 X [10.sup.5]
kilogram-meters
horsepower-hours
0.7457
kilowatt-hours
horsepower-hours
2.684 X [10.sup.6] joules
inches
2.540
centimeters
inches
254.0
millimeters
MULTIPLY
BY TO OBTAIN
inches of mercury
0.03342
atmospheres
inches of mercury
1.133 feet of
water
inches of mercury
345.3
kgs/sq meter
inches of mercury
70.73 pounds/sq
foot
inches of mercury
0.4912 pounds/sq
inch
inches of water
0.002458
atmospheres
inches of water
0.07355
inches of mercury
inches of water
25.40 kgs/square
meter
inches of water
0.5781
ounces/square inch
inches of water
5.204
pounds/square foot
inches of water
0.03613
pounds/square inch
joules
0.0009458 B.t.u.
joules
0.73756
foot-pounds
joules
0.0002778 watt-hours
joules
1.0
watt-seconds
kilograms
980,665 dynes
kilograms
[10.sup.3] grams
kilograms
2.2046 pounds
kilograms
1.102 X [10.sup.-3] short tons
kilogram-calories
3.968 B.t.u.
kilogram-calories
3,086
foot-pounds
kilogram-calories
1.558 X [10.sup.-3]
horsepower-hours
kilogram-calories
4,183
joules
kilogram-calories
426.6
kilogram-meters
kilogram-calories/min.
51.43
foot-pounds/second
kilogram-calories/min.
0.09351 horsepower
kilogram-calories/min.
0.06972
kilowatts
kilograms/hectare
.893
pounds/acre
kilometers
[10.sup.5]
centimeters
kilometers
0.6214 miles
kilometers
3,281 feet
kilometers
1,000 meters
kilometers
1093.6 yards
kilometers/hour
27.78
centimetere/sec
kilometers/hour
54.68
feet/minute
kilometers/hour
0.9113
feet/second
kilometers/hour
0.5396 knots/hour
kilometers/hour
16.67
meters/hour
kilometers/hour
0.6214 miles/hour
kilowatts
56.92
B.t.u./minute
kilowatts
4.425 X [10.sup.4]
foot-pounds/minute
kilowatts
737.6
foot-pounds/second
kilowatts
1.341 horsepower
kilowatts
14.34
kg-calories/min
kilowatts
[10.sup.3] watts
kilowatts-hours
3,412 B.t.u.
kilowatts-hours
2.655 X [10.sup.6]
foot-pounds
kilowatts-hours
1.341
horsepower-hours
kilowatts-hours
3.6 X [10.sup.6] joules
kilowatts-hours
860.5
kilogram-calories
kilowatts-hours
3.671 X [10.sup.5]
kilogram-meters
meters
100
centimeters
meters
3.2808 feet
meters
39.37 inches
meters
[10.sup.-3] kilometers
meters
[10.sup.3]
millimeters
meters
1.0936 yards
meter-kilograms
9.807 X [10.sup.7]
centimeter-dynes
MULTIPLY
BY TO OBTAIN
meter-kilograms
[10.sup.5]
centimeter-grams
meter-kilograms
7.233 pound-feet
meters/minute
1.667
centimeters/second
meters/minute
3.281
feet/minute
meters/minute
0.05468
feet/second
meters/minute
0.06
kilometers/hour
meters/minute
0.03728 miles/hour
meters/second
196.8
feet/minute
meters/second
3.281
feet/second
meters/second
3.6
kilometers/hour
meters/second
0.06
kilometers/minute
meters/second
2.237 miles/hour
meters/second
0.03728
miles/minute
miles
1.609 X [10.sup.5]
centimeters
miles
5,280 feet
miles
1.6093 kilometers
miles
1,760 yards
miles/min
88.0
feet/second
miles/min
1.6093
kilometers/minute
miles/min
0.8684
knots/minute
ounces
8.0
drams
ounces
437.5 grains
ounces
28.35 grams
ounces
0.625 pounds
ounces/square inch
0.0625
pounds/square inch
pints (dry)
33.60 cubic
inches
pints (liquid)
28.87 cubic
inches
pounds
444,823 dynes
pounds
7,000 grains
pounds
453.6 grams
pounds
0.45 kilograms
pounds of water
0.01602 cubic feet
pounds of water
27.68 cubic
inches
pounds of water
0.1198
gallons
pounds of water/min.
2.669 X [10.sup.-4] cubic
feet/second
pounds/cubic foot
0.01602
grams/cubic cms.
pounds/cubic foot
16.02 kgs/cubic
meter
pounds/cubic foot
5.787 X [10.sup.-4]
pounds/cubic inch
pounds/square foot
4.882 kgs/sq
meter
pounds/square foot
6.944 X [10.sup.-3]
pounds/square inch
pounds/square inch
0.06304
atmospheres
pounds/square inch
703.1 kgs/square
meter
pounds/square inch
144.0
pounds/square foot
quarts (dry)
67.20 cubic
inches
quarts (liquid)
57.75 cubic
inches
quadrants (angle)
90 degrees
quadrants (angle)
5,400 minutes
quadrants (angle)
1.571 radians
radians
57.30 degrees
radians
3,438
minutes
radians/second
57.30
degrees/second
raidans/second
0.1592
revolutions/second
revolutions
360.0 degrees
revolutions
4.0
quadrants
revolutions
6.283 radians
revolutions/minute
6.0
degrees/second
square centimeters
1.076 X [10.sup.-3] square
feet
square centimeters
0.1550
square inches
square centimeters
[10.sup.-6] square
meters
MULTIPLY
BY TO OBTAIN
square centimeters
100 square
millimeters
square feet
2.296 X [10.sup.-5] acres
square feet
929.0 square
centimeters
square feet
144.0 square
inches
square feet
0.09290 square
meters
square feet
3.587 X [10.sup.-8] square
miles
square feet
0.1111 square
yards
square inches
6.452 square
centimeters
square inches
645.2 square
millimeters
square meters
2.471 X [10.sup.-4] acres
square meters
10.764 square
feet
square meters
3.861 X [10.sup.-7] square
miles
square meters
1.196 square
yards
square miles
640.0 acres
square miles
2.7878 X [10.sup.7] square
feet
square miles
2.590 square
kilometers
square miles
3.098 X [10.sup.6] square
yards
square yards
2.066 X [10.sup.-4] acres
square yards
9.0 square
feet
square yards
0.8361 square
meters
square yards
3.228 X [10.sup.-7 square
miles
temp (degs C) + 237
1.0 abs temp
(degs K)
temp (degs C) + 17.8
1.8 temp (degs
F)
temp (deqs F) - 32
5/9 temp (degs
C)
tons (long)
1,016 kilograms
tons (long)
2,240
pounds
tons (metric)
[10.sup.3] kilograms
tons (metric)
2,205 pounds
tons (short)
907.2 kilograms
tons (short)
2,000 pounds
tons (short)/sq. foot
9,765 kgs/square
meter
tons (short)/sq. foot
13.89
pounds/square inch
tons (short)/sq. inch
1.406 X [10.sup.6] kgs/square
meter
tons (short)/sq. inch
2,000
pounds/square inch
yards
0.9144 meters
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Abbott, Ira H. and A. E. Von Doenhoff.
Theory of Wing
Sections.
New York:
Dover Publications, Inc., 1949.
Abelson, Phillip H., ed.
Energy: Use, Conservation and
Supply.
Washington, D.C.:
American Association for the
Advancement of
Science, 1974.
A Glossary of Energy Terms in Appropriate Technology.
Norman,
Oklahoma: Science and Public Policy Program,
University of
Oklahoma, 1975.
Angrist, Stanley W., ed.
Direct Energy Conversion (3rd.
ed.).
Boston, Massachusetts:
Allyn and Bacon, Inc.,
1976.
Anderson, Bruce and Michael Riordan, The Solar Home
Book; Heating,
Cooling and Designing with the Sun.
Harrisville, New
Hampsh ire: Cheshire Books, 1976.
Anderson, Russell E., Biological Paths to Self-Reliance.
Environmental
Engineering Service. New York:
Von
Nostrand Reinhold
Company, 1979.
Application of Solar Technology to Today's Energy Needs.
Washington,
D.C.: United States Department of
Energy.
1978.
Backus, Charles E.
Solar Cells. Institute of
Electrical
and Electronic
Engineers. New York:
Wiley-Interscience,
1976.
Beedell, Suzanne.
Windmills. New York:
Charles Scribner's
Sons, 1975.
Bente, Paul F.
Bio-Energy Directory.
Washington, D.C.:
Bio-Energy Council,
1980.
Block, C. and W. Jezewski.
Illustrated Automobile Dictionary
in Six
Languages. Boston, Massachusetts:
Kluwer-Boston,
Inc., 1978.
Beeckman, W. B.
Elsevier's Wood Dictionary (vol. 3:
Research,
Manufacture, Utilization). New
York: Elsevier-North
Holland Publishing
Co., 1968.
Clark, Wilson.
Energy Survival: The Alternative
to
Extinction.
New York:
Doubleday and Co., Inc., 1975.
Clason, W. E.
Elsevier's Dictionary of Measurement and
Control.
New York:
Elsevier-North Holland Publishing
Co., 1977.
Clean Fuels from Biomass and Wastes, Symposium II, January
1977.
Chicago:
Institute of Gas Technology, 1977.
Coe, Gigi. Present
Value: Constructing a Substantial
Future.
Friends of the Earth.
San Francisco, California:
State of California
Office of Appropriate Technology.
1979.
Clegg, Peter D. and Ralph Wolfe.
Home Energy for the
Eighties.
Charlotte, Vermont:
Garden Way Publishing Co.,
1979.
Collazo, Javier L., ed., Encyclopedic Dictionary of
Technical Terms (3
vols.). New York:
McGraw-Hill Books,
Inc., 1980.
Congdon, R. J.
Introduction to Appropriate Technology.
Emmaus,
Pennsylvania: Rodale Books, Inc., 1977.
Crawley, Gerald M.
Energy. New York:
Macmillan Publishing
Co., Inc., 1975.
Dancy, Rev. Harold K.
Manual on Building Construction.
London:
Intermediate Technology Publications, 1977.
Daniels, Farrington.
Direct Use of the Sun's Energy.
New
York:
Ballantine Books, Division of Random House,
Inc.,
1964.
Darrow, Ken and Rick Pam.
Appropriate Technology Sourcebook
(2 vols.).
Stanford, California:
Volunteers in
Asia, 1976.
Davis, C. V. and K. E. Sorenson.
Handbook of Applied
Hydraulics.
New York:
McGraw-Hill Books, Inc., 1968.
Duffie, John A. and William A. Beckman.
Solar Energy
Thermal
Processes. New York:
Wiley-Interscience, 1974.
Earl, Derek E.
Forest Energy and Economic Development.
New York:
Oxford University Press, 1975.
Eccli, Sandy, ed.
Alternative Sources of Energy:
Practical
Technology and
Philosophy for a Decentralized
Society.
New York:
Seabury Press, Inc., 1974.
Energy Alternatives:
A Comparative Analysis. Norman
Oklahoma:
The Science and Public Policy Program,
University of
Oklahoma, 1975.
Energy Audit Workbook.
Washington, D.C.: United States
Department of
Energy, 1979.
Energy Information Data Base:
Subject Thesaurus.
Washington,
D.C.:
Technical Information Center, United States
Department of
Energy, 1979.
Energy Microthesaurus.
Springfield, Virginia: National
Technical
Information Service, 1976.
Fact Sheet #18--Alternative Energy Sources:
A Glossary of
Terms.
Washington D.C.:
United States Department of
Energy, 1981.
Fisher, R. and B. Yanda.
The Food and Heat Producing
Greenhouse:
Design, Construction and Operation.
Santa
Fe, New
Mexico: John Muir Publications, 1979.
Fraenkel, Peter.
Food from Windmills.
London: Intermediate
Technology
Publications, 1977.
Fraenkel, Peter. The
Power Guide: A Catalogue of Small-Scale
Power
Equipment. London:
Intermediate Technology
Publications, 1979.
Freeman, Christina and Leo Pyle.
Methane Generation by
Anaerobic Digestion:
An Annotated Bibliography.
London:
Intermediate
Technology Publications, 1977.
Freese, Stanley.
Windmills and Millwrighting.
North
Pomfret,
Vermont: David and Charles, Inc., 1971.
Fry, L. John.
Practical Building of Methane Power Plants
for Rural Energy
Independence. Santa Barbara,
California:
L. J. Fry, 1974.
Fuel From Farms--A Guide to Small-Scale Ethanol Production.
Solar Energy Data
Bank. Golden, Colorado:
SoIar
Energy Research
Institute, United States Department of
Energy, 1980.
Golding, E. W. The
Generation of Electricity by Wind
Power.
New York:
John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 1977.
Gray, T. J. and O. K. Gashus.
Tidal Power. New York:
Plenum Publishing
Corp., 1972.
Hackleman, Michael and David House.
Wind and Windspinners.
Sangus,
California: Earthmind, 1974.
Handbook of Homemade Power.
The Mother Earth News Staff,
New York:
Bantam Books Inc., 1974.
Hand, Jackson. Solar
Heating and Cooling. New York:
Harper and Row
Publishers, Inc., 1978.
Havens, David. The
Woodburner's Handbook. Brunswick,
Maine:
Harpswell Press, 1975.
Hays, Denis. Enerqy
for Development: Third World Options.
World Watch
Institute. New York:
Unipub, 1977.
House, D. The
Compleat Biogas Handbook, Aurora, Oregon:
At
Home Everywhere,
1978.
Hunt, V. Daniel.
Energy Dictionary. New
York: Von Nostrand
Reinhold Company,
1979.
Jequier, Nicolas and Gerar Blanc.
Appropriate Technology
Directory.
Paris:
Development Center of the Organization
for Economic
Co-operation and Development, 1979.
Klass, D. L. Energy
from Biomass and Wastes: 1979 Update.
Chicago:
Institute for Gas Technology, 1980.
Kondo, K. Elsevier's
Dictionary of Automobile Engineering.
New York:
Elsevier-North Holland Publishing Co.,
1977.
Lee, Kaiman.
Encyclopedia of Energy-Efficient Buildinq
Design:
391 Practical Case Studies (2 vols.).
Newtonville,
Massachusetts:
Environmental Design and Research
Center, 1977.
Lee, Kaiman and Jaqueline Masloff.
Kaiman's Encyclopedia
of Energy Topics (2
vols.). Newtonville, Massachusetts:
Environmental
Design and Research Center, 1979.
Leckie, Jim et. al.
Other Homes and Garbage. San
Francisco,
California:
Sierra Publications, 1975.
Loftness, Robert L.
Energy Handbook. New York:
Von
Nostrand Reinhold
Company, 1978.
Mages, Loren J.
Electric Generating Systems.
Indianapolis,
Indiana:
Theodore Audel, 1970.
Mantell, C. L.
Batteries and Energy Systems.
New York:
McGraw-Hill Books,
Inc., 1970.
Mazria, Edward. The
Passive Solar Energy Book: Expanded
Professional
Edition. Emmaus, Pennsylvania:
Rodale
Books, Inc., 1979.
McCullagh, James, ed.
Pedal Power: In Work, Leisure,
and
Transportation. Emmaus,
Pennsylvania: Rodale Books,
Inc., 1977.
McGuigan, Dermot.
Harnessing Water Power for Home Energy.
Charlotte,
Vermont: Garden Way Publishing, Inc.,
1978.
Merrill, Richard and Thomas Gage, eds.
Energy Primer:
Updated and Revised
Version. New York:
Dell Publishing
Company, 1974.
Meynell, Peter-John.
Methane: Planning a
Digester. New
York:
Schocken Books, Inc., 1978.
Mole, W. M.
International Glossary of Hydrology.
World
Meteorological
Organization and the United Nations
Education,
Scientific and Cultural Organization, New
York:
Unipub, 1974.
Neville, Richard C.
Solar Energy Conversion. New
York:
Elsevier-North
Holland Publishing Co., 1978.
Pachauri, R. K.
Energy and Economic Development in India.
New York:
Praeger Publishers, 1977.
Parker, Sybil.
Encyclopedia of Energy (2nd. ed.).
New
York:
McGraw-Hill Book Co., 1980.
Park, Jack.
Simplified Wind Power Systems for Experimenters
(2nd. ed.).
Sylmar, California:
Helion, 1975.
Park, Jack. The Wind
Power Book. Palo Alto, California:
Cheshire Books,
1980.
Putnam, P. C. Power
from the Wind. New York:
Von Nostrand
Reinhold Company,
1974.
Proceedings of the United Nation Conference on New
Sources of Energy,
New York, New York: Unipub, 1961.
Reed, T. B. and R. M. Lerner.
Methanol: A Versatile
Fuel
for Immediate
Use. Washington, D.C.:
American Association
for the Advancement
of Science, 1973.
Reynolds, John.
Windmills and Watermills. New
York:
Praeger Publishers,
1970.
Ross M. H. and R. H. Williams.
Our Energy: Regaining
Control.
New York:
McGraw-Hill Book Co., 1980.
Sachs, Peter. Wind
Forces in Engineering (2nd. ed.).
Elmsford, New
York: Pergamon Press, Inc. 1972.
Schlegel, H. G.
Microbial Energy Conversion.
Elmsford, New
York:
Pergamon Press, Inc.
Shefter, Y. Wind
Powered Machines. Springfield,
Virginia:
National Technical
lnformation Service, 1974.
Shelton, Jay and Andrew Shapiro.
The Woodburner's Encyclopedia.
Waitsfield,
Vermont: Vermont Crossroads Press,
1976.
Stafford, D. A.
Methane Production from Waste Organic
Matter.
Boca Raton, Florida:
CRC Press, 1977.
Stoner, Carol H.
Producing Your Own Power: How to
Make
Nature's Energy
Sources Work for You. Emmaus,
Pennsylvania:
Rodale Press, Inc.
1974.
Sullivan, F. P. and N. C. McNerney.
Energy Reference Handbook
(3rd. ed.).
Rockville, Maryland:
Government Institutes,
Inc.
Tweney, C. F. and L. E. C. Hughes, eds.
Chamber's Technical
Dictionary (3rd.
ed., revised, with supplement). New
York:
Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1958.
Todd, David Keith, ed.
Water Encyclopedia. Syosset, New
York:
Water Information Center, 1970.
Van Buren, Ariane and Leo Pyle, eds.
A Chinese Biogas
Manual.
Translated from Chinese by Michael Crook,
London:
Intermediate Technology Publications, 1979.
Veziroglu, T. Nejat, ed.
Alternative Energy Sources:
Proceedings--Miami
International
Conference on Alternative
Energy
Sources. Washington, D.C.:
Hemisphere Publishing
Corp., 1978.
VITA Construction Manual and Technical Bulletin Series,
Washington,
D.C.: Volunteers in Technical
Assistance,
Inc.
Vivian, John. Wood
Heat: New and Improved Edition.
Emmaus,
Pennsylvania:
Rodale Press, Inc., 1978.
Water Pumping Windmill Designs:
A Hand Book. Bombay,
India.
Tata Research Institute, 1981.
Watt, Simon. Chinese
Chain and Washer Pumps. London:
Intermediate
Technology Publications, 1977.
Wood and Energy.
Washington, D.C.: United States
Department
of Energy, 1980.
Wood Conserving Cookstoves:
A Design Guide. Washington,
D.C.:
Volunteers in Technical Assistance and
Intermediate
Technology
Development Group, 1979.
Yule, John-David, ed.
Phaidon Concise Encyclopedia of
Science and
Technology. Oxford:
Phaidon Press, Ltd.,
1978.
========================================
========================================

